
Silver nitrate is an inorganic compound with chemical formula AgNO
3. It is a versatile precursor to many other silver compounds, such as those used in photography. It is far less sensitive to light than the halides. It was once called lunar caustic because silver was called luna by ancient alchemists who associated silver with the moon. In solid silver nitrate, the silver ions are three-coordinated in a trigonal planar arrangement.

Lead(II) nitrate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Pb(NO3)2. It commonly occurs as a colourless crystal or white powder and, unlike most other lead(II) salts, is soluble in water.
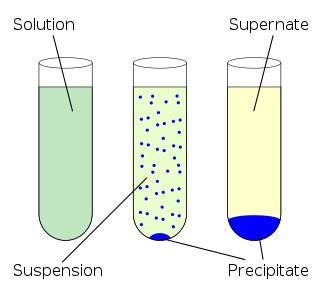
In an aqueous solution, precipitation is the "sedimentation of a solid material from a liquid solution". The solid formed is called the precipitate. In case of an inorganic chemical reaction leading to precipitation, the chemical reagent causing the solid to form is called the precipitant.

Cadmium chloride is a white crystalline compound of cadmium and chloride, with the formula CdCl2. This salt is a hygroscopic solid that is highly soluble in water and slightly soluble in alcohol. The crystal structure of cadmium chloride (described below), is a reference for describing other crystal structures. Also known are CdCl2•H2O and the hemipentahydrate CdCl2•2.5H2O.

Silver oxide is the chemical compound with the formula Ag2O. It is a fine black or dark brown powder that is used to prepare other silver compounds.
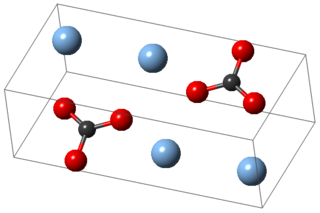
Silver carbonate is the chemical compound with the formula Ag2CO3. This salt is yellow but typical samples are grayish due to the presence of elemental silver. It is poorly soluble in water, like most transition metal carbonates.

Silver sulfate is the inorganic compound with the formula Ag2SO4. It is a white solid with low solubility in water.

Silver azide is the chemical compound with the formula AgN3. It is a silver(I) salt of hydrazoic acid. It forms a colorless crystals. Like most azides, it is a primary explosive.
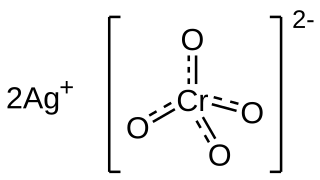
Silver chromate is an inorganic compound with formula Ag2CrO4 which appears as distinctively coloured brown-red crystals. The compound is insoluble and its precipitation is indicative of the reaction between soluble chromate and silver precursor salts (commonly potassium/sodium chromate with silver nitrate). This reaction is important for two uses in the laboratory: in analytical chemistry it constitutes the basis for the Mohr method of argentometry, whereas in neuroscience it is used in the Golgi method of staining neurons for microscopy.
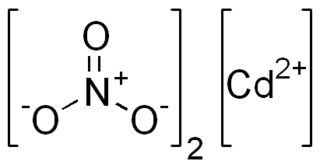
Cadmium nitrate describes any of the related members of a family of inorganic compounds with the general formula Cd(NO3)2·xH2O. The most commonly encountered form being the tetrahydrate.The anhydrous form is volatile, but the others are colourless crystalline solids that are deliquescent, tending to absorb enough moisture from the air to form an aqueous solution. Like other cadmium compounds, cadmium nitrate is known to be carcinogenic. According to X-ray crystallography, the tetrahydrate features octahedral Cd2+ centers bound to six oxygen ligands.

Iron(III) nitrate, or ferric nitrate, is the name used for a series of inorganic compounds with the formula Fe(NO3)3.(H2O)n. Most common is the nonahydrate Fe(NO3)3.(H2O)9. The hydrates are all pale colored, water-soluble paramagnetic salts.

Mercury(I) sulfate, commonly called mercurous sulphate (UK) or mercurous sulfate (US) is the chemical compound Hg2SO4. Mercury(I) sulfate is a metallic compound that is a white, pale yellow or beige powder. It is a metallic salt of sulfuric acid formed by replacing both hydrogen atoms with mercury(I). It is highly toxic; it could be fatal if inhaled, ingested, or absorbed by skin.
Silver selenite is an inorganic compound of formula Ag2SeO3.
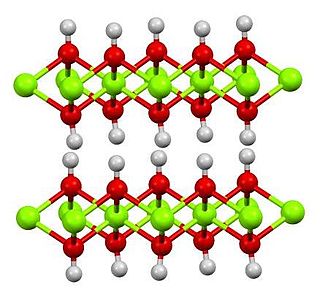
Cadmium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula Cd(OH)2. It is a white crystalline ionic compound that is a key component of nickel–cadmium battery.

Mercury(I) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of mercury and nitric acid with the formula Hg2(NO3)2. A yellow solid, the compound is used as a precursor to other Hg22+ complexes. The structure of the hydrate has been determined by X-ray crystallography. It consists of a [H2O-Hg-Hg-OH2]2+ center, with a Hg-Hg distance of 254 pm.

Silver phosphate or silver orthophosphate is a light sensitive, yellow, water-insoluble chemical compound composed of silver and phosphate ions of formula Ag3PO4.
Barium tungstate is an inorganic chemical compound of barium and the tungstate anion.

Bismuth(III) nitrate is a salt composed of bismuth in its cationic +3 oxidation state and nitrate anions. The most common solid form is the pentahydrate. It is used in the synthesis of other bismuth compounds. It is available commercially. It is the only nitrate salt formed by a group 15 element, indicative of bismuth's metallic nature.

Thulium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of thulium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Tm(NO3)3. The compound forms dark-green crystals, readily soluble in water, also forms crystalline hydrates.


 [2]
[2] 















