In chemistry, an interhalogen compound is a molecule which contains two or more different halogen atoms and no atoms of elements from any other group.
Chlorine trifluoride is an interhalogen compound with the formula ClF3. It is a colorless, poisonous, corrosive, and extremely reactive gas that condenses to a pale-greenish yellow liquid, the form in which it is most often sold. It is famous for its extreme oxidation properties. The compound is primarily of interest in plasmaless cleaning and etching operations in the semiconductor industry, in nuclear reactor fuel processing, historically as a component in rocket fuels, and various other industrial operations owing to its corrosive nature.
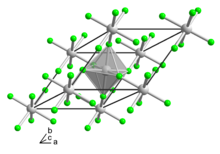
Manganese(III) fluoride (also known as Manganese trifluoride) is the inorganic compound with the formula MnF3. This red/purplish solid is useful for converting hydrocarbons into fluorocarbons, i.e., it is a fluorination agent. It forms a hydrate and many derivatives.
Phosphorus trifluoride (formula PF3), is a colorless and odorless gas. It is highly toxic and reacts slowly with water. Its main use is as a ligand in metal complexes. As a ligand, it parallels carbon monoxide in metal carbonyls, and indeed its toxicity is due to its binding with the iron in blood hemoglobin in a similar way to carbon monoxide.
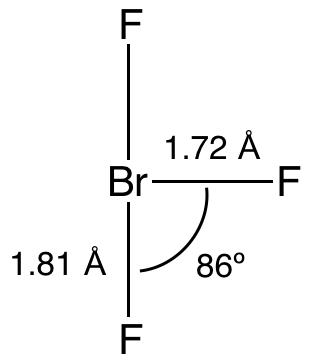
Bromine trifluoride is an interhalogen compound with the formula BrF3. At room temperature, it is a straw-coloured liquid with a pungent odor which decomposes violently on contact with water and organic compounds. It is a powerful fluorinating agent and an ionizing inorganic solvent. It is used to produce uranium hexafluoride (UF6) in the processing and reprocessing of nuclear fuel.

Cobalt(III) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula CoF3. Hydrates are also known. The anhydrous compound is a hygroscopic brown solid. It is used to synthesize organofluorine compounds.

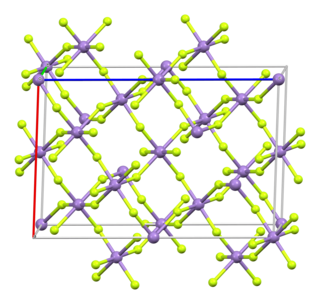
Iron(III) fluoride, also known as ferric fluoride, are inorganic compounds with the formula FeF3(H2O)x where x = 0 or 3. They are mainly of interest by researchers, unlike the related iron(III) chloride. Anhydrous iron(III) fluoride is white, whereas the hydrated forms are light pink.

Gold(III) fluoride, AuF3, is an orange solid that sublimes at 300 °C. It is a powerful fluorinating agent. It is very sensitive to moisture, yielding gold(III) hydroxide and hydrofluoric acid.
Arsenic trifluoride is a chemical compound of arsenic and fluorine with the chemical formula AsF3. It is a colorless liquid which reacts readily with water. Like other inorganic arsenic compounds, it is highly toxic.

Indium(III) fluoride or indium trifluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula InF3. It is a white solid.

Palladium(II,IV) fluoride, also known as palladium trifluoride, is a chemical compound of palladium and fluorine. It has the empirical formula PdF3, but is better described as the mixed-valence compound palladium(II) hexafluoropalladate(IV), PdII[PdIVF6], and is often written as Pd[PdF6] or Pd2F6.
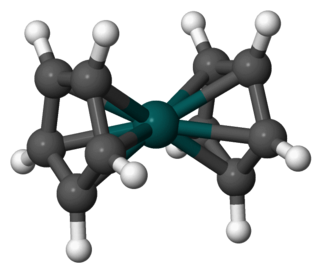
Rhodocene is a chemical compound with the formula [Rh(C5H5)2]. Each molecule contains an atom of rhodium bound between two planar aromatic systems of five carbon atoms known as cyclopentadienyl rings in a sandwich arrangement. It is an organometallic compound as it has (haptic) covalent rhodium–carbon bonds. The [Rh(C5H5)2] radical is found above 150 °C (302 °F) or when trapped by cooling to liquid nitrogen temperatures (−196 °C [−321 °F]). At room temperature, pairs of these radicals join via their cyclopentadienyl rings to form a dimer, a yellow solid.
Trifluorides are compounds in which one atom or ion has three fluorine atoms or ions associated. Many metals form trifluorides, such as iron, the rare-earth elements, and the metals in the groups 3, 13 and 15 of the periodic table. Most metal trifluorides are poorly soluble in water except ferric fluoride and indium(III) fluoride, but several are soluble in other solvents.

Rhodium hexafluoride, also rhodium(VI) fluoride, (RhF6) is the inorganic compound of rhodium and fluorine. A black volatile solid, it is a highly reactive material which starts to slowly thermally decompose already at room temperature and a rare example of a rhodium(VI) compound. It is one of seventeen known binary hexafluorides.

Bromine monofluoride is a quite unstable interhalogen compound with the chemical formula BrF. It can be produced through the reaction of bromine trifluoride (or bromine pentafluoride) and bromine. Due to its lability, the compound can be detected but not isolated:

Neptunium(VI) fluoride (NpF6) is the highest fluoride of neptunium, it is also one of seventeen known binary hexafluorides. It is a volatile orange crystalline solid. It is relatively hard to handle, being very corrosive, volatile and radioactive. Neptunium hexafluoride is stable in dry air but reacts vigorously with water.

Rhodium(III) bromide refers to inorganic compounds of the formula RhBr3(H2O)n where n = 0 or approximately three. Both forms are brown solids. The hydrate is soluble in water and lower alcohols. It is used to prepare rhodium bromide complexes. Rhodium bromides are similar to the chlorides, but have attracted little academic or commercial attention.
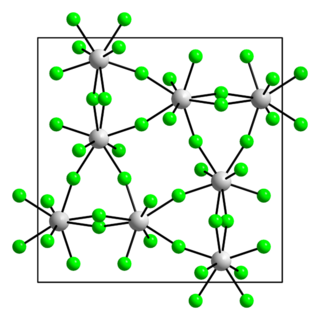
Protactinium(V) fluoride is a fluoride of protactinium with the chemical formula PaF5.

Zirconium trifluoride is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula ZrF3. This is a salt of zirconium and hydrofluoric acid, forms black crystals.