
Erbium is a chemical element; it has symbol Er and atomic number 68. A silvery-white solid metal when artificially isolated, natural erbium is always found in chemical combination with other elements. It is a lanthanide, a rare-earth element, originally found in the gadolinite mine in Ytterby, Sweden, which is the source of the element's name.

Holmium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ho and atomic number 67. It is a rare-earth element and the eleventh member of the lanthanide series. It is a relatively soft, silvery, fairly corrosion-resistant and malleable metal. Like many other lanthanides, holmium is too reactive to be found in native form, as pure holmium slowly forms a yellowish oxide coating when exposed to air. When isolated, holmium is relatively stable in dry air at room temperature. However, it reacts with water and corrodes readily, and also burns in air when heated.

Chromium(III) fluoride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CrF3. It forms several hydrates. The compound CrF3 is a green crystalline solid that is insoluble in common solvents, but the hydrates [Cr(H2O)6]F3 (violet) and [Cr(H2O)6]F3·3H2O (green) are soluble in water. The anhydrous form sublimes at 1100–1200 °C.

Iron(III) fluoride, also known as ferric fluoride, are inorganic compounds with the formula FeF3(H2O)x where x = 0 or 3. They are mainly of interest by researchers, unlike the related iron(III) chloride. Anhydrous iron(III) fluoride is white, whereas the hydrated forms are light pink.

Scandium(III) fluoride, ScF3, is an ionic compound. This salt is slightly soluble in water but dissolves in the presence of excess fluoride to form the ScF63− anion.
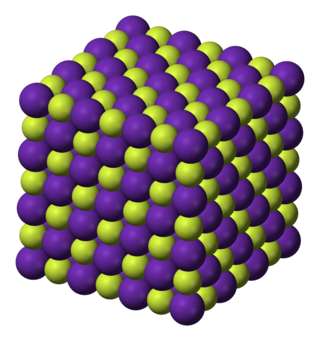
Rubidium fluoride (RbF) is the fluoride salt of rubidium. It is a cubic crystal with rock-salt structure.
Arsenic trifluoride is a chemical compound of arsenic and fluorine with the chemical formula AsF3. It is a colorless liquid which reacts readily with water.
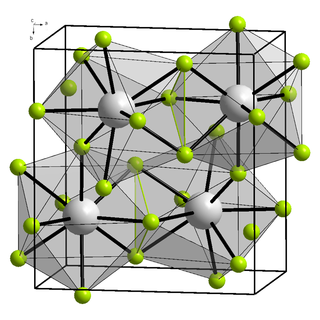
Bismuth(III) fluoride or bismuth trifluoride is a chemical compound of bismuth and fluorine. The chemical formula is BiF3. It is a grey-white powder melting at 649 °C.
Dysprosium(III) fluoride is an inorganic compound of dysprosium with a chemical formula DyF3.
Praseodymium(III) fluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula PrF3, being the most stable fluoride of praseodymium.
Europium(III) fluoride is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula EuF3.
Gadolinium(III) fluoride is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula GdF3.

Holmium (III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of holmium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Ho(NO3)3. The compound forms yellowish crystals, dissolves in water, also forms crystalline hydrates.

Lutetium(III) acetate is the acetate salt of lutetium with the chemical formula of Lu(CH3COO)3.
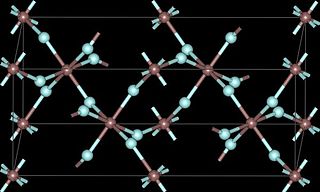
Ruthenium(III) fluoride is a fluoride of ruthenium, with the chemical formula of RuF3.
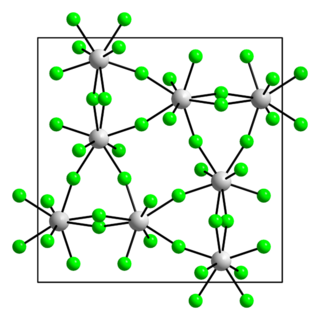
Protactinium(V) fluoride is a fluoride of protactinium with the chemical formula PaF5.

Holmium(III) sulfide is the sulfide of holmium, with the chemical formula of Ho2S3. Like other rare earth sulfides, it is used as a high-performance inorganic pigment.

Holmium(III) iodide is an iodide of holmium, with the chemical formula of HoI3. It is used as a component of metal halide lamps.
Erbium compounds are compounds containing the element erbium (Er). These compounds are usually dominated by erbium in the +3 oxidation state, although the +2, +1 and 0 oxidation states have also been reported.
Americium compounds are compounds containing the element americium (Am). These compounds can form in the +2, +3, and +4, although the +3 oxidation state is the most common. The +5, +6 and +7 oxidation states have also been reported.













