
Uranium tetrafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula UF4. It is a green solid with an insignificant vapor pressure and low solubility in water. Uranium in its tetravalent (uranous) state is important in various technological processes. In the uranium refining industry it is known as green salt.

Plutonium hexafluoride is the highest fluoride of plutonium, and is of interest for laser enrichment of plutonium, in particular for the production of pure plutonium-239 from irradiated uranium. This pure plutonium is needed to avoid premature ignition of low-mass nuclear weapon designs by neutrons produced by spontaneous fission of plutonium-240.
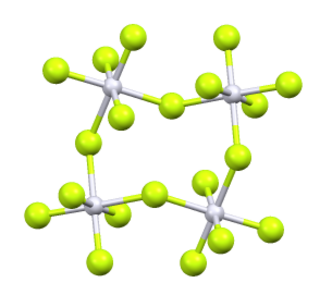
Iridium(V) fluoride, IrF5, is a chemical compound of iridium and fluorine. A highly reactive yellow low melting solid, it has a tetrameric structure, Ir4F20, which contains octahedrally coordinated iridium atoms. This structure is shared with RuF5 and OsF5. It can be prepared by the controlled decomposition of IrF6 or the reduction of IrF6 with silicon powder or H2 in anhydrous HF.
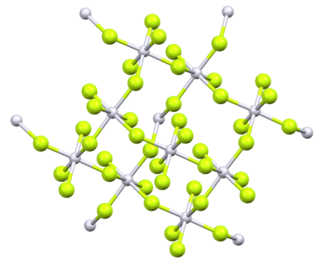
Platinum tetrafluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula PtF
4. In the solid state, the compound features platinum(IV) in octahedral coordination geometry.
Yttrium oxyfluoride is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula YOF. Under normal conditions, the compound is a colorless solid.
Praseodymium(III) oxalate is an inorganic compound, a salt of praseodymium metal and oxalic acid with the chemical formula C6O12Pr2. The compound forms light green crystals, insoluble in water, also forms crystalline hydrates.
Praseodymium(III) nitride is a binary inorganic compound of praseodymium and nitrogen. Its chemical formula is PrN. The compound forms black crystals, and reacts with water.
Neptunium (IV) oxalate is an inorganic compound, a salt of neptunium and oxalic acid with the chemical formula Np(C2O4)2. The compound is slightly soluble in water, forms crystalline hydrates—green crystals.
Neptunium silicide is a binary inorganic compound of neptunium and silicon with the chemical formula NpSi
2. The compound forms crystals and does not dissolve in water.

Holmium (III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of holmium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Ho(NO3)3. The compound forms yellowish crystals, dissolves in water, also forms crystalline hydrates.

Ytterbium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of ytterbium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Yb(NO3)3. The compound forms colorless crystals, dissolves in water, and also forms crystalline hydrates.
Lutetium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of lutetium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Lu(NO3)3. The compound forms colorless crystals, dissolves in water, and also forms crystalline hydrates. The compound is poisonous.
Erbium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of erbium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Er(NO3)3. The compound forms pink crystals, readily soluble in water, also forms crystalline hydrates.
Polonium tetranitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of polonium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Po(NO3)4. The compound is radioactive, forms white crystals.

Praseodymium(III) acetate is an inorganic salt composed of a Praseodymium atom trication and three acetate groups as anions. This compound commonly forms the dihydrate, Pr(O2C2H3)3·2H2O.
Praseodymium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal praseodymium (Pr). In these compounds, praseodymium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as PrCl3, Pr(NO3)3 and Pr(CH3COO)3. However, compounds with praseodymium in the +2 and +4 oxidation states, and unlike other lanthanides, the +5 oxidation state, are also known.

Praseodymium(III) iodide is an inorganic salt, consisting of the rare-earth metal praseodymium with hydrogen iodide with the chemical formula PrI3. It forms green crystals. It is soluble in water.

Protactinium(IV) bromide is an inorganic compound. It is an actinide halide, composed of protactinium and bromine. It is radioactive, and has the chemical formula of PaBr4. It may be due to the brown color of bromine that causes the appearance of protactinium(IV) bromide to be brown crystals. Its crystal structure is tetragonal. Protactinium(IV) bromide is sublimed in a vacuum at 400 °C. The protactinium(IV) halide closest in structure to protactinium(IV) bromide is protactinium(IV) chloride.
Praseodymium bismuthide is a binary inorganic compound of praseodymium and bismuth with the chemical formula of PrBi. It forms crystals.

Praseodymium antimonide is a binary inorganic compound of praseodymium and antimony with the formula PrSb.














