
Gold(III) bromide is a dark-red to black crystalline solid. It has the empirical formula AuBr3, but exists primarily as a dimer with the molecular formula Au2Br6 in which two gold atoms are bridged by two bromine atoms. It is commonly referred to as gold(III) bromide, gold tribromide, and rarely but traditionally auric bromide, and sometimes as digold hexabromide. As is similar with the other gold halides, this compound is unique for being a coordination complex of a group 11 transition metal that is stable in an oxidation state of +3 whereas copper or silver complexes persist in oxidation states of +1 or +2.

Tantalum(V) bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula Ta2Br10. Its name comes from the compound's empirical formula, TaBr5. It is a diamagnetic, orange solid that hydrolyses readily. The compound adopts an edge-shared bioctahedral structure, which means that two TaBr5 units are joined by a pair of bromide bridges. There is no bond between the Ta centres. Niobium(V) chloride, niobium(V) bromide, niobium(V) iodide, tantalum(V) chloride, and tantalum(V) iodide all share this structural motif.
Tin(II) bromide is a chemical compound of tin and bromine with a chemical formula of SnBr2. Tin is in the +2 oxidation state. The stability of tin compounds in this oxidation state is attributed to the inert pair effect.
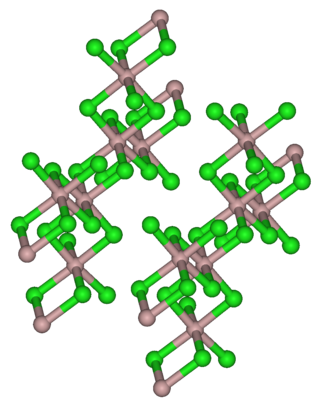
Indium(III) bromide, (indium tribromide), InBr3, is a chemical compound of indium and bromine. It is a Lewis acid and has been used in organic synthesis.

Cerium(III) bromide is an inorganic compound with the formula CeBr3. This white hygroscopic solid is of interest as a component of scintillation counters.

Niobium(V) bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula Nb2Br10. Its name comes from the compound's empirical formula, NbBr5. It is a diamagnetic, orange solid that hydrolyses readily. The compound adopts an edge-shared bioctahedral structure, which means that two NbBr5 units are joined by a pair of bromide bridges. There is no bond between the Nb centres. Niobium(V) chloride, niobium(V) iodide, tantalum(V) chloride, tantalum(V) bromide, and tantalum(V) iodide all share this structural motif.
Scandium bromide, or ScBr3, is a trihalide, hygroscopic, water-soluble chemical compound of scandium and bromine.

Neodymium(III) bromide is an inorganic salt of bromine and neodymium the formula NdBr3. The anhydrous compound is an off-white to pale green solid at room temperature, with an orthorhombic PuBr3-type crystal structure. The material is hygroscopic and forms a hexahydrate in water (NdBr3· 6H2O), similar to the related neodymium(III) chloride.
Samarium(III) bromide is a crystalline compound of one samarium and three bromine atoms with the chemical formula of SmBr3. Samarium(III) bromide is a dark brown powder at room temperature. The compound has a crystal structure isotypic to that of plutonium(III) bromide.
Holmium(III) bromide is a crystalline compound made of one holmium atom and three bromine atoms. Holmium bromide is a yellow powder at room temperature. Holmium bromide is hygroscopic. Holmium bromide is odorless.
Thulium(III) bromide is a crystalline compound of one thulium atom and three bromine atoms. The salt is a white powder at room temperature. It is hygroscopic.
Lutetium(III) bromide is a crystalline compound made of one lutetium atom and three bromine atoms. It takes the form of a white powder at room temperature. It is hygroscopic. It is odorless.
The telluride bromides are chemical compounds that contain both telluride ions (Te2−) and bromide ions (Br−). They are in the class of mixed anion compounds or chalcogenide halides.
Plutonium(III) bromide is an inorganic salt of bromine and plutonium with the formula PuBr3. This radioactive green solid has few uses, however its crystal structure is often used as a structural archetype in crystallography.

Rhodium(III) bromide refers to inorganic compounds of the formula RhBr3(H2O)n where n = 0 or approximately three. Both forms are brown solids. The hydrate is soluble in water and lower alcohols. It is used to prepare rhodium bromide complexes. Rhodium bromides are similar to the chlorides, but have attracted little academic or commercial attention.

Californium(III) bromide is an inorganic compound, a salt with a chemical formula CfBr3. Like in californium oxide (Cf2O3) and other californium halides, including californium(III) fluoride (CfF3), californium(III) chloride, and californium(III) iodide (CfI3), the californium atom has an oxidation state of +3.

Ruthenium(III) bromide is a chemical compound of ruthenium and bromine with the formula RuBr3. It is a dark brown solid that decomposes above 400 °C.
Praseodymium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal praseodymium (Pr). In these compounds, praseodymium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as PrCl3, Pr(NO3)3 and Pr(CH3COO)3. However, compounds with praseodymium in the +2 and +4 oxidation states, and unlike other lanthanides, the +5 oxidation state, are also known.

Praseodymium(III) iodide is an inorganic salt, consisting of the rare-earth metal praseodymium and iodine, with the chemical formula PrI3. It forms green crystals. It is soluble in water.









