
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy uses, particularly in stainless steels. It improves strength, workability, and resistance to wear. Manganese oxide is used as an oxidising agent; as a rubber additive; and in glass making, fertilisers, and ceramics. Manganese sulfate can be used as a fungicide.
A period 4 element is one of the chemical elements in the fourth row of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when chemical behaviour begins to repeat, meaning that elements with similar behaviour fall into the same vertical columns. The fourth period contains 18 elements beginning with potassium and ending with krypton – one element for each of the eighteen groups. It sees the first appearance of d-block in the table.

Manganese dioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula MnO
2. This blackish or brown solid occurs naturally as the mineral pyrolusite, which is the main ore of manganese and a component of manganese nodules. The principal use for MnO
2 is for dry-cell batteries, such as the alkaline battery and the zinc–carbon battery. MnO
2 is also used as a pigment and as a precursor to other manganese compounds, such as KMnO
4. It is used as a reagent in organic synthesis, for example, for the oxidation of allylic alcohols. MnO
2 has an α-polymorph that can incorporate a variety of atoms in the "tunnels" or "channels" between the manganese oxide octahedra. There is considerable interest in α-MnO
2 as a possible cathode for lithium-ion batteries.

Group 7, numbered by IUPAC nomenclature, is a group of elements in the periodic table. It contains manganese (Mn), technetium (Tc), rhenium (Re) and bohrium (Bh). This group lies in the d-block of the periodic table, and are hence transition metals. This group is sometimes called the manganese group or manganese family after its lightest member; however, the group itself has not acquired a trivial name because it belongs to the broader grouping of the transition metals.
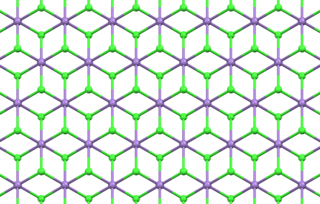
Manganese(II) chloride is the dichloride salt of manganese, MnCl2. This inorganic chemical exists in the anhydrous form, as well as the dihydrate (MnCl2·2H2O) and tetrahydrate (MnCl2·4H2O), with the tetrahydrate being the most common form. Like many Mn(II) species, these salts are pink, with the paleness of the color being characteristic of transition metal complexes with high spin d5 configurations.

Methylcyclopentadienyl manganese tricarbonyl (MMT or MCMT) is an organomanganese compound with the formula (C5H4CH3)Mn(CO)3. Initially marketed as a supplement for use in leaded gasoline, MMT was later used in unleaded gasoline to increase the octane rating. Following the implementation of the Clean Air Act (United States) (CAA) in 1970, MMT continued to be used alongside tetraethyl lead (TEL) in the US as leaded gasoline was phased out (prior to TEL finally being banned from US gasoline in 1995), and was also used in unleaded gasoline until 1977. Ethyl Corporation obtained a waiver from the U.S. EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) in 1995, which allows the use of MMT in US unleaded gasoline (not including reformulated gasoline) at a treat rate equivalent to 8.3 mg Mn/L (manganese per liter).
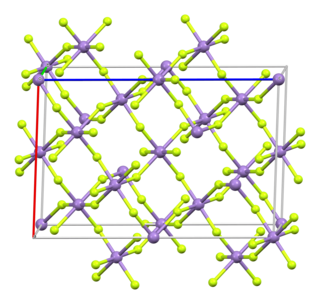
Manganese(III) fluoride (also known as Manganese trifluoride) is the inorganic compound with the formula MnF3. This red/purplish solid is useful for converting hydrocarbons into fluorocarbons, i.e., it is a fluorination agent. It forms a hydrate and many derivatives.

A permanganate is a chemical compound with the manganate(VII) ion, MnO−
4, the conjugate base of permanganic acid. Because the manganese atom has a +7 oxidation state, the permanganate(VII) ion is a strong oxidising agent. The ion is a transition metal ion with a tetrahedral structure. Permanganate solutions are purple in colour and are stable in neutral or slightly alkaline media. The exact chemical reaction depends on the carbon-containing reactants present and the oxidant used. For example, trichloroethane (C2H3Cl3) is oxidised by permanganate ions to form carbon dioxide (CO2), manganese dioxide (MnO2), hydrogen ions (H+), and chloride ions (Cl−).

Manganese carbonate is a compound with the chemical formula MnCO3. Manganese carbonate occurs naturally as the mineral rhodochrosite but it is typically produced industrially. It is a pale pink, water-insoluble solid. Approximately 20,000 metric tonnes were produced in 2005.
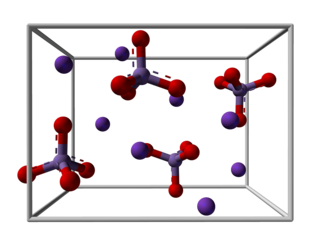
Potassium manganate is the inorganic compound with the formula K2MnO4. This green-colored salt is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of potassium permanganate, a common chemical. Occasionally, potassium manganate and potassium permanganate are confused, but these compounds's properties are distinct.
Alloy steel is steel that is alloyed with a variety of elements in total amounts between 1.0% and 50% by weight to improve its mechanical properties.

Manganese(II) sulfate usually refers to the inorganic compound with the formula MnSO4·H2O. This pale pink deliquescent solid is a commercially significant manganese(II) salt. Approximately 260,000 tonnes of manganese(II) sulfate were produced worldwide in 2005. It is the precursor to manganese metal and many other chemical compounds. Manganese-deficient soil is remediated with this salt.
Phosphate conversion coating is a chemical treatment applied to steel parts that creates a thin adhering layer of iron, zinc, or manganese phosphates, to achieve corrosion resistance, lubrication, or as a foundation for subsequent coatings or painting. It is one of the most common types of conversion coating. The process is also called phosphate coating, phosphatization, phosphatizing, or phosphating. It is also known by the trade name Parkerizing, especially when applied to firearms and other military equipment.

Manganese(II,III) oxide is the chemical compound with formula Mn3O4. Manganese is present in two oxidation states +2 and +3 and the formula is sometimes written as MnO·Mn2O3. Mn3O4 is found in nature as the mineral hausmannite.

Manganese(II) oxide is an inorganic compound with chemical formula MnO. It forms green crystals. The compound is produced on a large scale as a component of fertilizers and food additives.

Manganese(II) fluoride is the chemical compound composed of manganese and fluoride with the formula MnF2. It is a light pink solid, the light pink color being characteristic for manganese(II) compounds. It is made by treating manganese and diverse compounds of manganese(II) in hydrofluoric acid. Like some other metal difluorides, MnF2 crystallizes in the rutile structure, which features octahedral Mn centers.
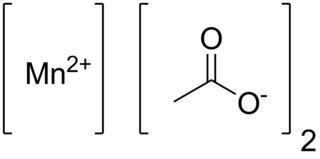
Manganese(II) acetate are chemical compounds with the formula Mn(CH3CO2)2·(H2O)n where n = 0, 2, 4. These materials are white or pale pink solids. Some of these compounds are used as a catalyst and as fertilizer.
Organomanganese chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to manganese chemical bond. In a 2009 review, Cahiez et al. argued that as manganese is cheap and benign, organomanganese compounds have potential as chemical reagents, although currently they are not widely used as such despite extensive research.

Manganese(II) nitrate refers to the inorganic compounds with formula Mn(NO3)2·(H2O)n. These compounds are nitrate salts containing varying amounts of water. A common derivative is the tetrahydrate, Mn(NO3)2·4H2O, but mono- and hexahydrates are also known as well as the anhydrous compound. Some of these compounds are useful precursors to the oxides of manganese. Typical of a manganese(II) compound, it is a paramagnetic pale pink solid.
Manganese(III) chloride is the hypothetical inorganic compound with the formula MnCl3.

















