
Bromine is a chemical element with the symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a similarly coloured vapour. Its properties are intermediate between those of chlorine and iodine. Isolated independently by two chemists, Carl Jacob Löwig and Antoine Jérôme Balard, its name was derived from the Ancient Greek βρῶμος (bromos) meaning "stench", referring to its sharp and pungent smell.

Iridium is a chemical element with the symbol Ir and atomic number 77. A very hard, brittle, silvery-white transition metal of the platinum group, it is considered the second-densest naturally occurring metal with a density of 22.56 g/cm3 (0.815 lb/cu in) as defined by experimental X-ray crystallography. It is one of the most corrosion-resistant metals, even at temperatures as high as 2,000 °C (3,630 °F). However, corrosion-resistance is not quantifiable in absolute terms; although only certain molten salts and halogens are corrosive to solid iridium, finely divided iridium dust is much more reactive and can be flammable, whereas gold dust is not flammable but can be attacked by substances that iridium resists, such as aqua regia.
Hydrobromic acid is a strong acid formed by dissolving the diatomic molecule hydrogen bromide (HBr) in water. "Constant boiling" hydrobromic acid is an aqueous solution that distills at 124.3 °C (255.7 °F) and contains 47.6% HBr by mass, which is 8.77 mol/L. Hydrobromic acid has a pKa of −9, making it a stronger acid than hydrochloric acid, but not as strong as hydroiodic acid. Hydrobromic acid is one of the strongest mineral acids known.

Hydrogen bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula HBr. It is a hydrogen halide consisting of hydrogen and bromine. A colorless gas, it dissolves in water, forming hydrobromic acid, which is saturated at 68.85% HBr by weight at room temperature. Aqueous solutions that are 47.6% HBr by mass form a constant-boiling azeotrope mixture that boils at 124.3 °C. Boiling less concentrated solutions releases H2O until the constant-boiling mixture composition is reached.
A bromide ion is the negatively charged form (Br−) of the element bromine, a member of the halogens group on the periodic table. Most bromides are colorless. Bromides have many practical roles, being found in anticonvulsants, flame-retardant materials, and cell stains. Although uncommon, chronic toxicity from bromide can result in bromism, a syndrome with multiple neurological symptoms. Bromide toxicity can also cause a type of skin eruption, see potassium bromide. The bromide ion has an ionic radius of 196 pm.
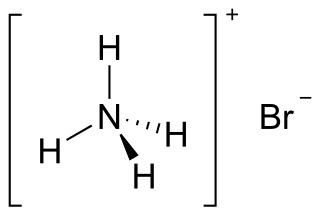
Ammonium bromide, NH4Br, is the ammonium salt of hydrobromic acid. The chemical crystallizes in colorless prisms, possessing a saline taste; it sublimes on heating and is easily soluble in water. On exposure to air it gradually assumes a yellow color because of the oxidation of traces of bromide (Br−) to bromine (Br2).

Lithium bromide (LiBr) is a chemical compound of lithium and bromine. Its extreme hygroscopic character makes LiBr useful as a desiccant in certain air conditioning systems.

Hypobromous acid is a weak, unstable acid with chemical formula of HOBr. It is mainly produced and handled in an aqueous solution. It is generated both biologically and commercially as a disinfectant. Salts of hypobromite are rarely isolated as solids.

Zinc bromide (ZnBr2) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula ZnBr2. It is a colourless salt that shares many properties with zinc chloride (ZnCl2), namely a high solubility in water forming acidic solutions, and good solubility in organic solvents. It is hygroscopic and forms a dihydrate ZnBr2·2H2O.
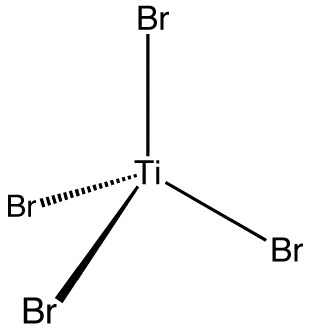
Titanium tetrabromide is the chemical compound with the formula TiBr4. It is the most volatile transition metal bromide. The properties of TiBr4 are an average of TiCl4 and TiI4. Some key properties of these four-coordinated Ti(IV) species are their high Lewis acidity and their high solubility in nonpolar organic solvents. TiBr4 is diamagnetic, reflecting the d0 configuration of the metal centre.
Antimony tribromide (SbBr3) is a chemical compound containing antimony in its +3 oxidation state.
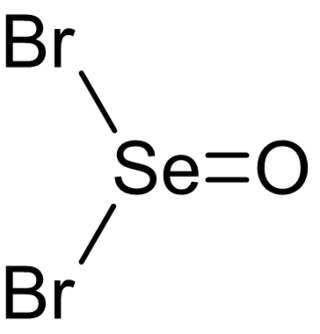
Selenium oxybromide (SeOBr2) is a selenium oxohalide chemical compound.
Osmium compounds are compounds containing the element osmium (Os). Osmium forms compounds with oxidation states ranging from −2 to +8. The most common oxidation states are +2, +3, +4, and +8. The +8 oxidation state is notable for being the highest attained by any chemical element aside from iridium's +9 and is encountered only in xenon, ruthenium, hassium, iridium, and plutonium. The oxidation states −1 and −2 represented by the two reactive compounds Na
2[Os
4(CO)
13] and Na
2[Os(CO)
4] are used in the synthesis of osmium cluster compounds.
Bromine compounds are compounds containing the element bromine (Br). These compounds usually form the -1, +1, +3 and +5 oxidation states. Bromine is intermediate in reactivity between chlorine and iodine, and is one of the most reactive elements. Bond energies to bromine tend to be lower than those to chlorine but higher than those to iodine, and bromine is a weaker oxidising agent than chlorine but a stronger one than iodine. This can be seen from the standard electrode potentials of the X2/X− couples (F, +2.866 V; Cl, +1.395 V; Br, +1.087 V; I, +0.615 V; At, approximately +0.3 V). Bromination often leads to higher oxidation states than iodination but lower or equal oxidation states to chlorination. Bromine tends to react with compounds including M–M, M–H, or M–C bonds to form M–Br bonds.

Barium bromide is the chemical compound with the formula BaBr2. It is ionic in nature.

Cobalt(II) bromide (CoBr2) is an inorganic compound. In its anhydrous form, it is a green solid that is soluble in water, used primarily as a catalyst in some processes.

Silicon tetrabromide, also known as tetrabromosilane, is the inorganic compound with the formula SiBr4. This colorless liquid has a suffocating odor due to its tendency to hydrolyze with release of hydrogen bromide. The general properties of silicon tetrabromide closely resemble those of the more commonly used silicon tetrachloride.

Bromous acid is the inorganic compound with the formula of HBrO2. It is an unstable compound, although salts of its conjugate base – bromites – have been isolated. In acidic solution, bromites decompose to bromine.

Bismuth tribromide is an inorganic compound of bismuth and bromine with the chemical formula BiBr3.
Iridium(IV) iodide is a binary chemical compound of iridium and iodide with the chemical formula IrI
4.













