
Dysprosium is a chemical element; it has symbol Dy and atomic number 66. It is a rare-earth element in the lanthanide series with a metallic silver luster. Dysprosium is never found in nature as a free element, though, like other lanthanides, it is found in various minerals, such as xenotime. Naturally occurring dysprosium is composed of seven isotopes, the most abundant of which is 164Dy.

Erbium is a chemical element; it has symbol Er and atomic number 68. A silvery-white solid metal when artificially isolated, natural erbium is always found in chemical combination with other elements. It is a lanthanide, a rare-earth element, originally found in the gadolinite mine in Ytterby, Sweden, which is the source of the element's name.

Einsteinium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Es and atomic number 99. It was named in honor of Albert Einstein and is a member of the actinide series and is the seventh transuranium element.

Holmium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ho and atomic number 67. It is a rare-earth element and the eleventh member of the lanthanide series. It is a relatively soft, silvery, fairly corrosion-resistant and malleable metal. Like many other lanthanides, holmium is too reactive to be found in native form, as pure holmium slowly forms a yellowish oxide coating when exposed to air. When isolated, holmium is relatively stable in dry air at room temperature. However, it reacts with water and corrodes readily, and also burns in air when heated.

Thulium is a chemical element; it has symbol Tm and atomic number 69. It is the thirteenth element in the lanthanide series of metals. It is the second-least abundant lanthanide in the Earth's crust, after radioactively unstable promethium. It is an easily workable metal with a bright silvery-gray luster. It is fairly soft and slowly tarnishes in air. Despite its high price and rarity, thulium is used as a dopant in solid-state lasers, and as the radiation source in some portable X-ray devices. It has no significant biological role and is not particularly toxic.
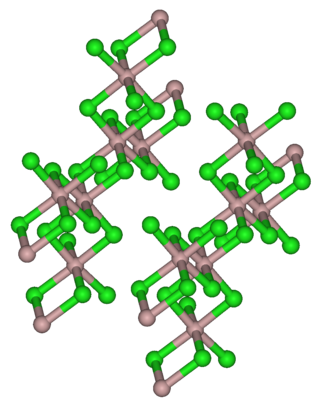
Yttrium(III) bromide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula YBr3. It is a white solid. Anhydrous yttrium(III) bromide can be produced by reacting yttrium oxide or yttrium(III) bromide hydrate and ammonium bromide. The reaction proceeds via the intermediate (NH4)3YBr6. Another method is to react yttrium carbide (YC2) and elemental bromine. Yttrium(III) bromide can be reduced by yttrium metal to YBr or Y2Br3. It can react with osmium to produce Y4Br4Os.
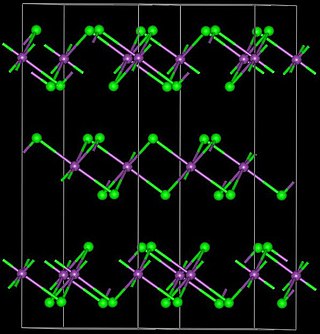
Holmium(III) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula HoCl3. It is a common salt but is mainly used in research. It can be used to produce pure holmium. It exhibits the same color-changing behavior seen in holmium oxide, being a yellow in natural lighting and a bright pink color in fluorescent lighting.
Praseodymium(III) bromide is a crystalline compound of one praseodymium atom and three bromine atoms.

Neodymium(III) bromide is an inorganic salt of bromine and neodymium the formula NdBr3. The anhydrous compound is an off-white to pale green solid at room temperature, with an orthorhombic PuBr3-type crystal structure. The material is hygroscopic and forms a hexahydrate in water (NdBr3· 6H2O), similar to the related neodymium(III) chloride.

Samarium(II) bromide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula SmBr
2. It is a brown solid that is insoluble in most solvents but degrades readily in air.
Samarium(III) bromide is a crystalline compound of one samarium and three bromine atoms with the chemical formula of SmBr3. Samarium(III) bromide is a dark brown powder at room temperature. The compound has a crystal structure isotypic to that of plutonium(III) bromide.

Europium(II) bromide is a crystalline compound of one europium atom and two bromine atoms. Europium(II) bromide is a white powder at room temperature, and odorless. Europium dibromide is hygroscopic.
Europium(III) bromide is a crystalline compound, a salt, made of one europium and three bromine atoms. Europium tribromide is a grey powder at room temperature. It is odorless. Europium tribromide is hygroscopic.
Gadolinium(III) bromide is a crystalline compound of gadolinium atoms and three bromine atoms. This salt is hygroscopic.
Thulium(III) bromide is a crystalline compound of one thulium atom and three bromine atoms. The salt is a white powder at room temperature. It is hygroscopic.
Lutetium(III) bromide is a crystalline compound made of one lutetium atom and three bromine atoms. It takes the form of a white powder at room temperature. It is hygroscopic. It is odorless.
Praseodymium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal praseodymium (Pr). In these compounds, praseodymium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as PrCl3, Pr(NO3)3 and Pr(CH3COO)3. However, compounds with praseodymium in the +2 and +4 oxidation states, and unlike other lanthanides, the +5 oxidation state, are also known.

Holmium(III) iodide is an iodide of holmium, with the chemical formula of HoI3. It is used as a component of metal halide lamps.
Erbium compounds are compounds containing the element erbium (Er). These compounds are usually dominated by erbium in the +3 oxidation state, although the +2, +1 and 0 oxidation states have also been reported.
Holmium nitride is a binary inorganic compound of holmium and nitrogen with the chemical formula HoN.











