
Sulfuric acid or sulphuric acid, known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formula H2SO4. It is a colorless, odorless and viscous liquid that is miscible with water.

Calcium sulfide is the chemical compound with the formula CaS. This white material crystallizes in cubes like rock salt. CaS has been studied as a component in a process that would recycle gypsum, a product of flue-gas desulfurization. Like many salts containing sulfide ions, CaS typically has an odour of H2S, which results from small amount of this gas formed by hydrolysis of the salt.

Chlorosulfuric acid (IUPAC name: sulfurochloridic acid) is the inorganic compound with the formula HSO3Cl. It is also known as chlorosulfonic acid, being the sulfonic acid of chlorine. It is a distillable, colorless liquid which is hygroscopic and a powerful lachrymator. Commercial samples usually are pale brown or straw colored.

Arsenic tribromide is the inorganic compound with the formula AsBr3. This pyramidal molecule is the only known binary arsenic bromide. AsBr3 is noteworthy for its very high refractive index of approximately 2.3. It also has a very high diamagnetic susceptibility. The compound exists as colourless deliquescent crystals that fume in moist air.

Ditellurium bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula Te2Br. It is one of the few stable lower bromides of tellurium. Unlike sulfur and selenium, tellurium forms families of polymeric subhalides where the chalcogen/halide ratio is less than 2.

Iron(II) bromide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula FeBr2. The anhydrous compound is a yellow or brownish-colored paramagnetic solid. Several hydrates of FeBr2 are also known, all being pale colored solids. It is a common precursor to other iron compounds in research laboratory, but no applications exist for this compound.
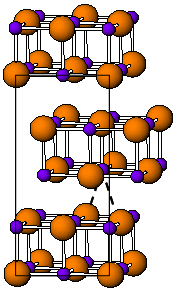
Indium(I) bromide is a chemical compound of indium and bromine. It is a red crystalline compound that is isostructural with β-TlI and has a distorted rock salt structure. Indium(I) bromide is generally made from the elements, heating indium metal with InBr3. It has been used in the sulfur lamp. In organic chemistry, it has been found to promote the coupling of α, α-dichloroketones to 1-aryl-butane-1,4-diones. Oxidative addition reactions with for example alkyl halides to give alkyl indium halides and with NiBr complexes to give Ni-In bonds are known. It is unstable in water decomposing into indium metal and indium tribromide. When indium dibromide is dissolved in water, InBr is produced as a, presumably, insoluble red precipitate, that then rapidly decomposes.
A polysulfane is a chemical compound of formula H2Sx, where x > 1, although disulfane, H2S2 is sometimes excluded. Polysulfanes consist of unbranched chains of sulfur atoms terminated with hydrogen. Compounds containing 2–8 concatenated sulfur atoms have been isolated, longer chain compounds have been detected, but only in solution. H2S2 is colourless, higher members are yellow with the colour increasing with the sulfur content. Even a trace of alkali will cause chemical decomposition, and containers need to be treated with acid to remove any traces of alkali.
In the chemical literature the term polysulfanes is sometimes used for compounds containing −(Sn)−, e.g. organic polysulfanes R−(Sn)−R.
Polonium hydride (also known as polonium dihydride, hydrogen polonide, or polane) is a chemical compound with the formula PoH2. It is a liquid at room temperature, the second hydrogen chalcogenide with this property after water. It is very unstable chemically and tends to decompose into elemental polonium and hydrogen; like all polonium compounds, it is highly radioactive. It is a volatile and very labile compound, from which many polonides can be derived.

Trisulfane is the inorganic compound with the formula H2S3. It is a pale yellow volatile liquid with a camphor-like odor. It decomposes readily to hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and elemental sulfur. It is produced by distillation of the polysulfane oil obtained by acidification of polysulfide salts.

Sulfur tetrachloride is an inorganic compound with chemical formula SCl4. It has only been obtained as an unstable pale yellow solid. The corresponding SF4 is a stable, useful reagent.

Polonium dioxide (also known as polonium(IV) oxide) is a chemical compound with the formula PoO2. It is one of three oxides of polonium, the other two being polonium monoxide (PoO) and polonium trioxide (PoO3). It is a pale yellow crystalline solid at room temperature. Under lowered pressure (such as a vacuum), it decomposes into elemental polonium and oxygen at 500 °C. It is the most stable oxide of polonium and is an interchalcogen.
Polonium dibromide (also known as polonium(II) bromide) is a chemical compound with the formula PoBr2. This salt is a purple-brown crystalline solid at room temperature. It sublimes (decomposing slightly) at 110 °C/30 μ and decomposes when melted in nitrogen gas at 270–280 °C.
Molybdenum(II) bromide is an inorganic compound with the formula MoBr2. It forms yellow-red crystals.

Disulfur dibromide is the inorganic compound with the formula S2Br2. It is a yellow-brown liquid that fumes in air. It is prepared by direct combination of the elements and purified by vacuum distillation. The compound has no particular application, unlike the related sulfur compound disulfur dichloride.
A halous acid, also known as a halogenous acid, is an oxyacid consisting of a halogen atom in the +3 oxidation state single-bonded to a hydroxyl group and double-bonded to an oxygen atom. Examples include chlorous acid, bromous acid, and iodous acid. The conjugate base is a halite.
Selenium tetrabromide is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula SeBr4.

Xenon dibromide is an unstable chemical compound with the chemical formula XeBr2. It was only created by the decomposition of iodine-129:
Tetraoxygen difluoride is an inorganic chemical compound of oxygen, belonging to the family of oxygen fluorides. It consists of two O2F units bound together with a weak O-O bond, and is the dimer of the O2F radical.
Polonium sulfide is an inorganic compound of polonium and sulfur with the chemical formula PoS. The compound is radioactive, forms black crystals.















