Berkelium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Bk and atomic number 97. It is a member of the actinide and transuranium element series. It is named after the city of Berkeley, California, the location of the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory where it was discovered in December 1949. Berkelium was the fifth transuranium element discovered after neptunium, plutonium, curium and americium.

Curium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Cm and atomic number 96. This transuranic actinide element was named after eminent scientists Marie and Pierre Curie, both known for their research on radioactivity. Curium was first intentionally made by the team of Glenn T. Seaborg, Ralph A. James, and Albert Ghiorso in 1944, using the cyclotron at Berkeley. They bombarded the newly discovered element plutonium with alpha particles. This was then sent to the Metallurgical Laboratory at University of Chicago where a tiny sample of curium was eventually separated and identified. The discovery was kept secret until after the end of World War II. The news was released to the public in November 1947. Most curium is produced by bombarding uranium or plutonium with neutrons in nuclear reactors – one tonne of spent nuclear fuel contains ~20 grams of curium.
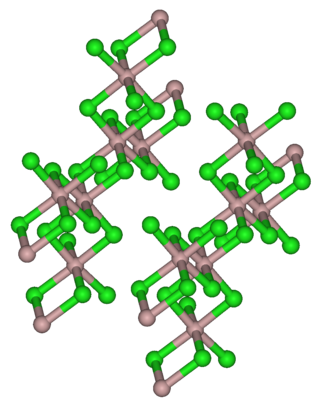
Indium(III) bromide, (indium tribromide), InBr3, is a chemical compound of indium and bromine. It is a Lewis acid and has been used in organic synthesis.
There are three sets of Indium halides, the trihalides, the monohalides, and several intermediate halides. In the monohalides the oxidation state of indium is +1 and their proper names are indium(I) fluoride, indium(I) chloride, indium(I) bromide and indium(I) iodide.

Plutonium(III) chloride is a chemical compound with the formula PuCl3. This ionic plutonium salt can be prepared by reacting the metal with hydrochloric acid.

Cerium(III) bromide is an inorganic compound with the formula CeBr3. This white hygroscopic solid is of interest as a component of scintillation counters.
William Houlder Zachariasen, more often known as W. H. Zachariasen, was a Norwegian-American physicist, specializing in X-ray crystallography and famous for his work on the structure of glass.

Actinide chemistry is one of the main branches of nuclear chemistry that investigates the processes and molecular systems of the actinides. The actinides derive their name from the group 3 element actinium. The informal chemical symbol An is used in general discussions of actinide chemistry to refer to any actinide. All but one of the actinides are f-block elements, corresponding to the filling of the 5f electron shell; lawrencium, a d-block element, is also generally considered an actinide. In comparison with the lanthanides, also mostly f-block elements, the actinides show much more variable valence. The actinide series encompasses the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103, actinium through lawrencium.
Americium(III) bromide or americium tribromide is the chemical compound composed of americium and bromine with the formula AmBr3, with americium in a +3 oxidation state. The compound is a crystalline solid.
Praseodymium(III) bromide is a crystalline compound of one praseodymium atom and three bromine atoms.

Neodymium(III) bromide is an inorganic salt of bromine and neodymium the formula NdBr3. The anhydrous compound is an off-white to pale green solid at room temperature, with an orthorhombic PuBr3-type crystal structure. The material is hygroscopic and forms a hexahydrate in water (NdBr3· 6H2O), similar to the related neodymium(III) chloride.
Samarium(III) bromide is a crystalline compound of one samarium and three bromine atoms with the chemical formula of SmBr3. Samarium(III) bromide is a dark brown powder at room temperature. The compound has a crystal structure isotypic to that of plutonium(III) bromide.

Rhodium(III) bromide refers to inorganic compounds of the formula RhBr3(H2O)n where n = 0 or approximately three. Both forms are brown solids. The hydrate is soluble in water and lower alcohols. It is used to prepare rhodium bromide complexes. Rhodium bromides are similar to the chlorides, but have attracted little academic or commercial attention.

Californium(III) bromide is an inorganic compound, a salt with a chemical formula CfBr3. Like in californium oxide (Cf2O3) and other californium halides, including californium(III) fluoride (CfF3), californium(III) chloride, and californium(III) iodide (CfI3), the californium atom has an oxidation state of +3.
Actinium(III) bromide is a radioactive white crystalline solid that is a salt of actinium. It is prepared by reacting actinium(III) oxide with aluminium bromide at 750 °C.

Ruthenium(III) bromide is a chemical compound of ruthenium and bromine with the formula RuBr3. It is a dark brown solid that decomposes above 400 °C.
Curium compounds are compounds containing the element curium (Cm). Curium usually forms compounds in the +3 oxidation state, although compounds with curium in the +4, +5 and +6 oxidation states are also known.
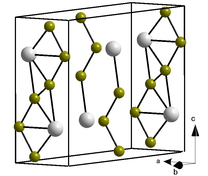
Curium(III) bromide is the bromide salt of curium. It has an orthorhombic crystal structure.
Actinium compounds are compounds containing the element actinium (Ac). Due to actinium's intense radioactivity, only a limited number of actinium compounds are known. These include: AcF3, AcCl3, AcBr3, AcOF, AcOCl, AcOBr, Ac2S3, Ac2O3, AcPO4 and Ac(NO3)3. Except for AcPO4, they are all similar to the corresponding lanthanum compounds. They all contain actinium in the oxidation state +3. In particular, the lattice constants of the analogous lanthanum and actinium compounds differ by only a few percent.

Berkelium bromide is a bromide of berkelium, with the chemical formula BkBr3.