Plutonium hydride is a non-stoichiometric chemical compound with the formula PuH2+x. It is one of two characterised hydrides of plutonium, the other is PuH3. PuH2 is non-stoichiometric with a composition range of PuH2 – PuH2.7. Additionally metastable stoichiometries with an excess of hydrogen (PuH2.7 – PuH3) can be formed. PuH2 has a cubic structure. It is readily formed from the elements at 1 atmosphere at 100–200 °C: When the stoichiometry is close to PuH2 it has a silver appearance, but gets blacker as the hydrogen content increases, additionally the color change is associated with a reduction in conductivity.

Plutonium hexafluoride is the highest fluoride of plutonium, and is of interest for laser enrichment of plutonium, in particular for the production of pure plutonium-239 from irradiated uranium. This isotope of plutonium is needed to avoid premature ignition of low-mass nuclear weapon designs by neutrons produced by spontaneous fission of plutonium-240.

Californium oxychloride is a radioactive salt first discovered in measurable quantities in 1960. It is composed of a single californium cation and oxychloride consisting of one chloride and one oxide anion. It was the first californium compound ever isolated.
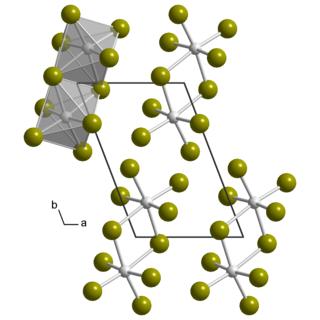
Uranium pentabromide is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula U2Br10.

Neptunium(VI) fluoride (NpF6) is the highest fluoride of neptunium, it is also one of seventeen known binary hexafluorides. It is an orange volatile crystalline solid. It is relatively hard to handle, being very corrosive, volatile and radioactive. Neptunium hexafluoride is stable in dry air but reacts vigorously with water.
Fluorine forms a great variety of chemical compounds, within which it always adopts an oxidation state of −1. With other atoms, fluorine forms either polar covalent bonds or ionic bonds. Most frequently, covalent bonds involving fluorine atoms are single bonds, although at least two examples of a higher order bond exist. Fluoride may act as a bridging ligand between two metals in some complex molecules. Molecules containing fluorine may also exhibit hydrogen bonding. Fluorine's chemistry includes inorganic compounds formed with hydrogen, metals, nonmetals, and even noble gases; as well as a diverse set of organic compounds. For many elements the highest known oxidation state can be achieved in a fluoride. For some elements this is achieved exclusively in a fluoride, for others exclusively in an oxide; and for still others the highest oxidation states of oxides and fluorides are always equal.

Actinium(III) fluoride (AcF3) is an inorganic compound, a salt of actinium and fluorine.

Curium(III) fluoride or curium trifluoride is the chemical compound composed of curium and fluorine with the formula CmF3. It is a white, nearly insoluble salt that has the same crystal structure as LaF3. It precipitates as a hydrate when fluoride ions are added to a weakly acidic Cm(III) solution; alternatively it can be synthesized by reacting hydrofluoric acid with Cm(OH)3. The anhydrous form is then obtained by desiccation or by treatment with hydrogen fluoride gas.
Neptunium(III) fluoride or neptunium trifluoride is a salt of neptunium and fluorine with the formula NpF3.
Neptunium(V) fluoride or neptunium pentafluoride is a chemical compound of neptunium and fluorine with the formula NpF5.
Plutonium arsenide is a binary inorganic compound of plutonium and arsenic with the formula PuAs.
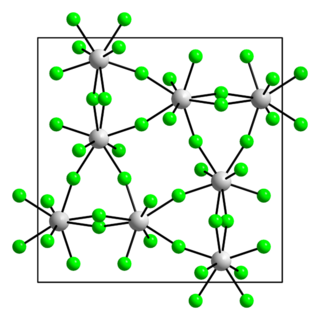
Protactinium(V) fluoride is a fluoride of protactinium with the chemical formula PaF5.
Americium hexafluoride is an inorganic chemical compound of americium metal and fluorine with the chemical formula AmF
6. It is still a hypothetical compound. Synthesis by fluorination of americium tetrafluoride was unsuccessfully attempted in 1990. A thermochromatographic identification in 1986 remains inconclusive. Calculations suggest that it may be distorted from octahedral symmetry.

Ytterbium(II) fluoride is a binary inorganic compound of ytterbium and fluorine with the chemical formula YbF2.
Rhenium pentafluoride is a binary inorganic compound of rhenium and fluorine with the chemical formula ReF5. This is a salt of rhenium and hydrofluoric acid.
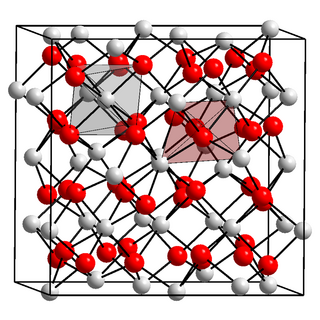
Berkelium(III) oxide is a binary inorganic compound of berkelium and oxygen with the chemical formula Bk
2O
3.
Einsteinium fluoride is a binary inorganic chemical compound of einsteinium and fluorine with the chemical formula EsF3.
Einsteinium tetrafluoride is a binary inorganic chemical compound of einsteinium and fluorine with the chemical formula EsF4. The compound was observed by thermochromatography.
Californium(III) oxybromide is a inorganic compound of californium, bromine, and oxygen with the formula CfOBr.
Californium(III) oxyiodide is a inorganic compound of californium, iodine, and oxygen with the formula CfOI.








