Related Research Articles
Tungsten(VI) fluoride, also known as tungsten hexafluoride, is an inorganic compound with the formula WF6. It is a toxic, corrosive, colorless gas, with a density of about 13 kg/m3 (22 lb/cu yd) (roughly 11 times heavier than air). It is one of the densest known gases under standard conditions. WF6 ls commonly used by the semiconductor industry to form tungsten films, through the process of chemical vapor deposition. This layer is used in a low-resistivity metallic "interconnect". It is one of seventeen known binary hexafluorides.
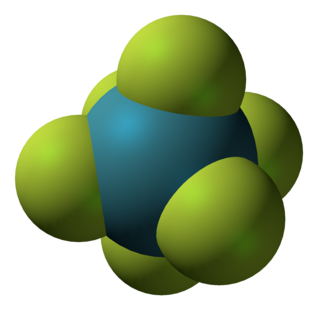
Xenon hexafluoride is a noble gas compound with the formula XeF6. It is one of the three binary fluorides of xenon, the other two being XeF2 and XeF4. All known are exergonic and stable at normal temperatures. XeF6 is the strongest fluorinating agent of the series. It is a colorless solid that readily sublimes into intensely yellow vapors.

Iron(III) fluoride, also known as ferric fluoride, are inorganic compounds with the formula FeF3(H2O)x where x = 0 or 3. They are mainly of interest by researchers, unlike the related iron(III) chlorides. Anhydrous iron(III) fluoride is white, whereas the hydrated forms are light pink.
Tellurium hexafluoride is the inorganic compound of tellurium and fluorine with the chemical formula TeF6. It is a colorless, highly toxic gas with an unpleasant odor.

Technetium hexafluoride or technetium(VI) fluoride (TcF6) is a yellow inorganic compound with a low melting point. It was first identified in 1961. In this compound, technetium has an oxidation state of +6, the highest oxidation state found in the technetium halides. In this respect, technetium differs from rhenium, which forms a heptafluoride, ReF7. Technetium hexafluoride occurs as an impurity in uranium hexafluoride, as technetium is a fission product of uranium (spontaneous fission in natural uranium, possible contamination from induced fission inside the reactor in reprocessed uranium). The fact that the boiling point of the hexafluorides of uranium and technetium are very close to each other presents a problem in using fluoride volatility in nuclear reprocessing.

Plutonium hexafluoride is the highest fluoride of plutonium, and is of interest for laser enrichment of plutonium, in particular for the production of pure plutonium-239 from irradiated uranium. This pure plutonium is needed to avoid premature ignition of low-mass nuclear weapon designs by neutrons produced by spontaneous fission of plutonium-240.
A hexafluoride is a chemical compound with the general formula QXnF6, QXnF6m−, or QXnF6m+. Many molecules fit this formula. An important hexafluoride is hexafluorosilicic acid (H2SiF6), which is a byproduct of the mining of phosphate rock. In the nuclear industry, uranium hexafluoride (UF6) is an important intermediate in the purification of this element.

Iridium hexafluoride, also iridium(VI) fluoride, (IrF6) is a compound of iridium and fluorine and one of the seventeen known binary hexafluorides. It is one of only a few compounds with iridium in the oxidation state +6.

Molybdenum hexafluoride, also molybdenum(VI) fluoride, is the inorganic compound with the formula MoF6. It is the highest fluoride of molybdenum. It is a colourless solid and melts just below room temperature and boils in 34 °C. It is one of the seventeen known binary hexafluorides.
Palladium fluoride is the name of a series of binary compounds of palladium and fluorine. These include:

Palladium(II) fluoride, also known as palladium difluoride, is the chemical compound of palladium and fluorine with the formula PdF2.

Palladium(II,IV) fluoride, also known as palladium trifluoride, is a chemical compound of palladium and fluorine. It has the empirical formula PdF3, but is better described as the mixed-valence compound palladium(II) hexafluoropalladate(IV), PdII[PdIVF6], and is often written as Pd[PdF6] or Pd2F6.

Palladium(IV) fluoride, also known as palladium tetrafluoride, is the chemical compound of palladium and fluorine with the chemical formula PdF4. The palladium atoms in PdF4 are in the +4 oxidation state.

Rhodium hexafluoride, also rhodium(VI) fluoride, (RhF6) is the inorganic compound of rhodium and fluorine. A black volatile solid, it is a highly reactive material, and a rare example of a rhodium(VI) compound. It is one of seventeen known binary hexafluorides.

Rhenium hexafluoride, also rhenium(VI) fluoride, (ReF6) is a compound of rhenium and fluorine and one of the seventeen known binary hexafluorides.
Polonium hexafluoride (PoF6) is a possible chemical compound of polonium and fluorine and one of the seventeen known binary hexafluorides.

Osmium hexafluoride, also osmium(VI) fluoride, (OsF6) is a compound of osmium and fluorine, and one of the seventeen known binary hexafluorides.
Chromium pentafluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula CrF5. It is a red volatile solid that melts at 34 °C. It is the highest known chromium fluoride, since the hypothetical chromium hexafluoride has not yet been synthesized.
Fluorine forms a great variety of chemical compounds, within which it always adopts an oxidation state of −1. With other atoms, fluorine forms either polar covalent bonds or ionic bonds. Most frequently, covalent bonds involving fluorine atoms are single bonds, although at least two examples of a higher order bond exist. Fluoride may act as a bridging ligand between two metals in some complex molecules. Molecules containing fluorine may also exhibit hydrogen bonding. Fluorine's chemistry includes inorganic compounds formed with hydrogen, metals, nonmetals, and even noble gases; as well as a diverse set of organic compounds. For many elements the highest known oxidation state can be achieved in a fluoride. For some elements this is achieved exclusively in a fluoride, for others exclusively in an oxide; and for still others the highest oxidation states of oxides and fluorides are always equal.
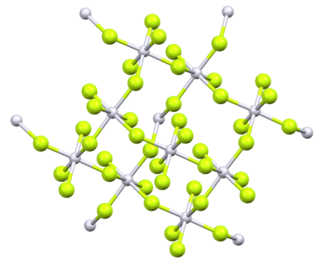
Platinum tetrafluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula PtF
4. In the solid state, the compound features platinum(IV) in octahedral coordination geometry.
References
- ↑ "Palladium hexafluoride". Russian Journal of Inorganic Chemistry. British Library Lending Division with the cooperation of the Royal Society of Chemistry. 29 (1–6): 283. 1984. Retrieved 29 March 2023.
- ↑ David, Jorge; Fuentealba, Patricio; Restrepo, Albeiro. "Relativistic effects on the hexafluorides of group 10 metals" (PDF). Retrieved 29 March 2023.
- 1 2 Griffith, William P.; Robinson, Stephen D.; Swars, Kurt (29 June 2013). Pd Palladium: Palladium Compounds. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 48. ISBN 978-3-662-09188-3 . Retrieved 29 March 2023.
- ↑ Aullón, Gabriel; Alvarez, Santiago (1 April 2007). "On the Existence of Molecular Palladium(VI) Compounds: Palladium Hexafluoride". Inorganic Chemistry . 46 (7): 2700–2703. doi:10.1021/ic0623819. ISSN 0020-1669. PMID 17326630 . Retrieved 29 March 2023.