
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a vacuum deposition method used to produce high-quality, and high-performance, solid materials. The process is often used in the semiconductor industry to produce thin films.

Tungsten(VI) fluoride, also known as tungsten hexafluoride, is an inorganic compound with the formula WF6. It is a toxic, corrosive, colorless gas, with a density of about 13 kg/m3 (22 lb/cu yd). It is the only known gaseous transition metal compound and the densest known gas under standard ambient temperature and pressure. WF6 is commonly used by the semiconductor industry to form tungsten films, through the process of chemical vapor deposition. This layer is used in a low-resistivity metallic "interconnect". It is one of seventeen known binary hexafluorides.
Atomic layer deposition (ALD) is a thin-film deposition technique based on the sequential use of a gas-phase chemical process; it is a subclass of chemical vapour deposition. The majority of ALD reactions use two chemicals called precursors. These precursors react with the surface of a material one at a time in a sequential, self-limiting, manner. A thin film is slowly deposited through repeated exposure to separate precursors. ALD is a key process in fabricating semiconductor devices, and part of the set of tools for synthesizing nanomaterials.

Uranium tetrafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula UF4. It is a green solid with an insignificant vapor pressure and low solubility in water. Uranium in its tetravalent (uranous) state is important in various technological processes. In the uranium refining industry it is known as green salt.
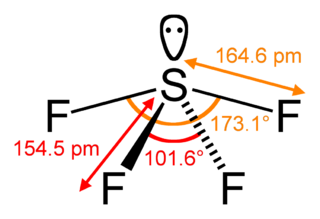
Sulfur tetrafluoride is a chemical compound with the formula SF4. It is a colorless corrosive gas that releases dangerous hydrogen fluoride gas upon exposure to water or moisture. Sulfur tetrafluoride is a useful reagent for the preparation of organofluorine compounds, some of which are important in the pharmaceutical and specialty chemical industries.
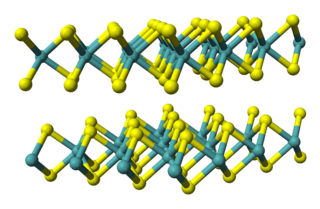
Tungsten disulfide is an inorganic chemical compound composed of tungsten and sulfur with the chemical formula WS2. This compound is part of the group of materials called the transition metal dichalcogenides. It occurs naturally as the rare mineral tungstenite. This material is a component of certain catalysts used for hydrodesulfurization and hydrodenitrification.
Electron-beam physical vapor deposition, or EBPVD, is a form of physical vapor deposition in which a target anode is bombarded with an electron beam given off by a charged tungsten filament under high vacuum. The electron beam causes atoms from the target to transform into the gaseous phase. These atoms then precipitate into solid form, coating everything in the vacuum chamber with a thin layer of the anode material.

Tungsten oxytetrafluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula WOF4. It is a colorless diamagnetic solid. The compound is one of many oxides of tungsten. It is usually encountered as product of the partial hydrolysis of tungsten hexafluoride.

Tantalum nitride (TaN) is a chemical compound, a nitride of tantalum. There are multiple phases of compounds, stoichimetrically from Ta2N to Ta3N5, including TaN.

Evaporation is a common method of thin-film deposition. The source material is evaporated in a vacuum. The vacuum allows vapor particles to travel directly to the target object (substrate), where they condense back to a solid state. Evaporation is used in microfabrication, and to make macro-scale products such as metallized plastic film.
A hexafluoride is a chemical compound with the general formula QXnF6, QXnF6m−, or QXnF6m+. Many molecules fit this formula. An important hexafluoride is hexafluorosilicic acid (H2SiF6), which is a byproduct of the mining of phosphate rock. In the nuclear industry, uranium hexafluoride (UF6) is an important intermediate in the purification of this element.

Molybdenum hexafluoride, also molybdenum(VI) fluoride, is the inorganic compound with the formula MoF6. It is the highest fluoride of molybdenum. It is a colourless solid and melts just below room temperature and boils in 34 °C. It is one of the seventeen known binary hexafluorides.

Vanadium(V) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula VF5. It is a colorless volatile liquid that freezes near room temperature. It is a highly reactive compound, as indicated by its ability to fluorinate organic substances.
Fluorine forms a great variety of chemical compounds, within which it always adopts an oxidation state of −1. With other atoms, fluorine forms either polar covalent bonds or ionic bonds. Most frequently, covalent bonds involving fluorine atoms are single bonds, although at least two examples of a higher order bond exist. Fluoride may act as a bridging ligand between two metals in some complex molecules. Molecules containing fluorine may also exhibit hydrogen bonding. Fluorine's chemistry includes inorganic compounds formed with hydrogen, metals, nonmetals, and even noble gases; as well as a diverse set of organic compounds. For many elements the highest known oxidation state can be achieved in a fluoride. For some elements this is achieved exclusively in a fluoride, for others exclusively in an oxide; and for still others the highest oxidation states of oxides and fluorides are always equal.
Laser chemical vapor deposition (LCVD) is a chemical process used to produce high purity, high performance films, fibers, and mechanical hardware (MEMS). It is a form of chemical vapor deposition in which a laser beam is used to locally heat the semiconductor substrate, causing the vapor deposition chemical reaction to proceed faster at that site. The process is used in the semiconductor industry for spot coating, the MEMS industry for 3-D printing of hardware such as springs and heating elements,2,6,7,9 and the composites industry for boron and ceramic fibers. As with conventional CVD, one or more gas phase precursors are thermally decomposed, and the resulting chemical species 1) deposit on a surface, or 2) react, form the desired compound, and then deposit on a surface, or a combination of (1) and (2).

A-234 is an organophosphate nerve agent. It was developed in the Soviet Union under the FOLIANT program and is one of the group of compounds referred to as Novichok agents that were revealed by Vil Mirzayanov. In March 2018 the Russian ambassador to the UK, Alexander Yakovenko, claimed to have been informed by British authorities that A-234 had been identified as the agent used in the poisoning of Sergei and Yulia Skripal. Vladimir Uglev, one of the inventors of the Novichok series of compounds, said he was "99 percent sure that it was A-234" in relation to the 2018 Amesbury poisonings, noting its unusually high persistence in the environment.

Tungsten(V) fluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula WF5. It is a hygroscopic yellow solid. Like most pentafluorides, it adopts a tetrameric structure, consisting of [WF5]4 molecules. In this way, each W center achieves octahedral coordination.

Neodymium(III) acetylacetonate is a coordination compound with the chemical formula Nd(O2C5H7)3. Although many sources discuss this anhydrous acetylacetonate complex, it is the dihydrate Nd(O2C5H7)3(H2O)2 that has been characterized by X-ray crystallography. It commonly occurs as a white powder. Upon heating under vacuum, other dihydrated lanthanide trisacetylacetonates convert to oxo-clusters M4O(C5H7O2)10. This result suggests that Nd(O2C5H7)3 may not exist.
Hafnium compounds are compounds containing the element hafnium (Hf). Due to the lanthanide contraction, the ionic radius of hafnium(IV) (0.78 ångström) is almost the same as that of zirconium(IV) (0.79 angstroms). Consequently, compounds of hafnium(IV) and zirconium(IV) have very similar chemical and physical properties. Hafnium and zirconium tend to occur together in nature and the similarity of their ionic radii makes their chemical separation rather difficult. Hafnium tends to form inorganic compounds in the oxidation state of +4. Halogens react with it to form hafnium tetrahalides. At higher temperatures, hafnium reacts with oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, boron, sulfur, and silicon. Some compounds of hafnium in lower oxidation states are known.

Lithium hexafluorotungstate is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula LiWF6.













