Related Research Articles

Neil Bartlett was a British chemist who specialized in fluorine and compounds containing fluorine, and became famous for creating the first noble gas compounds. He taught chemistry at the University of British Columbia and the University of California, Berkeley.

Xenon hexafluoroplatinate is the product of the reaction of platinum hexafluoride with xenon, in an experiment that proved the chemical reactivity of the noble gases. This experiment was performed by Neil Bartlett at the University of British Columbia, who formulated the product as "Xe+[PtF6]−", although subsequent work suggests that Bartlett's product was probably a salt mixture and did not in fact contain this specific salt.
In chemistry, noble gas compounds are chemical compounds that include an element from the noble gases, group 18 of the periodic table. Although the noble gases are generally unreactive elements, many such compounds have been observed, particularly involving the element xenon.
Xenon hexafluoride is a noble gas compound with the formula XeF6. It is one of the three binary fluorides of xenon that have been studied experimentally, the other two being XeF2 and XeF4. All known are exergonic and stable at normal temperatures. XeF6 is the strongest fluorinating agent of the series. It is a colorless solid that readily sublimes into intensely yellow vapors.
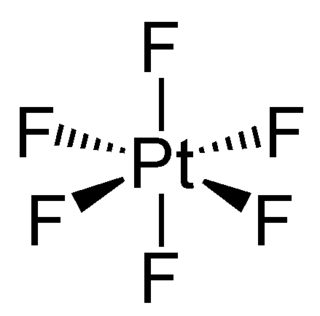
Platinum hexafluoride is the chemical compound with the formula PtF6, and is one of seventeen known binary hexafluorides. It is a dark-red volatile solid that forms a red gas. The compound is a unique example of platinum in the +6 oxidation state. With only four d-electrons, it is paramagnetic with a triplet ground state. PtF6 is a strong fluorinating agent and one of the strongest oxidants, capable of oxidising xenon and O2. PtF6 is octahedral in both the solid state and in the gaseous state. The Pt-F bond lengths are 185 picometers.
Tellurium hexafluoride is the inorganic compound of tellurium and fluorine with the chemical formula TeF6. It is a colorless, highly toxic gas with an unpleasant odor.

Gold(V) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula Au2F10. This fluoride compound features gold in its highest known oxidation state. This red solid dissolves in hydrogen fluoride but these solutions decompose, liberating fluorine.

Krypton difluoride, KrF2 is a chemical compound of krypton and fluorine. It was the first compound of krypton discovered. It is a volatile, colourless solid at room temperature. The structure of the KrF2 molecule is linear, with Kr−F distances of 188.9 pm. It reacts with strong Lewis acids to form salts of the KrF+ and Kr
2F+
3 cations.

The dioxygenyl ion, O+
2, is a rarely-encountered oxycation in which both oxygen atoms have a formal oxidation state of +1/2. It is formally derived from oxygen by the removal of an electron:
Dioxygenyl hexafluoroplatinate is a compound with formula O2PtF6. It is a hexafluoroplatinate of the unusual dioxygenyl cation, O2+, and is the first known compound containing this cation. It can be produced by the reaction of dioxygen with platinum hexafluoride. The fact that PtF
6 is strong enough to oxidise O
2, whose first ionization potential is 12.2 eV, led Neil Bartlett to correctly surmise that it might be able to oxidise xenon (first ionization potential 12.13 eV). This led to the discovery of xenon hexafluoroplatinate, which proved that the noble gases, previously thought to be inert, are able to form chemical compounds.

Plutonium hexafluoride is the highest fluoride of plutonium, and is of interest for laser enrichment of plutonium, in particular for the production of pure plutonium-239 from irradiated uranium. This isotope of plutonium is needed to avoid premature ignition of low-mass nuclear weapon designs by neutrons produced by spontaneous fission of plutonium-240.
A hexafluoride is a chemical compound with the general formula QXnF6, QXnF6m−, or QXnF6m+. Many molecules fit this formula. An important hexafluoride is hexafluorosilicic acid (H2SiF6), which is a byproduct of the mining of phosphate rock. In the nuclear industry, uranium hexafluoride (UF6) is an important intermediate in the purification of this element.

Molybdenum hexafluoride, also molybdenum(VI) fluoride, is the inorganic compound with the formula MoF6. It is the highest fluoride of molybdenum. It is a colourless solid and melts just below room temperature and boils in 34 °C. It is one of the seventeen known binary hexafluorides.

Rhodium hexafluoride, also rhodium(VI) fluoride, (RhF6) is the inorganic compound of rhodium and fluorine. A black volatile solid, it is a highly reactive material which starts to slowly thermally decompose already at room temperature and a rare example of a rhodium(VI) compound. It is one of seventeen known binary hexafluorides.

Rhenium hexafluoride, also rhenium(VI) fluoride, (ReF6) is a compound of rhenium and fluorine and one of the seventeen known binary hexafluorides.
Chromium pentafluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula CrF5. It is a red volatile solid that melts at 34 °C. It is the highest known chromium fluoride, since the hypothetical chromium hexafluoride has not yet been synthesized.
Fluorine forms a great variety of chemical compounds, within which it always adopts an oxidation state of −1. With other atoms, fluorine forms either polar covalent bonds or ionic bonds. Most frequently, covalent bonds involving fluorine atoms are single bonds, although at least two examples of a higher order bond exist. Fluoride may act as a bridging ligand between two metals in some complex molecules. Molecules containing fluorine may also exhibit hydrogen bonding. Fluorine's chemistry includes inorganic compounds formed with hydrogen, metals, nonmetals, and even noble gases; as well as a diverse set of organic compounds. For many elements the highest known oxidation state can be achieved in a fluoride. For some elements this is achieved exclusively in a fluoride, for others exclusively in an oxide; and for still others the highest oxidation states of oxides and fluorides are always equal.
Palladium hexafluoride is an inorganic chemical compound of palladium metal and fluorine with the chemical formula PdF6. It is reported to be a still hypothetical compound. This is one of many palladium fluorides.

Americium hexafluoride is an inorganic chemical compound of americium metal and fluorine with the chemical formula AmF
6. It is still a hypothetical compound. Synthesis by fluorination of americium tetrafluoride was unsuccessfully attempted in 1990. A thermochromatographic identification in 1986 remains inconclusive. Calculations suggest that it may be distorted from octahedral symmetry.
Caesium heptafluoroxenate is an inorganic compound of caesium, and fluorine, and xenon with the chemical formula CsXeF7.
References
- ↑ Compton, R. N.; Klots, Cornelius E. (1989). Iones, Molecules, and Energy. Oak Ridge National Laboratory . p. 169. Retrieved 2 May 2023.
- ↑ Groult, Henri; Leroux, Frederic; Tressaud, Alain (4 November 2016). Modern Synthesis Processes and Reactivity of Fluorinated Compounds: Progress in Fluorine Science. Elsevier. p. 563. ISBN 978-0-12-803790-4 . Retrieved 2 May 2023.
- ↑ Hargittai, Istvan; Hargittai, Magdolna (21 March 2003). Candid Science Iii: More Conversations With Famous Chemists. World Scientific. p. 47. ISBN 978-1-78326-111-6 . Retrieved 2 May 2023.
- ↑ Hargittai, Istvan (13 April 2010). Drive and Curiosity: What Fuels the Passion for Science. Prometheus Books. ISBN 978-1-61614-469-2 . Retrieved 2 May 2023.
- ↑ Craciun, Raluca; Picone, Désireé; Long, Rebecca T.; Li, Shenggang; Dixon, David A.; Peterson, Kirk A.; Christe, Karl O. (1 February 2010). "Third Row Transition Metal Hexafluorides, Extraordinary Oxidizers, and Lewis Acids: Electron Affinities, Fluoride Affinities, and Heats of Formation of WF6, ReFF6, OsF6, IrF6, PtF6, and AuF6". Inorganic Chemistry . 49 (3): 1056–1070. doi:10.1021/ic901967h. ISSN 0020-1669. PMID 20052991.
- ↑ Bartlett, Neil (26 October 2001). Oxidation Of Oxygen And Related Chemistry, The: Selected Papers Of Neil Bartlett. World Scientific. p. 201. ISBN 978-981-4498-50-0 . Retrieved 2 May 2023.