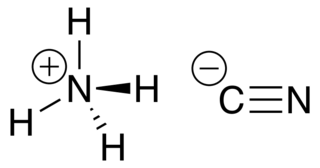In chemistry, cyanide is a chemical compound that contains a C≡N functional group. This group, known as the cyano group, consists of a carbon atom triple-bonded to a nitrogen atom.

In chemistry, a salt or ionic compound is a chemical compound consisting of an assembly of positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions), which results in a compound with no net electric charge. The constituent ions are held together by electrostatic forces termed ionic bonds.

Sodium cyanide is a compound with the formula NaCN and the structure Na+−C≡N. It is a white, water-soluble solid. Cyanide has a high affinity for metals, which leads to the high toxicity of this salt. Its main application, in gold mining, also exploits its high reactivity toward metals. It is a moderately strong base.
Gold cyanidation is a hydrometallurgical technique for extracting gold from low-grade ore by converting the gold to a water-soluble coordination complex. It is the most commonly used leaching process for gold extraction. Cyanidation is also widely used in the extraction of silver, usually after froth flotation.
In organic chemistry, a nitrile is any organic compound that has a −C≡N functional group. The name of the compound is composed of a base, which includes the carbon of the −C≡N, suffixed with "nitrile", so for example CH3CH2C≡N is called "propionitrile". The prefix cyano- is used interchangeably with the term nitrile in industrial literature. Nitriles are found in many useful compounds, including methyl cyanoacrylate, used in super glue, and nitrile rubber, a nitrile-containing polymer used in latex-free laboratory and medical gloves. Nitrile rubber is also widely used as automotive and other seals since it is resistant to fuels and oils. Organic compounds containing multiple nitrile groups are known as cyanocarbons.

Potassium cyanide is a compound with the formula KCN. It is a colorless salt, similar in appearance to sugar, that is highly soluble in water. Most KCN is used in gold mining, organic synthesis, and electroplating. Smaller applications include jewellery for chemical gilding and buffing. Potassium cyanide is highly toxic, and a dose of 200 to 300 milligrams will kill nearly any human.
Benzonitrile is the chemical compound with the formula C6H5(CN), abbreviated PhCN. This aromatic organic compound is a colorless liquid with a sweet bitter almond odour. It is mainly used as a precursor to the resin benzoguanamine.
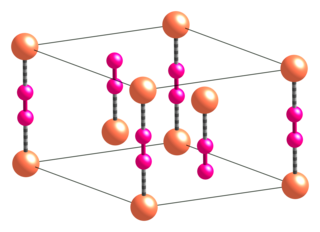
Copper(I) cyanide is an inorganic compound with the formula CuCN. This off-white solid occurs in two polymorphs; impure samples can be green due to the presence of Cu(II) impurities. The compound is useful as a catalyst, in electroplating copper, and as a reagent in the preparation of nitriles.

Silver cyanide is the chemical compound with the formula AgCN. It is a white salt that is precipitated upon treatment of solutions containing Ag+ with cyanide, which is used in some schemes to recover silver from solution. Silver cyanide is used in silver-plating.

Zinc cyanide is the inorganic compound with the formula Zn(CN)2. It is a white solid that is used mainly for electroplating zinc but also has more specialized applications for the synthesis of organic compounds.

Gold compounds are compounds by the element gold (Au). Although gold is the most noble of the noble metals, it still forms many diverse compounds. The oxidation state of gold in its compounds ranges from −1 to +5, but Au(I) and Au(III) dominate its chemistry. Au(I), referred to as the aurous ion, is the most common oxidation state with soft ligands such as thioethers, thiolates, and organophosphines. Au(I) compounds are typically linear. A good example is Au(CN)−2, which is the soluble form of gold encountered in mining. The binary gold halides, such as AuCl, form zigzag polymeric chains, again featuring linear coordination at Au. Most drugs based on gold are Au(I) derivatives.
Acetone cyanohydrin (ACH) is an organic compound used in the production of methyl methacrylate, the monomer of the transparent plastic polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), also known as acrylic. It liberates hydrogen cyanide easily, so it is used as a source of such. For this reason, this cyanohydrin is also highly toxic.

Sodium aurothiosulfate, or sanocrysin, is the inorganic compound with the formula Na3[Au(S2O3)2]·2H2O. It is the trisodium salt of the coordination complex of gold(I), [Au(S2O3)2]3−. The dihydrate, which is colorless, crystallizes with two waters of crystallization. The compound has some medicinal properties as well as potential for hydrometallurgy.
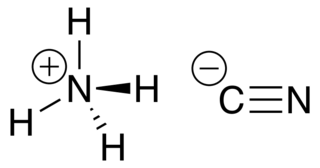
Ammonium cyanide is an unstable inorganic compound with the formula NH4CN.
Cyanometallates or cyanometalates are a class of coordination compounds, most often consisting only of cyanide ligands. Most are anions. Cyanide is a highly basic and small ligand, hence it readily saturates the coordination sphere of metal ions. The resulting cyanometallate anions are often used as building blocks for more complex structures called coordination polymers, the best known example of which is Prussian blue, a common dyestuff.
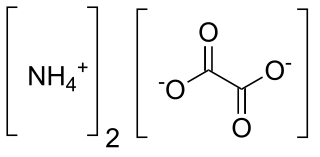
Ammonium oxalate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula [NH4]2C2O4. Its formula is often written as (NH4)2C2O4 or (COONH4)2. It is an ammonium salt of oxalic acid. It consists of ammonium cations ([NH4]+) and oxalate anions (C2O2−4). The structure of ammonium oxalate is ([NH4]+)2[C2O4]2−. Ammonium oxalate sometimes comes as a monohydrate ([NH4]2C2O4·H2O). It is a colorless or white salt under standard conditions and is odorless and non-volatile. It occurs in many plants and vegetables.

Calcium cyanide is the inorganic compound with the formula Ca(CN)2. It is the calcium salt derived from hydrocyanic acid. It is a white solid, although the pure material is rarely encountered. It slowly hydrolyses in solution or moist air to release hydrogen cyanide and is very toxic.
Potassium dicyanoaurate is an inorganic compound with formula K[Au(CN)2]. It is a colorless to white solid that is soluble in water and slightly soluble in alcohol. The salt itself is often not isolated, but solutions of the dicyanoaurate ion are generated on a large scale in the extraction of gold from its ores.
Aluminium cyanide is a metallic cyanide with a chemical formula of Al(CN)3. It is a white solid that undergoes hydrolysis to produce aluminium hydroxide and hydrogen cyanide.
Gold(I) cyanide is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula AuCN. It is the binary cyanide of gold(I). It is an odourless, tasteless yellow solid. Wet gold(I) cyanide is unstable to light and will become greenish. Gold(I) cyanide itself is only of academic interest, but its derivative dicyanoaurate is an intermediate in gold cyanidation, the extraction of gold from its ores.