
Zinc chloride is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula ZnCl2·nH2O, with n ranging from 0 to 4.5, forming hydrates. Zinc chloride, anhydrous and its hydrates, are colorless or white crystalline solids, and are highly soluble in water. Five hydrates of zinc chloride are known, as well as four forms of anhydrous zinc chloride.

Europium(III) chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula EuCl3. The anhydrous compound is a yellow solid. Being hygroscopic it rapidly absorbs water to form a white crystalline hexahydrate, EuCl3·6H2O, which is colourless. The compound is used in research.

Ammonium hydrosulfide is the chemical compound with the formula [NH4]SH.

Iron(II) fluoride or ferrous fluoride is an inorganic compound with the molecular formula FeF2. It forms a tetrahydrate FeF2·4H2O that is often referred to by the same names. The anhydrous and hydrated forms are white crystalline solids.
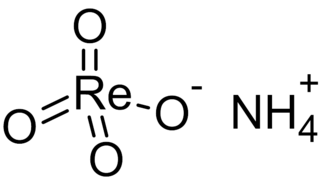
Ammonium perrhenate (APR) is the ammonium salt of perrhenic acid, NH4ReO4. It is the most common form in which rhenium is traded. It is a white salt; soluble in ethanol and water, and mildly soluble in NH4Cl. It was first described soon after the discovery of rhenium.

A double salt is a salt that contains two or more different cations or anions. Examples of double salts include alums (with the general formula MIMIII(SO4)2·12H2O) and Tutton's salts (with the general formula (MI)2MII(SO4)2·6H2O). Other examples include potassium sodium tartrate, ammonium iron(II) sulfate (Mohr's salt), potassium uranyl sulfate (used to discover radioactivity) and bromlite BaCa(CO3)2. The fluorocarbonates contain fluoride and carbonate anions. Many coordination complexes form double salts.

Zirconium(IV) fluoride describes members of a family inorganic compounds with the formula ZrF4(H2O)x. All are colorless, diamagnetic solids. Anhydrous Zirconium(IV) fluoride is a component of ZBLAN fluoride glass.

Yttrium(III) chloride is an inorganic compound of yttrium and chloride. It exists in two forms, the hydrate (YCl3(H2O)6) and an anhydrous form (YCl3). Both are colourless salts that are highly soluble in water and deliquescent.
Dysprosium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of dysprosium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Dy(NO3)3. The compound forms yellowish crystals, dissolves in water, forms a crystalline hydrate.
Polonium sulfide is an inorganic compound of polonium and sulfur with the chemical formula PoS. The compound is radioactive and forms black crystals.
Thallium(I) hexafluorophosphate is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula TlPF6.
Ammonium hexafluorostannate is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula (NH4)2SnF6.
Ammonium hexafluorovanadate is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula (NH4)3VF6.
Ammonium hexachlorostannate is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula (NH4)2SnCl6.
Ammonium hexafluorogermanate is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula (NH4)2GeF6.
Ammonium hexachloropalladate is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula (NH4)2PdCl6.
Ammonium hexachlororhodate(III) is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula (NH4)3RhCl6.
Ammonium hexachloroosmate(IV) is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula (NH4)2OsCl6.
Ammonium hexabromoplatinate is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula (NH4)2PtBr6.
Ammonium dihydrogen arsenate is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula NH4H2AsO4.










