
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, but only the gray form, which has a metallic appearance, is important to industry.

The nitrite ion has the chemical formula NO−
2. Nitrite is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name nitrite can also refer to organic compounds with the – ONO group, which are esters of nitrous acid.

Arsenic trisulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula As2S3. It is a dark yellow solid that is insoluble in water. It also occurs as the mineral orpiment (Latin: auripigment), which has been used as a pigment called King's yellow. It is produced in the analysis of arsenic compounds. It is a group V/VI, intrinsic p-type semiconductor and exhibits photo-induced phase-change properties. The other principal arsenic sulfide is As4S4, a red-orange solid known as the mineral realgar.
Substances, mixtures, and exposure circumstances in this list have been classified as group 1 by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC): The agent (mixture) is carcinogenic to humans. The exposure circumstance entails exposures that are carcinogenic to humans. This category is used when there is sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in humans. Exceptionally, an agent (mixture) may be placed in this category when evidence of carcinogenicity in humans is less than sufficient but there is sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in experimental animals and strong evidence in exposed humans that the agent (mixture) acts through a relevant mechanism of carcinogenicity.
The agents in this list have been classified in group 2A by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). The term "agent" encompasses both substances and exposure circumstances that pose a risk. This designation is applied when there is limited evidence of carcinogenicity in humans as well as sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in experimental animals. In some cases, an agent may be classified in this group when there is inadequate evidence of carcinogenicity in humans along with sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in experimental animals and strong evidence that the carcinogenesis is mediated by a mechanism that also operates in humans. Exceptionally, an agent may be classified in this group solely on the basis of limited evidence of carcinogenicity in humans.

Arsenic trioxide, sold under the brand name Trisenox among others, is an inorganic compound and medication. As an industrial chemical, whose major uses include in the manufacture of wood preservatives, pesticides, and glass. As a medication, it is used to treat a type of cancer known as acute promyelocytic leukemia. For this use it is given by injection into a vein.
Lead hydrogen arsenate, also called lead arsenate, acid lead arsenate or LA, chemical formula PbHAsO4, is an inorganic insecticide used primarily against the potato beetle. Lead arsenate was the most extensively used arsenical insecticide. Two principal formulations of lead arsenate were marketed: basic lead arsenate (Pb5OH(AsO4)3, CASN: 1327-31-7) and acid lead arsenate (PbHAsO4.
The arsenate ion is AsO3−
4. An arsenate (compound) is any compound that contains this ion. Arsenates are salts or esters of arsenic acid. The arsenic atom in arsenate has a valency of 5 and is also known as pentavalent arsenic or As(V). Arsenate resembles phosphate in many respects, since arsenic and phosphorus occur in the same group (column) of the periodic table. Arsenates are moderate oxidizers, with an electrode potential of +0.56 V for reduction to arsenites.

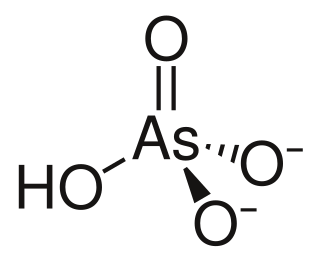
Arsenic acid is the chemical compound with the formula H3AsO4. More descriptively written as AsO(OH)3, this colorless acid is the arsenic analogue of phosphoric acid. Arsenate and phosphate salts behave very similarly. Arsenic acid as such has not been isolated, but is only found in solution, where it is largely ionized. Its hemihydrate form (H3AsO4·1/2H2O) does form stable crystals. Crystalline samples dehydrate with condensation at 100 °C.
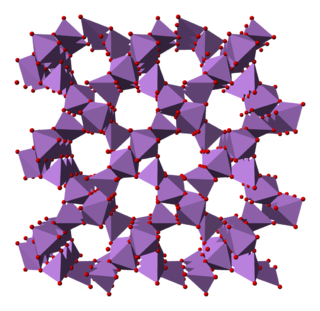
Arsenic pentoxide is the inorganic compound with the formula As2O5. This glassy, white, deliquescent solid is relatively unstable, consistent with the rarity of the As(V) oxidation state. More common, and far more important commercially, is arsenic(III) oxide (As2O3). All inorganic arsenic compounds are highly toxic and thus find only limited commercial applications.
Chromated copper arsenate (CCA) is a wood preservative containing compounds of chromium, copper, and arsenic, in various proportions. It is used to impregnate timber and other wood products, especially those intended for outdoor use, in order to protect them from attack by microbes and insects. Like other copper-based wood preservatives, it imparts a greenish tint to treated timber.

Nickel(II) sulfate, or just nickel sulfate, usually refers to the inorganic compound with the formula NiSO4(H2O)6. This highly soluble blue green coloured salt is a common source of the Ni2+ ion for electroplating.

Ammonium heptamolybdate is the inorganic compound whose chemical formula is (NH4)6Mo7O24, normally encountered as the tetrahydrate. A dihydrate is also known. It is a colorless solid, often referred to as ammonium paramolybdate or simply as ammonium molybdate, although "ammonium molybdate" can also refer to ammonium orthomolybdate, (NH4)2MoO4, and several other compounds. It is one of the more common molybdenum compounds.

Calcium chromate is an inorganic compound with the formula CaCrO4, i.e. the chromate salt of calcium. It is a bright yellow solid which is normally found in the dihydrate form CaCrO4·2H2O. A very rare anhydrous mineral form exists in nature, which is known as chromatite.

Sodium chromate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CrO4. It exists as a yellow hygroscopic solid, which can form tetra-, hexa-, and decahydrates. It is an intermediate in the extraction of chromium from its ores.

Disodium methyl arsonate (DSMA) is the organoarsenic compound with the formula CH3AsO3Na2. It is a colorless, water-soluble solid derived from methanearsonic acid. It is used as a herbicide. Tradenames include Metharsinat, Arrhenal, Disomear, Metharsan, Stenosine, Tonarsan, Tonarsin, Arsinyl, Arsynal, and Diarsen.
Arsenic biochemistry refers to biochemical processes that can use arsenic or its compounds, such as arsenate. Arsenic is a moderately abundant element in Earth's crust, and although many arsenic compounds are often considered highly toxic to most life, a wide variety of organoarsenic compounds are produced biologically and various organic and inorganic arsenic compounds are metabolized by numerous organisms. This pattern is general for other related elements, including selenium, which can exhibit both beneficial and deleterious effects. Arsenic biochemistry has become topical since many toxic arsenic compounds are found in some aquifers, potentially affecting many millions of people via biochemical processes.
Ammonium orthomolybdate is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula (NH4)2MoO4. It is a white solid that is prepared by treating molybdenum trioxide with aqueous ammonia. Upon heating these solutions, ammonia is lost, to give ammonium heptamolybdate ((NH4)6Mo7O24.4H2O). Ammonium orthomolybdate is used as a corrosion inhibitor and is an intermediate in some schemes to win molybdenum from its ores.

The arsenic (As) cycle is the biogeochemical cycle of natural and anthropogenic exchanges of arsenic terms through the atmosphere, lithosphere, pedosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere. Although arsenic is naturally abundant in the Earth's crust, long-term exposure and high concentrations of arsenic can be detrimental to human health.
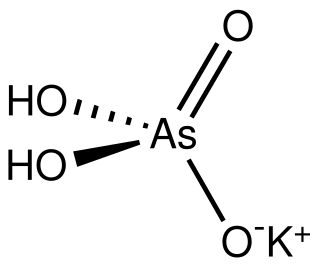
Monopotassium arsenate is the inorganic compound with the formula KH2AsO4. A white solid, this salt is used to prepared other arsenic-containing compounds, mainly pesticides. It is prepared by calcining arsenic oxide and potassium nitrate, followed by extraction with water.














