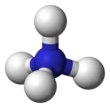
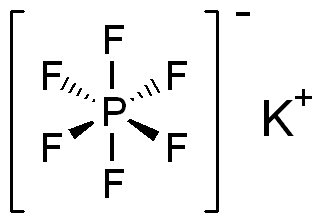The nitronium ion, NO+2, is a cation. It is an onium ion because its nitrogen atom has +1 charge, similar to ammonium ion NH+4. It is created by the removal of an electron from the paramagnetic nitrogen dioxide molecule NO2, or the protonation of nitric acid HNO3.
In chemistry, a salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, which results in a compound with no net electric charge. A common example is table salt, with positively charged sodium ions and negatively charged chloride ions.
Anions that interact weakly with cations are termed non-coordinating anions, although a more accurate term is weakly coordinating anion. Non-coordinating anions are useful in studying the reactivity of electrophilic cations. They are commonly found as counterions for cationic metal complexes with an unsaturated coordination sphere. These special anions are essential components of homogeneous alkene polymerisation catalysts, where the active catalyst is a coordinatively unsaturated, cationic transition metal complex. For example, they are employed as counterions for the 14 valence electron cations [(C5H5)2ZrR]+ (R = methyl or a growing polyethylene chain). Complexes derived from non-coordinating anions have been used to catalyze hydrogenation, hydrosilylation, oligomerization, and the living polymerization of alkenes. The popularization of non-coordinating anions has contributed to increased understanding of agostic complexes wherein hydrocarbons and hydrogen serve as ligands. Non-coordinating anions are important components of many superacids, which result from the combination of Brønsted acids and Lewis acids.

Ammonium fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula NH4F. It crystallizes as small colourless prisms, having a sharp saline taste, and is highly soluble in water. Like all fluoride salts, it is moderately toxic in both acute and chronic overdose.

Ammonium hydrosulfide is the chemical compound with the formula (NH4)HS.

Ammonium hydrogen fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula NH4HF2 or NH4F·HF. It is produced from ammonia and hydrogen fluoride. This colourless salt is a glass-etchant and an intermediate in a once-contemplated route to hydrofluoric acid.

Ammonium metavanadate is the inorganic compound with the formula NH4VO3. It is a white salt, although samples are often yellow owing to impurities of V2O5. It is an important intermediate in the purification of vanadium.

Ammonium hexachloroplatinate, also known as ammonium chloroplatinate, is the inorganic compound with the formula (NH4)2[PtCl6]. It is a rare example of a soluble platinum(IV) salt that is not hygroscopic. It forms intensely yellow solutions in water. In the presence of 1M NH4Cl, its solubility is only 0.0028 g/100 mL.

Hexafluorophosphate is an anion with chemical formula of PF−
6. It is an octahedral species that imparts no color to its salts. PF−
6 is isoelectronic with sulfur hexafluoride, SF6, and the hexafluorosilicate dianion, SiF2−
6, and fluoroantimonate SbF−
6. Being poorly nucleophilic, hexafluorophosphate is classified as a non-coordinating anion.
Hexafluorophosphoric acid is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula HPF
6. This strong Brønsted acid features a non-coordinating anion, hexafluorophosphate. It is formed from the reaction of hydrogen fluoride with phosphorus pentafluoride.

Lithium hexafluorophosphate is an inorganic compound with the formula LiPF6. It is a white crystalline powder.
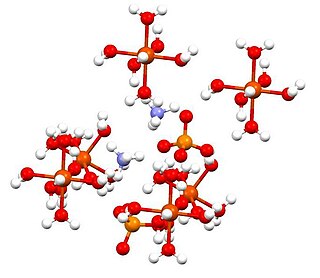
Ammonium iron(II) sulfate, or Mohr's salt, is the inorganic compound with the formula (NH4)2Fe(SO4)2(H2O)6. Containing two different cations, Fe2+ and NH4+, it is classified as a double salt of ferrous sulfate and ammonium sulfate. It is a common laboratory reagent because it is readily crystallized, and crystals resist oxidation by air. Like the other ferrous sulfate salts, ferrous ammonium sulfate dissolves in water to give the aquo complex [Fe(H2O)6]2+, which has octahedral molecular geometry. Its mineral form is mohrite.
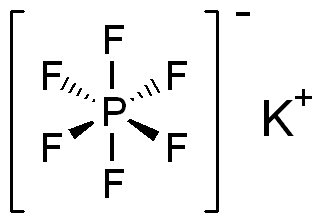
Potassium hexafluorophosphate is the chemical compound with the formula KPF6. This colourless salt consists of potassium cations and hexafluorophosphate anions. It is prepared by the reaction:

Silver hexafluorophosphate, sometimes referred to "silver PF-6," is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula AgPF6.

Sodium hexafluorophosphate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Na[PF6].

Tetrakis(acetonitrile)copper(I) hexafluorophosphate is a salt with the formula [Cu(CH3CN)4]PF6. It is a colourless solid that is used in the synthesis of other copper complexes. The cation [Cu(CH3CN)4]+ is a well-known example of a transition metal nitrile complex.

Ammonium thiocyanate is an inorganic compound with the formula NH4SCN. It is the salt of the ammonium cation and the thiocyanate anion.

Ferrocenium hexafluorophosphate is an organometallic compound with the formula [Fe(C5H5)2]PF6. This salt is composed of the cation [Fe(C5H5)2]+ and the hexafluorophosphate anion (PF−
6). The related tetrafluoroborate is also a popular reagent with similar properties. The cation is often abbreviated Fc+ or Cp2Fe+. The salt is deep blue in color and paramagnetic.

Tris(acetonitrile)cyclopentadienylruthenium hexafluorophosphate is an organoruthenium compound with the formula [(C5H5)Ru(NCCH3)3]PF6, abbreviated [CpRu(NCMe)3]PF6. It is a yellow-brown solid that is soluble in polar organic solvents. The compound is a salt consisting of the hexafluorophosphate anion and the cation [CpRu(NCMe)3]+. In coordination chemistry, it is used as a source of RuCp+ for further derivitization. In organic synthesis, it is a homogeneous catalyst. It enables C-C bond formation and promotes cycloadditions. The cyclopentadienyl ligand (Cp) is bonded in an η5 manner to the Ru(II) center.

Ammonium tetrafluoroborate (or ammonium fluoroborate) is an inorganic salt composed of the ammonium cation and the tetrafluoroborate anion, with the chemical formula NH4BF4. When heated to decomposition, ammonium tetrafluoroborate releases toxic fumes of hydrogen fluoride, nitrogen oxides, and ammonia.