
The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), caesium (Cs), and francium (Fr). Together with hydrogen they constitute group 1, which lies in the s-block of the periodic table. All alkali metals have their outermost electron in an s-orbital: this shared electron configuration results in their having very similar characteristic properties. Indeed, the alkali metals provide the best example of group trends in properties in the periodic table, with elements exhibiting well-characterised homologous behaviour. This family of elements is also known as the lithium family after its leading element.

Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula KOH, and is commonly called caustic potash.

Sodium fluoride (NaF) is an inorganic compound with the formula NaF. It is a colorless or white solid that is readily soluble in water. It is used in trace amounts in the fluoridation of drinking water to prevent tooth decay, and in toothpastes and topical pharmaceuticals for the same purpose. In 2021, it was the 291st most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 600,000 prescriptions. It is also used in metallurgy and in medical imaging.

Caesium fluoride or cesium fluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula CsF and it is a hygroscopic white salt. Caesium fluoride can be used in organic synthesis as a source of the fluoride anion. Caesium also has the highest electropositivity of all known elements and fluorine has the highest electronegativity of all known elements.

Oxygen fluorides are compounds of elements oxygen and fluorine with the general formula OnF2, where n = 1 to 6. Many different oxygen fluorides are known:

Sodium peroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula Na2O2. This yellowish solid is the product of sodium ignited in excess oxygen. It is a strong base. This metal peroxide exists in several hydrates and peroxyhydrates including Na2O2·2H2O2·4H2O, Na2O2·2H2O, Na2O2·2H2O2, and Na2O2·8H2O. The octahydrate, which is simple to prepare, is white, in contrast to the anhydrous material.

Potassium hydride, KH, is the inorganic compound of potassium and hydrogen. It is an alkali metal hydride. It is a white solid, although commercial samples appear gray. It is a powerful superbase that is useful in organic synthesis. It is sold commercially as a slurry (~35%) in mineral oil or sometimes paraffin wax to facilitate dispensing.

Hexafluorosilicic acid is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula H
2SiF
6. Aqueous solutions of hexafluorosilicic acid consist of salts of the cation and hexafluorosilicate anion. These salts and their aqueous solutions are colorless.

Zirconium(IV) fluoride describes members of a family inorganic compounds with the formula (ZrF4(H2O)x. All are colorless, diamagnetic solids. Anhydrous Zirconium(IV) fluoride' is a component of ZBLAN fluoride glass.
Titanium disilicide (TiSi2) is an inorganic chemical compound of titanium and silicon.

Manganese tetrafluoride, MnF4, is the highest fluoride of manganese. It is a powerful oxidizing agent and is used as a means of purifying elemental fluorine.
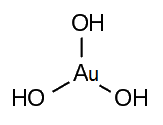
Gold(III) hydroxide, gold trihydroxide, or gold hydroxide is an inorganic compound, a hydroxide of gold, with formula Au(OH)3. It is also called auric acid with formula H3AuO3. It is easily dehydrated above 140 °C to gold(III) oxide. Salts of auric acid are termed aurates.
A monofluoride is a chemical compound with one fluoride per formula unit. For a binary compound, this is the formula XF.

Metal halides are compounds between metals and halogens. Some, such as sodium chloride are ionic, while others are covalently bonded. A few metal halides are discrete molecules, such as uranium hexafluoride, but most adopt polymeric structures, such as palladium chloride.
Fluorine forms a great variety of chemical compounds, within which it always adopts an oxidation state of −1. With other atoms, fluorine forms either polar covalent bonds or ionic bonds. Most frequently, covalent bonds involving fluorine atoms are single bonds, although at least two examples of a higher order bond exist. Fluoride may act as a bridging ligand between two metals in some complex molecules. Molecules containing fluorine may also exhibit hydrogen bonding. Fluorine's chemistry includes inorganic compounds formed with hydrogen, metals, nonmetals, and even noble gases; as well as a diverse set of organic compounds. For many elements the highest known oxidation state can be achieved in a fluoride. For some elements this is achieved exclusively in a fluoride, for others exclusively in an oxide; and for still others the highest oxidation states of oxides and fluorides are always equal.
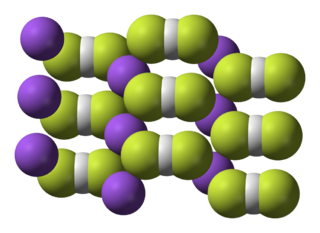
Sodium bifluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula Na[HF2]. It is a salt of sodium cation and bifluoride anion. It is a white, water-soluble solid that decomposes upon heating. Sodium bifluoride is non-flammable, hygroscopic, and has a pungent smell. Sodium bifluoride has a number of applications in industry.
Cobalt compounds are chemical compounds formed by cobalt with other elements.
Neptunium compounds are compounds containg the element neptunium (Np). Neptunium has five ionic oxidation states ranging from +3 to +7 when forming chemical compounds, which can be simultaneously observed in solutions. It is the heaviest actinide that can lose all its valence electrons in a stable compound. The most stable state in solution is +5, but the valence +4 is preferred in solid neptunium compounds. Neptunium metal is very reactive. Ions of neptunium are prone to hydrolysis and formation of coordination compounds.
Sodium hexafluorotitanate is an inorganic compound of sodium, fluorine, and titanium with the chemical formula Na2TiF6.















