
Stearic acid is a saturated fatty acid with an 18-carbon chain. The IUPAC name is octadecanoic acid. It is a waxy solid with the formula CH3(CH2)16CO2H. Its name comes from the Greek word στέαρ "stéar", which means tallow. The salts and esters of stearic acid are called stearates. As its ester, stearic acid is one of the most common saturated fatty acids found in nature following palmitic acid. The triglyceride derived from three molecules of stearic acid is called stearin.

Magnesium stearate is the chemical compound with the formula Mg(C
18H
35O
2)
2. It is a soap, consisting of salt containing two equivalents of stearate (the anion of stearic acid) and one magnesium cation (Mg2+). Magnesium stearate is a white, water-insoluble powder. Its applications exploit its softness, insolubility in many solvents, and low toxicity. It is used as a release agent and as a component or lubricant in the production of pharmaceuticals and cosmetics.

Sodium stearate is the sodium salt of stearic acid. This white solid is the most common soap. It is found in many types of solid deodorants, rubbers, latex paints, and inks. It is also a component of some food additives and food flavorings.
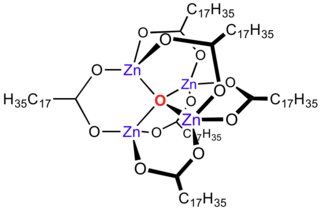
Zinc stearate is a "zinc soap" that is widely used industrially. In this context, soap is used in its formal sense, a metal salt of a fatty acid: in this case stearic acid. It is a white solid that repels water. It is insoluble in polar solvents such as alcohol and ether but soluble in aromatic hydrocarbons and chlorinated hydrocarbons when heated. It is the most powerful mold release agent among all metal soaps. It contains no electrolyte and has a hydrophobic effect. Its main application areas are the plastics and rubber industry, where it is used as a releasing agent and lubricant which can be easily incorporated.

Calcium stearate is a carboxylate salt of calcium, classified as a calcium soap. The salt is a component of some lubricants, surfactants, as well as many foodstuffs. It is a white waxy powder.
Potassium laurate is a metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C
12H
23KO
2. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Silver stearate is a metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C
18H
36AgO
2. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Tin(II) stearate is a metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C
18H
36SnO
2. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.

Copper(II) stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of copper and stearic acid with the formula Cu(C17H35COO)2. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Mercury(II) stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of mercury and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
36H
70HgO
4. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid. The compound is highly toxic by inhalation, ingestion, and skin absorption.

Cobalt(II) stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of cobalt and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
36H
70CoO
4. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Nickel(II) stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of nickel and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
36H
70NiO
4. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid. The compound is harmful if swallowed and may cause skin sensitization.
Strontium stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of strontium and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
36H
70SrO
4. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Zirconium stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of zirconium and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
72H
140ZrO
8.
Lanthanum stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of lanthanum and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
54H
108LaO
6. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Cerium stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of cerium and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
54H
105CeO
6. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Manganese stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of manganese and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
36H
70MnO
4. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Lead stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of lead and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
36H
70PbO
4. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid. The compound is toxic.
Caesium stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of сaesium and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
18H
35CsO
2. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Iron(III) stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of iron and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
54H
105FeO
6.








