 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Calcium di(octadecanoate) | |
| Other names E470 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.976 |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
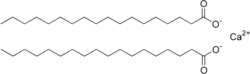
| C36H70CaO4 | |
| Molar mass | 607.030 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white to yellowish-white powder |
| Density | 1.08 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 155 °C (311 °F; 428 K) |
| 0.004 g/100 mL (15 °C) | |
| Solubility | soluble in hot pyridine slightly soluble in oil insoluble in alcohol, ether |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Calcium stearate is a carboxylate salt of calcium, classified as a calcium soap. The salt is a component of some lubricants, surfactants, as well as many foodstuffs. It is a white waxy powder. [1]
