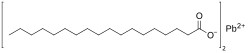
A triglyceride is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids. Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates, as well as vegetable fat. They are also present in the blood to enable the bidirectional transference of adipose fat and blood glucose from the liver, and are a major component of human skin oils.

Stearic acid is a saturated fatty acid with an 18-carbon chain. The IUPAC name is octadecanoic acid. It is a soft waxy solid with the formula CH3(CH2)16CO2H. The triglyceride derived from three molecules of stearic acid is called stearin. Stearic acid is a prevalent fatty-acid in nature, found in many animal and vegetable fats, but is usually higher in animal fat than vegetable fat. It has a melting point of 69.4 °C and a pKa of 4.50.
Lead(IV) acetate or lead tetraacetate is an metalorganic compound with chemical formula Pb(C2H3O2)4. It is a colorless solid that is soluble in nonpolar, organic solvents, indicating that it is not a salt. It is degraded by moisture and is typically stored with additional acetic acid. The compound is used in organic synthesis.
Polymer stabilizers are chemical additives which may be added to polymeric materials, such as plastics and rubbers, to inhibit or retard their degradation. Common polymer degradation processes include oxidation, UV-damage, thermal degradation, ozonolysis, combinations thereof such as photo-oxidation, as well as reactions with catalyst residues, dyes, or impurities. All of these degrade the polymer at a chemical level, via chain scission, uncontrolled recombination and cross-linking, which adversely affects many key properties such as strength, malleability, appearance and colour.
Cadmium stearate is a salt with the formula Cd(O2CC17H35)2. Classified as a metallic soap, this a white solid is used as a lubricant and as a heat- and light-stabilizer in polyvinyl chloride. The use of cadmium stearate is being phased out because of its toxicity.

Compounds of lead exist with lead in two main oxidation states: +2 and +4. The former is more common. Inorganic lead(IV) compounds are typically strong oxidants or exist only in highly acidic solutions.
Silver stearate is a metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C
18H
36AgO
2. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Tin(II) stearate is a metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C
18H
36SnO
2. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.

Copper(II) stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of copper and stearic acid with the formula Cu(C17H35COO)2. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Mercury(II) stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of mercury and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
36H
70HgO
4. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid. The compound is highly toxic by inhalation, ingestion, and skin absorption.

Cobalt(II) stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of cobalt and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
36H
70CoO
4. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Nickel(II) stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of nickel and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
36H
70NiO
4. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid. The compound is harmful if swallowed and may cause skin sensitization.
Strontium stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of strontium and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
36H
70SrO
4. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Zirconium stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of zirconium and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
72H
140ZrO
8.
Lanthanum stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of lanthanum and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
54H
108LaO
6. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Cerium stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of cerium and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
54H
105CeO
6. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Manganese stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of manganese and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
36H
70MnO
4. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Potassium stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of potassium and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
18H
35KO
2. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Caesium stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of caesium and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
18H
35CsO
2. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Iron(III) stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of iron and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
54H
105FeO
6.