
Sodium cyanide is a poisonous compound with the formula NaCN. It is a white, water-soluble solid. Cyanide has a high affinity for metals, which leads to the high toxicity of this salt. Its main application, in gold mining, also exploits its high reactivity toward metals. It is a moderately strong base.

Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula KOH, and is commonly called caustic potash.

Stearic acid is a saturated fatty acid with an 18-carbon chain. The IUPAC name is octadecanoic acid. It is a soft waxy solid with the formula CH3(CH2)16CO2H. The triglyceride derived from three molecules of stearic acid is called stearin. Stearic acid is a prevalent fatty-acid in nature, found in many animal and vegetable fats, but is usually higher in animal fat than vegetable fat. It has a melting point of 69.4 °C (156.9 °F) °C and a pKa of 4.50.

Barium chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula BaCl2. It is one of the most common water-soluble salts of barium. Like most other water-soluble barium salts, it is a white powder, highly toxic, and imparts a yellow-green coloration to a flame. It is also hygroscopic, converting to the dihydrate BaCl2·2H2O, which are colourless crystals with a bitter salty taste. It has limited use in the laboratory and industry.
Cyanogen chloride is a highly toxic chemical compound with the formula CNCl. This linear, triatomic pseudohalogen is an easily condensed colorless gas. More commonly encountered in the laboratory is the related compound cyanogen bromide, a room-temperature solid that is widely used in biochemical analysis and preparation.

Sodium azide is an inorganic compound with the formula NaN3. This colorless salt is the gas-forming component in some car airbag systems. It is used for the preparation of other azide compounds. It is an ionic substance, is highly soluble in water, and is acutely poisonous.

Mercury(I) chloride is the chemical compound with the formula Hg2Cl2. Also known as the mineral calomel (a rare mineral) or mercurous chloride, this dense white or yellowish-white, odorless solid is the principal example of a mercury(I) compound. It is a component of reference electrodes in electrochemistry.

Cadmium chloride is a white crystalline compound of cadmium and chloride, with the formula CdCl2. This salt is a hygroscopic solid that is highly soluble in water and slightly soluble in alcohol. The crystal structure of cadmium chloride (described below), is a reference for describing other crystal structures. Also known are CdCl2•H2O and the hemipentahydrate CdCl2•2.5H2O.

Germane is the chemical compound with the formula GeH4, and the germanium analogue of methane. It is the simplest germanium hydride and one of the most useful compounds of germanium. Like the related compounds silane and methane, germane is tetrahedral. It burns in air to produce GeO2 and water. Germane is a group 14 hydride.

Magnesium stearate is the chemical compound with the formula Mg(C
18H
35O
2)
2. It is a soap, consisting of salt containing two equivalents of stearate (the anion of stearic acid) and one magnesium cation (Mg2+). Magnesium stearate is a white, water-insoluble powder. Its applications exploit its softness, insolubility in many solvents, and low toxicity. It is used as a release agent and as a component or lubricant in the production of pharmaceuticals and cosmetics.

Cadmium fluoride (CdF2) is a mostly water-insoluble source of cadmium used in oxygen-sensitive applications, such as the production of metallic alloys. In extremely low concentrations (ppm), this and other fluoride compounds are used in limited medical treatment protocols. Fluoride compounds also have significant uses in synthetic organic chemistry. The standard enthalpy has been found to be -167.39 kcal. mole−1 and the Gibbs energy of formation has been found to be -155.4 kcal. mole−1, and the heat of sublimation was determined to be 76 kcal. mole−1.
Benzyl chloride, or α-chlorotoluene, is an organic compound with the formula C6H5CH2Cl. This colorless liquid is a reactive organochlorine compound that is a widely used chemical building block.

Cadmium oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula CdO. It is one of the main precursors to other cadmium compounds. It crystallizes in a cubic rocksalt lattice like sodium chloride, with octahedral cation and anion centers. It occurs naturally as the rare mineral monteponite. Cadmium oxide can be found as a colorless amorphous powder or as brown or red crystals. Cadmium oxide is an n-type semiconductor with a band gap of 2.18 eV at room temperature.

Organocadmium chemistry describes the physical properties, synthesis, reactions, and use of organocadmium compounds, which are organometallic compounds containing a carbon to cadmium chemical bond. Cadmium shares group 12 with zinc and mercury and their corresponding chemistries have much in common. The synthetic utility of organocadmium compounds is limited.

Cadmium cyanide is an inorganic compound with the formula Cd(CN)2. It is a white crystalline compound that is used in electroplating. It is very toxic, along with other cadmium and cyanide compounds.
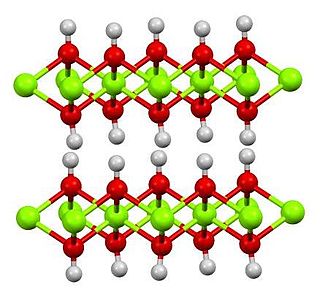
Cadmium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula Cd(OH)2. It is a white crystalline ionic compound that is a key component of nickel–cadmium battery.
A metallic soap is a metallic salt of a fatty acid. Theoretically, soaps can be made of any metal, although not all enjoy practical uses. Varying the metal can strongly affect the properties of the compound, particularly its solubility.
Tin(II) stearate is a metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C
18H
36SnO
2. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Mercury(II) stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of mercury and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
36H
70HgO
4. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid. The compound is highly toxic by inhalation, ingestion, and skin absorption.
Manganese stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of manganese and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
36H
70MnO
4. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.














