
The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), caesium (Cs), and francium (Fr). Together with hydrogen they constitute group 1, which lies in the s-block of the periodic table. All alkali metals have their outermost electron in an s-orbital: this shared electron configuration results in their having very similar characteristic properties. Indeed, the alkali metals provide the best example of group trends in properties in the periodic table, with elements exhibiting well-characterised homologous behaviour. This family of elements is also known as the lithium family after its leading element.

Caesium is a chemical element; it has symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of 28.5 °C, which makes it one of only five elemental metals that are liquid at or near room temperature. Caesium has physical and chemical properties similar to those of rubidium and potassium. It is pyrophoric and reacts with water even at −116 °C (−177 °F). It is the least electronegative element, with a value of 0.79 on the Pauling scale. It has only one stable isotope, caesium-133. Caesium is mined mostly from pollucite. Caesium-137, a fission product, is extracted from waste produced by nuclear reactors. It has the largest atomic radius of all elements whose radii have been measured or calculated, at about 260 picometers.

Stearic acid is a saturated fatty acid with an 18-carbon chain. The IUPAC name is octadecanoic acid. It is a soft waxy solid with the formula CH3(CH2)16CO2H. The triglyceride derived from three molecules of stearic acid is called stearin. Stearic acid is a prevalent fatty-acid in nature, found in many animal and vegetable fats, but is usually higher in animal fat than vegetable fat. It has a melting point of 69.4 °C (156.9 °F) °C and a pKa of 4.50.

Lithium aluminium hydride, commonly abbreviated to LAH, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Li[AlH4] or LiAlH4. It is a white solid, discovered by Finholt, Bond and Schlesinger in 1947. This compound is used as a reducing agent in organic synthesis, especially for the reduction of esters, carboxylic acids, and amides. The solid is dangerously reactive toward water, releasing gaseous hydrogen (H2). Some related derivatives have been discussed for hydrogen storage.

Caesium fluoride or cesium fluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula CsF. A hygroscopic white salt, caesium fluoride is used in the synthesis of organic compounds as a source of the fluoride anion. The compound is noteworthy from the pedagogical perspective as caesium also has the highest electropositivity of all commonly available elements and fluorine has the highest electronegativity.

Caesium chloride or cesium chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula CsCl. This colorless salt is an important source of caesium ions in a variety of niche applications. Its crystal structure forms a major structural type where each caesium ion is coordinated by 8 chloride ions. Caesium chloride dissolves in water. CsCl changes to NaCl structure on heating. Caesium chloride occurs naturally as impurities in carnallite, sylvite and kainite. Less than 20 tonnes of CsCl is produced annually worldwide, mostly from a caesium-bearing mineral pollucite.

Magnesium stearate is the chemical compound with the formula Mg(C
18H
35O
2)
2. It is a soap, consisting of salt containing two equivalents of stearate (the anion of stearic acid) and one magnesium cation (Mg2+). Magnesium stearate is a white, water-insoluble powder. Its applications exploit its softness, insolubility in many solvents, and low toxicity. It is used as a release agent and as a component or lubricant in the production of pharmaceuticals and cosmetics.

Caesium chromate or cesium chromate is an inorganic compound with the formula Cs2CrO4. It is a yellow crystalline solid that is the caesium salt of chromic acid, and it crystallises in the orthorhombic system.
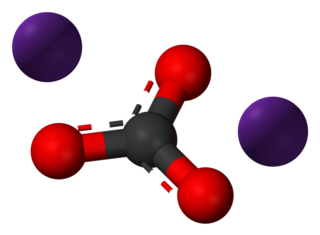
Caesium carbonate or cesium carbonate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula Cs2CO3. It is white crystalline solid. Caesium carbonate has a high solubility in polar solvents such as water, ethanol and DMF. Its solubility is higher in organic solvents compared to other carbonates like potassium carbonate and sodium carbonate, although it remains quite insoluble in other organic solvents such as toluene, p-xylene, and chlorobenzene. This compound is used in organic synthesis as a base. It also appears to have applications in energy conversion.

Caesium oxalate, or dicesium oxalate, or cesium oxalate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula Cs2C2O4. It is a caesium salt of oxalic acid. It consists of caesium cations Cs+ and oxalate anions C2O2−4.
Silver stearate is a metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C
18H
36AgO
2. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.

Copper(II) stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of copper and stearic acid with the formula Cu(C17H35COO)2. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Mercury(II) stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of mercury and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
36H
70HgO
4. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid. The compound is highly toxic by inhalation, ingestion, and skin absorption.

Cobalt(II) stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of cobalt and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
36H
70CoO
4. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Strontium stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of strontium and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
36H
70SrO
4. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Zirconium stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of zirconium and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
72H
140ZrO
8.
Cerium stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of cerium and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
54H
105CeO
6. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Manganese stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of manganese and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
36H
70MnO
4. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Potassium stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of potassium and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
18H
35KO
2. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Iron(III) stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of iron and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
54H
105FeO
6.











