 Cs+: __ Se2-: __ | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.045.848 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Cs2Se | |
| Molar mass | 344.771 g/mol |
| Appearance | colourless, highly hygroscopic crystals [1] |
| Density | 4.33 g·cm−3 [2] |
| hydrolyses [3] | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: [4] | |
   | |
| Danger | |
| H301, H331, H373, H410 | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions | Caesium oxide Caesium sulfide Caesium telluride Caesium polonide |
Other cations | Lithium selenide Sodium selenide Potassium selenide Rubidium selenide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
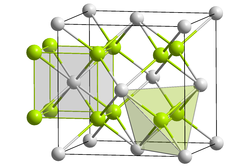
Caesium selenide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Cs2Se. It has an inverse fluorite structure, with space group . There are 4 units per unit cell, [1] and the other selenides from the same group are similar.
