Lithium aluminium hydride, commonly abbreviated to LAH, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Li[AlH4] or LiAlH4. It is a white solid, discovered by Finholt, Bond and Schlesinger in 1947. This compound is used as a reducing agent in organic synthesis, especially for the reduction of esters, carboxylic acids, and amides. The solid is dangerously reactive toward water, releasing gaseous hydrogen (H2). Some related derivatives have been discussed for hydrogen storage.

Sodium hydride is the chemical compound with the empirical formula NaH. This alkali metal hydride is primarily used as a strong yet combustible base in organic synthesis. NaH is a saline (salt-like) hydride, composed of Na+ and H− ions, in contrast to molecular hydrides such as borane, methane, ammonia, and water. It is an ionic material that is insoluble in all solvents (other than molten Na), consistent with the fact that H− ions do not exist in solution. Because of the insolubility of NaH, all reactions involving NaH occur at the surface of the solid.

Cerium(III) chloride (CeCl3), also known as cerous chloride or cerium trichloride, is a compound of cerium and chlorine. It is a white hygroscopic salt; it rapidly absorbs water on exposure to moist air to form a hydrate, which appears to be of variable composition, though the heptahydrate CeCl3·7H2O is known. It is highly soluble in water, and (when anhydrous) it is soluble in ethanol and acetone.

Sodium borohydride, also known as sodium tetrahydridoborate and sodium tetrahydroborate, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaBH4. This white solid, usually encountered as an aqueous basic solution, is a reducing agent that finds application in papermaking and dye industries. It is also used as a reagent in organic synthesis.

Praseodymium(III) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula PrCl3. Like other lanthanide trichlorides, it exists both in the anhydrous and hydrated forms. It is a blue-green solid that rapidly absorbs water on exposure to moist air to form a light green heptahydrate.

Aluminium chloride, also known as aluminium trichloride, is an inorganic compound with the formula AlCl3. It forms a hexahydrate with the formula [Al(H2O)6]Cl3, containing six water molecules of hydration. Both the anhydrous form and the hexahydrate are colourless crystals, but samples are often contaminated with iron(III) chloride, giving them a yellow colour.

Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to PPh3 or Ph3P. It is widely used in the synthesis of organic and organometallic compounds. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether.
Hydrogen selenide is an inorganic compound with the formula H2Se. This hydrogen chalcogenide is the simplest and most commonly encountered hydride of selenium. H2Se is a colorless, flammable gas under standard conditions. It is the most toxic selenium compound with an exposure limit of 0.05 ppm over an 8-hour period. Even at extremely low concentrations, this compound has a very irritating smell resembling that of decayed horseradish or 'leaking gas', but smells of rotten eggs at higher concentrations.

Tantalum(V) chloride, also known as tantalum pentachloride, is an inorganic compound with the formula TaCl5. It takes the form of a white powder and is commonly used as a starting material in tantalum chemistry. It readily hydrolyzes to form tantalum(V) oxychloride (TaOCl3) and eventually tantalum pentoxide (Ta2O5); this requires that it be synthesised and manipulated under anhydrous conditions, using air-free techniques.
Organoselenium chemistry is the science exploring the properties and reactivity of organoselenium compounds, chemical compounds containing carbon-to-selenium chemical bonds. Selenium belongs with oxygen and sulfur to the group 16 elements or chalcogens, and similarities in chemistry are to be expected. Organoselenium compounds are found at trace levels in ambient waters, soils and sediments.
Hydrogen telluride is the inorganic compound with the formula H2Te. A hydrogen chalcogenide and the simplest hydride of tellurium, it is a colorless gas. Although unstable in ambient air, the gas can exist at very low concentrations long enough to be readily detected by the odour of rotting garlic at extremely low concentrations; or by the revolting odour of rotting leeks at somewhat higher concentrations. Most compounds with Te–H bonds (tellurols) are unstable with respect to loss of H2. H2Te is chemically and structurally similar to hydrogen selenide, both are acidic. The H–Te–H angle is about 90°. Volatile tellurium compounds often have unpleasant odours, reminiscent of decayed leeks or garlic.

Aluminium selenide is the inorganic compound with the formula Al2Se3.

Selenium compounds commonly exist in the oxidation states −2, +2, +4, and +6.

Selenium monochloride is an inorganic compound with the formula Se2Cl2. Although it is called selenium monochloride, a more descriptive name might be diselenium dichloride. It is a reddish-brown, oily liquid that hydrolyses slowly. It exists in chemical equilibrium with SeCl2, SeCl4, chlorine, and elemental selenium. Selenium monochloride is mainly used as a reagent for the synthesis of Se-containing compounds.
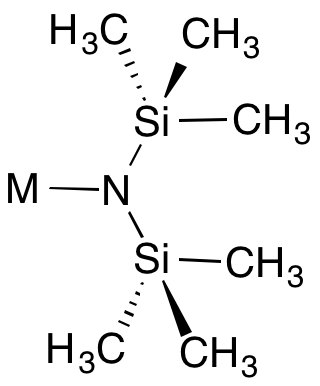
Metal bis(trimethylsilyl)amides are coordination complexes composed of a cationic metal with anionic bis(trimethylsilyl)amide ligands and are part of a broader category of metal amides.
Polysilicon hydrides are polymers containing only silicon and hydrogen. They have the formula where 0.2 ≤ n ≤ 2.5 and x is the number of monomer units. The polysilicon hydrides are generally colorless or pale-yellow/ocher powders that are easily hydrolyzed and ignite readily in air. The surfaces of silicon prepared by MOCVD using silane (SiH4) consist of a polysilicon hydride.

Metal halides are compounds between metals and halogens. Some, such as sodium chloride are ionic, while others are covalently bonded. A few metal halides are discrete molecules, such as uranium hexafluoride, but most adopt polymeric structures, such as palladium chloride.
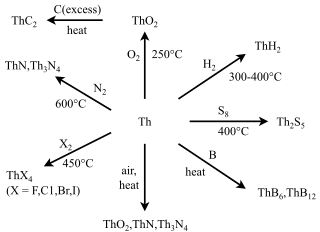
Many compounds of thorium are known: this is because thorium and uranium are the most stable and accessible actinides and are the only actinides that can be studied safely and legally in bulk in a normal laboratory. As such, they have the best-known chemistry of the actinides, along with that of plutonium, as the self-heating and radiation from them is not enough to cause radiolysis of chemical bonds as it is for the other actinides. While the later actinides from americium onwards are predominantly trivalent and behave more similarly to the corresponding lanthanides, as one would expect from periodic trends, the early actinides up to plutonium have relativistically destabilised and hence delocalised 5f and 6d electrons that participate in chemistry in a similar way to the early transition metals of group 3 through 8: thus, all their valence electrons can participate in chemical reactions, although this is not common for neptunium and plutonium.
Cerium compounds are compounds containing the element cerium (Ce), a lanthanide. Cerium exists in two main oxidation states, Ce(III) and Ce(IV). This pair of adjacent oxidation states dominates several aspects of the chemistry of this element. Cerium(IV) aqueous solutions may be prepared by reacting cerium(III) solutions with the strong oxidizing agents peroxodisulfate or bismuthate. The value of E⦵(Ce4+/Ce3+) varies widely depending on conditions due to the relative ease of complexation and hydrolysis with various anions, although +1.72 V is representative. Cerium is the only lanthanide which has important aqueous and coordination chemistry in the +4 oxidation state.
Neptunium compounds are compounds containg the element neptunium (Np). Neptunium has five ionic oxidation states ranging from +3 to +7 when forming chemical compounds, which can be simultaneously observed in solutions. It is the heaviest actinide that can lose all its valence electrons in a stable compound. The most stable state in solution is +5, but the valence +4 is preferred in solid neptunium compounds. Neptunium metal is very reactive. Ions of neptunium are prone to hydrolysis and formation of coordination compounds.