 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names D-Ox, Hydrolin, Reductone sodium hydrosulfite, sodium sulfoxylate, Sulfoxylate Vatrolite, Virtex L Hydrosulfit, Prayon Blankit, Albite A, Konite Zepar, Burmol, Arostit | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.991 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1384 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
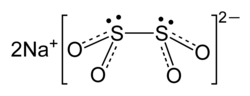
| Na2S2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 174.107 g/mol (anhydrous) 210.146 g/mol (dihydrate) |
| Appearance | white to grayish crystalline powder light-lemon colored flakes |
| Odor | faint sulfur odor |
| Density | 2.38 g/cm3 (anhydrous) 1.58 g/cm3 (dihydrate) |
| Melting point | 52 °C (126 °F; 325 K) |
| Boiling point | Decomposes |
| 18.2 g/100 mL (anhydrous, 20 °C) 21.9 g/100 mL (Dihydrate, 20 °C) | |
| Solubility | slightly soluble in alcohol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Danger | |
| H251, H302 | |
| P235+P410, P264, P270, P280, P301+P312, P330, P407, P413, P420, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 100 °C (212 °F; 373 K) |
| 200 °C (392 °F; 473 K) | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions | Sodium sulfite Sodium sulfate |
Related compounds | Sodium thiosulfate Sodium bisulfite Sodium metabisulfite Sodium bisulfate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Sodium dithionite (also known as sodium hydrosulfite) is a white crystalline powder with a sulfurous odor. Although it is stable in dry air, it decomposes in hot water and in acid solutions.

