 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CsO4Tc | |
| Molar mass | 295 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid [1] |
| Melting point | 590 °C [1] |
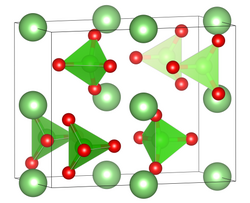
| Structure | |
| orthorhombic | |
| Pnma (No. 62) | |
a = 572.6 pm, b = 592.2 pm, c = 1436 pm | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions | caesium perchlorate caesium permanganate caesium perrhenate |
Other cations | pertechnetic acid lithium pertechnetate sodium pertechnetate potassium pertechnetate rubidium pertechnetate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Caesium pertechnetate is the pertechnetate salt of caesium, with the chemical formula of CsTcO4.