
Titanium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in sea water, aqua regia, and chlorine.

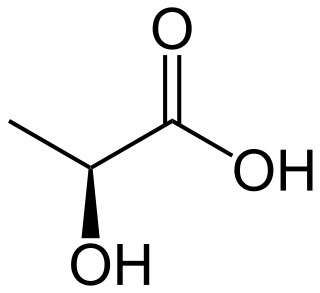
Lactic acid is an organic acid. It has the molecular formula CH3CH(OH)COOH. It is white in the solid state and it is miscible with water. When in the dissolved state, it forms a colorless solution. Production includes both artificial synthesis as well as natural sources. Lactic acid is an alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) due to the presence of a hydroxyl group adjacent to the carboxyl group. It is used as a synthetic intermediate in many organic synthesis industries and in various biochemical industries. The conjugate base of lactic acid is called lactate. The name of the derived acyl group is lactoyl.
Lactic acid fermentation is a metabolic process by which glucose or other six-carbon sugars are converted into cellular energy and the metabolite lactate, which is lactic acid in solution. It is an anaerobic fermentation reaction that occurs in some bacteria and animal cells, such as muscle cells.
Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters, containing a 1-oxacycloalkan-2-one structure, or analogues having unsaturation or heteroatoms replacing one or more carbon atoms of the ring.

Glucuronolactone or Glucurolactone (INN) is a naturally occurring substance that is an important structural component of nearly all connective tissues. It is sometimes used in energy drinks. Unfounded claims that glucuronolactone can be used to reduce "brain fog" are based on research conducted on energy drinks that contain other active ingredients that have been shown to improve cognitive function, such as caffeine. Glucuronolactone is also found in many plant gums.
ATC code A07Antidiarrheals, intestinal anti-inflammatory/anti-infective agents is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup A07 is part of the anatomical group A Alimentary tract and metabolism.

Maleic acid or cis-butenedioic acid is an organic compound that is a dicarboxylic acid, a molecule with two carboxyl groups. Its chemical formula is HO2CCH=CHCO2H. Maleic acid is the cis-isomer of butenedioic acid, whereas fumaric acid is the trans-isomer. It is mainly used as a precursor to fumaric acid, and relative to its parent maleic anhydride, which has many applications.
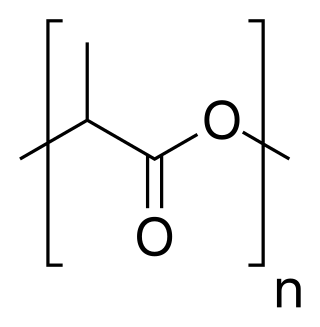
Polylactic acid, also known as poly(lactic acid) or polylactide (PLA), is a thermoplastic polyester with backbone formula (C
3H
4O
2)
n or [–C(CH
3)HC(=O)O–]
n, formally obtained by condensation of lactic acid C(CH
3)(OH)HCOOH with loss of water. It can also be prepared by ring-opening polymerization of lactide [–C(CH
3)HC(=O)O–]
2, the cyclic dimer of the basic repeating unit.
Dichloroacetic acid (DCA), sometimes called bichloroacetic acid (BCA), is the organic compound with formula CHCl2CO2H. It is an analogue of acetic acid, in which 2 of the 3 hydrogen atoms of the methyl group have been replaced by chlorine atoms. Like the other chloroacetic acids, it has various practical applications. The salts and esters of dichloroacetic acid are called dichloroacetates.
Alpha hydroxy acids, or α-hydroxy acids, are a class of chemical compounds that consist of a carboxylic acid with a hydroxyl group substituent on the adjacent (alpha) carbon. Prominent examples are glycolic acid, lactic acid, mandelic acid and citric acid.

Fentiazac is a thiazole-based nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) developed for use in joint and muscular pain. Like most other NSAIDs, it acts through inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis, via non-selective inhibition of both COX-1 and COX-2. First described in 1974, it was synthesized using the Hantzsch thiazole synthesis.

Sodium lactate is the sodium salt of lactic acid, and has a mild saline taste. It is produced by fermentation of a sugar source, such as corn or beets, and then, by neutralizing the resulting lactic acid to create a compound having the formula NaC3H5O3.
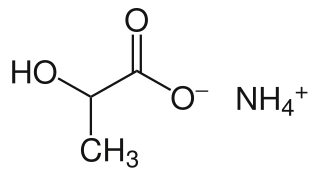
Ammonium lactate is a compound with formula NH4(C2H4(OH)COO). It is the ammonium salt of lactic acid. It has mild anti-bacterial properties.

Eritadenine is a chemical compound found in shiitake mushrooms. Eritadenine is an inhibitor of S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine hydrolase (SAHH) and has hypocholesterolemic activity.

Lithium lactate is a chemical compound, a salt of lithium and lactic acid with the formula CH3CH(OH)COOLi, an amorphous solid, very soluble in water.

Cadmium lactate is an organic chemical compound, a salt of cadmium and lactic acid with the formula Cd(C3H5O3)2.

Zinc lactate is a chemical compound, a salt of zinc and lactic acid with the formula Zn(C3H5O3)2.
Magnesium laurate is a metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C
24H
46MgO
4. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.

Strontium lactate is a chemical compound, a salt of strontium and lactic acid with the formula C
6H
10O
6Sr. This salt is stable and non-radioactive.
Cerium stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of cerium and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
54H
105CeO
6. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.














