A conjugate acid, within the Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, is a chemical compound formed when an acid donates a proton to a base—in other words, it is a base with a hydrogen ion added to it, as in the reverse reaction it loses a hydrogen ion. On the other hand, a conjugate base is what is left over after an acid has donated a proton during a chemical reaction. Hence, a conjugate base is a species formed by the removal of a proton from an acid, as in the reverse reaction it is able to gain a hydrogen ion. Because some acids are capable of releasing multiple protons, the conjugate base of an acid may itself be acidic.

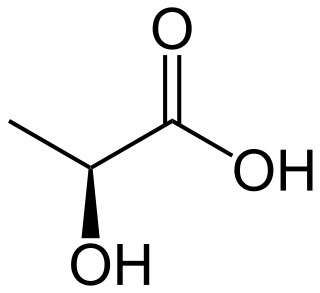
Lactic acid is an organic acid. It has a molecular formula CH3CH(OH)COOH. It is white in the solid state and it is miscible with water. When in the dissolved state, it forms a colorless solution. Production includes both artificial synthesis as well as natural sources. Lactic acid is an alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) due to the presence of a hydroxyl group adjacent to the carboxyl group. It is used as a synthetic intermediate in many organic synthesis industries and in various biochemical industries. The conjugate base of lactic acid is called lactate. The name of the derived acyl group is lactoyl.
Lactic acid fermentation is a metabolic process by which glucose or other six-carbon sugars are converted into cellular energy and the metabolite lactate, which is lactic acid in solution. It is an anaerobic fermentation reaction that occurs in some bacteria and animal cells, such as muscle cells.

Lactic acidosis is a medical condition characterized by a build-up of lactate in the body, with formation of an excessively low pH in the bloodstream. It is a form of metabolic acidosis, in which excessive acid accumulates due to a problem with the body's oxidative metabolism.

Strontium chloride (SrCl2) is a salt of strontium and chloride. It is a 'typical' salt, forming neutral aqueous solutions. As with all compounds of strontium, this salt emits a bright red colour in flame, and is commonly used in fireworks to that effect. Its properties are intermediate between those for barium chloride, which is more toxic, and calcium chloride.

The Cori cycle, named after its discoverers, Carl Ferdinand Cori and Gerty Cori, is a metabolic pathway in which lactate, produced by anaerobic glycolysis in muscles, is transported to the liver and converted to glucose, which then returns to the muscles and is cyclically metabolized back to lactate.

Calcium lactate is a white crystalline salt with formula C
6H
10CaO
6, consisting of two lactate anions H
3C(CHOH)CO−
2 for each calcium cation Ca2+
. It forms several hydrates, the most common being the pentahydrate C
6H
10CaO
6·5H
2O.
Dichloroacetic acid (DCA), sometimes called bichloroacetic acid (BCA), is the chemical compound with formula C H Cl
2COOH. It is an acid, an analogue of acetic acid, in which 2 of the 3 hydrogen atoms of the methyl group have been replaced by chlorine atoms. Like the other chloroacetic acids, it has various practical applications. The salts and esters of dichloroacetic acid are called dichloroacetates. Salts of DCA have been studied as potential drugs because they inhibit the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase.
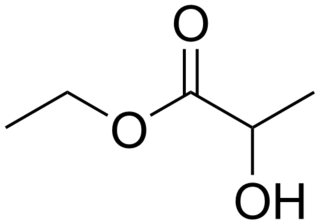
Ethyl lactate, also known as lactic acid ethyl ester, is the organic compound with the formula CH3CH(OH)CO2CH2CH3. It is the ethyl ester of lactic acid. A colorless liquid, it is a chiral ester. Being naturally derived, it is readily available as a single enantiomer. It is commonly used as a solvent. This compound is considered biodegradable and can be used as a water-rinsible degreaser. Ethyl lactate is found naturally in small quantities in a wide variety of foods including wine, chicken, and various fruits. The odor of ethyl lactate when dilute is mild, buttery, creamy, with hints of fruit and coconut.

Sodium lactate is the sodium salt of lactic acid, and has a mild saline taste. It is produced by fermentation of a sugar source, such as corn or beets, and then, by neutralizing the resulting lactic acid to create a compound having the formula NaC3H5O3.
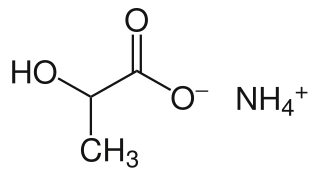
Ammonium lactate is a compound with formula NH4(C2H4(OH)COO). It is the ammonium salt of lactic acid. It has mild anti-bacterial properties.

Lithium lactate is a chemical compound, a salt of lithium and lactic acid with the formula CH3CH(OH)COOLi, an amorphous solid, very soluble in water.
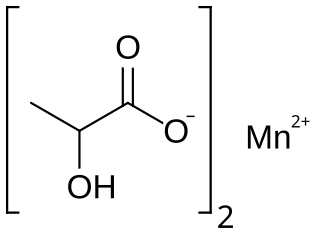
Manganese lactate is an organic chemical compound, a salt of manganese and lactic acid with the formula Mn(C3H5O3)2. The compound forms light pink crystals, soluble in water, forming crystalline hydrates.
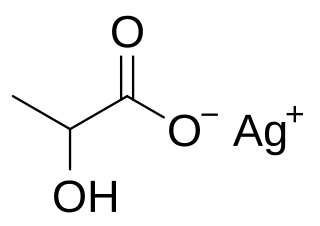
Silver lactate is an organic chemical compound, a salt of silver and lactic acid with the formula CH3CH(OH)COOAg.
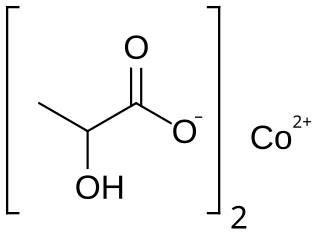
Cobalt lactate is a chemical compound, a salt of cobalt and lactic acid with the formula Co(C3H5O3)2.

Cadmium lactate is an organic chemical compound, a salt of cadmium and lactic acid with the formula Cd(C3H5O3)2.

Zinc lactate is a chemical compound, a salt of zinc and lactic acid with the formula Zn(C3H5O3)2.

Aluminium lactate is a chemical compound, a salt of aluminium and lactic acid with the formula Al(C3H5O3)3.
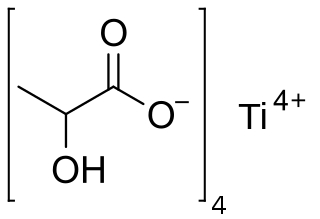
Titanium lactate is a chemical compound, a salt of titanium and lactic acid with the formula C
12H
20O
12Ti.
Cerium stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of cerium and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
54H
105CeO
6. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
















