Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in sea water, aqua regia, and chlorine.

Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium(IV) oxide or titania, is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula TiO
2. When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6 (PW6), or CI 77891. It is a white solid that is insoluble to water, although mineral forms can appear black. As a pigment, it has a wide range of applications, including paint, sunscreen, and food coloring. When used as a food coloring, it has E number E171. World production in 2014 exceeded 9 million tonnes. It has been estimated that titanium dioxide is used in two-thirds of all pigments, and pigments based on the oxide have been valued at a price of $13.2 billion.
The Kroll process is a pyrometallurgical industrial process used to produce metallic titanium from titanium tetrachloride. The Kroll process replaced the Hunter process for almost all commercial production.

The van Arkel–de Boer process, also known as the iodide process or crystal-bar process, was the first industrial process for the commercial production of pure ductile titanium, zirconium and some other metals. It was developed by Anton Eduard van Arkel and Jan Hendrik de Boer in 1925. Now it is used in the production of small quantities of ultrapure titanium and zirconium. It primarily involves the formation of the metal iodides and their subsequent decomposition to yield pure metal.

Titanocene dichloride is the organotitanium compound with the formula (η5-C5H5)2TiCl2, commonly abbreviated as Cp2TiCl2. This metallocene is a common reagent in organometallic and organic synthesis. It exists as a bright red solid that slowly hydrolyzes in air. It shows antitumour activity and was the first non-platinum complex to undergo clinical trials as a chemotherapy drug.
Titanium(III) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula TiCl3. At least four distinct species have this formula; additionally hydrated derivatives are known. TiCl3 is one of the most common halides of titanium and is an important catalyst for the manufacture of polyolefins.

Titanium tetraiodide is an inorganic compound with the formula TiI4. It is a black volatile solid, first reported by Rudolph Weber in 1863. It is an intermediate in the van Arkel–de Boer process for the purification of titanium.
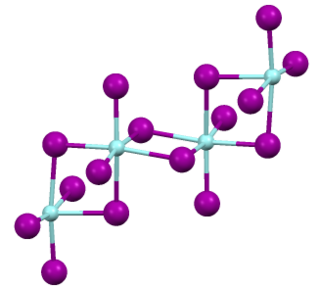
Zirconium(IV) iodide is the chemical compound with the formula ZrI4. It is the most readily available iodide of zirconium. It is an orange-coloured solid that degrades in the presence of water. The compound was once prominent as an intermediate in the purification of zirconium metal.

Titanium(II) chloride is the chemical compound with the formula TiCl2. The black solid has been studied only moderately, probably because of its high reactivity. Ti(II) is a strong reducing agent: it has a high affinity for oxygen and reacts irreversibly with water to produce H2. The usual preparation is the thermal disproportionation of TiCl3 at 500 °C. The reaction is driven by the loss of volatile TiCl4:
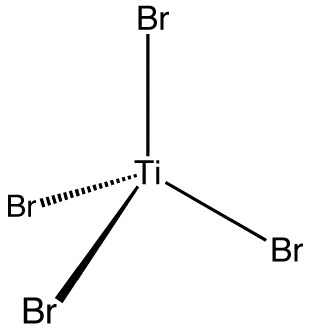
Titanium tetrabromide is the chemical compound with the formula TiBr4. It is the most volatile transition metal bromide. The properties of TiBr4 are an average of TiCl4 and TiI4. Some key properties of these four-coordinated Ti(IV) species are their high Lewis acidity and their high solubility in nonpolar organic solvents. TiBr4 is diamagnetic, reflecting the d0 configuration of the metal centre.

Titanium(IV) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula TiF4. It is a white hygroscopic solid. In contrast to the other tetrahalides of titanium, it adopts a polymeric structure. In common with the other tetrahalides, TiF4 is a strong Lewis acid.

Titanium disulfide is an inorganic compound with the formula TiS2. A golden yellow solid with high electrical conductivity, it belongs to a group of compounds called transition metal dichalcogenides, which consist of the stoichiometry ME2. TiS2 has been employed as a cathode material in rechargeable batteries.
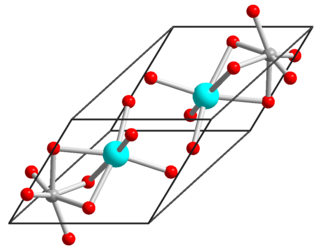
Nickel(II) titanate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula NiTiO3 nickel(II) titanate, also known as nickel titanium oxide, is a coordination compound between nickel(II), titanium(IV) and oxide ions. It has the appearance of a yellow powder. There are several methods of synthesis for nickel(II) titanate. The first method involves nickel(II) titanate's melting temperature of over 500 °C at which its precursor decomposes to give nickel(II) titanate as a residue. Nickel(II) titanate has been used as a catalyst for toluene oxidation. The second method involved using enthalpy and entropy on the reaction to synthesize nickel(II) titanate through its phase transition.

Molybdenum(III) bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula MoBr3. It is a black solid that is insoluble in most solvents but dissolves in donor solvents such as pyridine.
Titanium(III) bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula TiBr3. It is a blue black paramagnetic solid with a reddish reflection. It has few applications, although it is a catalyst for the polymerization of alkenes.

Titanium nitrate is the inorganic compound with formula Ti(NO3)4. It is a colorless, diamagnetic solid that sublimes readily. It is an unusual example of a volatile binary transition metal nitrate. Ill defined species called titanium nitrate are produced upon dissolution of titanium or its oxides in nitric acid.
Titanium(III) iodide is an inorganic compound with the formula TiI3. It is a dark violet solid that is insoluble in solvents, except upon decomposition.

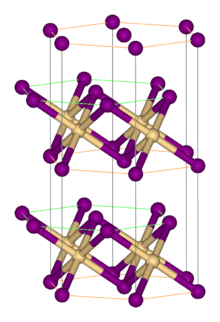
Titanium(II) bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula TiBr2. It is a black micaceous solid. It adopts the cadmium iodide structure, featuring octahedral Ti(II) centers. It arises via the reaction of the elements:
An iodide nitride is a mixed anion compound containing both iodide (I−) and nitride ions (N3−). Another name is metalloiodonitrides. They are a subclass of halide nitrides or pnictide halides. Some different kinds include ionic alkali or alkaline earth salts, small clusters where metal atoms surround a nitrogen atom, layered group 4 element 2-dimensional structures, and transition metal nitrido complexes counter-balanced with iodide ions. There is also a family with rare earth elements and nitrogen and sulfur in a cluster.