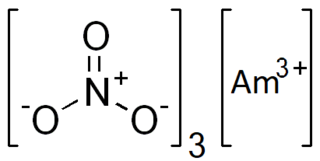Americium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Am and atomic number 95. It is radioactive and a transuranic member of the actinide series in the periodic table, located under the lanthanide element europium and was thus named after the Americas by analogy.

Samarium(II) iodide is an inorganic compound with the formula SmI2. When employed as a solution for organic synthesis, it is known as Kagan's reagent. SmI2 is a green solid and solutions are green as well. It is a strong one-electron reducing agent that is used in organic synthesis.

Zinc iodide is the inorganic compound with the formula ZnI2. It exists both in anhydrous form and as a dihydrate. Both are white and readily absorb water from the atmosphere. It has no major application.

Americium dioxide (AmO2) is a black compound of americium. In the solid state AmO2 adopts the fluorite, CaF2 structure. It is used as a source of alpha particles.

Barium iodide is an inorganic compound with the formula BaI2. The compound exists as an anhydrous and a hydrate (BaI2(H2O)2), both of which are white solids. When heated, hydrated barium iodide converts to the anhydrous salt. The hydrated form is freely soluble in water, ethanol, and acetone.
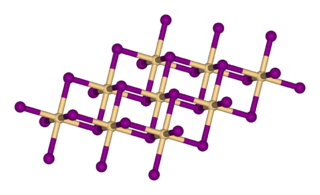
Calcium iodide (chemical formula CaI2) is the ionic compound of calcium and iodine. This colourless deliquescent solid is a salt that is highly soluble in water. Its properties are similar to those for related salts, such as calcium chloride. It is used in photography. It is also used in cat food as a source of iodine.
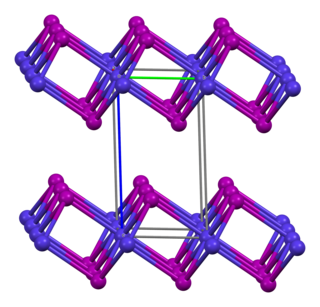
Cobalt(II) iodide or cobaltous iodide are the inorganic compounds with the formula CoI2 and the hexahydrate CoI2(H2O)6. These salts are the principal iodides of cobalt.

Americium(III) chloride or americium trichloride is the chemical compound composed of americium and chlorine with the formula AmCl3. This salt forms pink hexagonal crystals. In the solid state each americium atom has nine chlorine atoms as near neighbours, at approximately the same distance, in a tricapped trigonal prismatic configuration.

Americium(IV) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula AmF4. It is a tan solid. In terms of its structure, solid AmF4 features 8-coordinate Am centers interconnected by doubly bridging fluoride ligands.
Americium(III) iodide or americium triiodide is the chemical compound, a salt composed of americium and iodine with the formula AmI3.
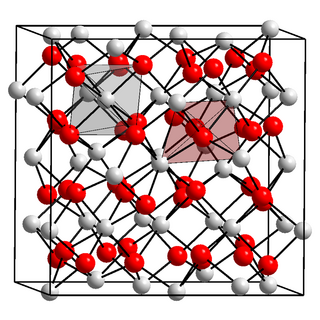
Americium(III) oxide or americium sesquioxide is an oxide of the element americium. It has the empirical formula Am2O3. Since all isotopes of americium are only artificially produced, americium (III) oxide has no natural occurrence. The colour depends on the crystal structure, of which there are more than one. It is soluble in acids.

Americium(III) hydroxide is a radioactive inorganic compound with the chemical formula Am(OH)3. It consists of one americium atom and three hydroxy groups. It was first discovered in 1944, closely related to the Manhattan Project. However, these results were confidential and were only released to the public in 1945. It was the first isolated sample of an americium compound, and the first americium compound discovered.
Americium(II) chloride, also known as dichloroamericium, is the chemical compound composed of americium and chloride with the formula AmCl2.

Europium(II) iodide is the iodide salt of divalent europium cation.

Chromium(II) iodide is the inorganic compound with the formula CrI2. It is a red-brown or black solid. The compound is made by thermal decomposition of chromium(III) iodide. Like many metal diiodides, CrI2 adopts the "cadmium iodide structure" motif, i.e., it features sheets of octahedral Cr(II) centers interconnected by bridging iodide ligands. Reflecting the effects of its d4 configuration, chromium's coordination sphere is highly distorted.
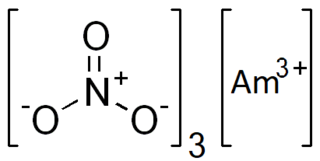
Americium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of americium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Am(NO3)3. The compound is soluble in water and radioactive.

Berkelium(III) chloride also known as berkelium trichloride, is a chemical compound with the formula BkCl3. It is a water-soluble green salt with a melting point of 603 °C. This compound forms the hexahydrate, BkCl3·6H2O.
Europium(III) iodide is an inorganic compound containing europium and iodine with the chemical formula EuI3.
Americium compounds are compounds containing the element americium (Am). These compounds can form in the +2, +3, and +4, although the +3 oxidation state is the most common. The +5, +6 and +7 oxidation states have also been reported.
Americium hexafluoride is an inorganic chemical compound of americium metal and fluorine with the chemical formula AmF
6. It is still a hypothetical compound. Synthesis by fluorination of americium tetrafluoride was unsuccessfully attempted in 1990. A thermochromatographic identification in 1986 remains inconclusive. Calculations suggest that it may be distorted from octahedral symmetry.