
Radium chloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula RaCl2. It is a radium salt of hydrogen chloride. It was the first radium compound isolated in a pure state. Marie Curie and André-Louis Debierne used it in their original separation of radium from barium. The first preparation of radium metal was by the electrolysis of a solution of this salt using a mercury cathode.

Sodium iodide (chemical formula NaI) is an ionic compound formed from the chemical reaction of sodium metal and iodine. Under standard conditions, it is a white, water-soluble solid comprising a 1:1 mix of sodium cations (Na+) and iodide anions (I−) in a crystal lattice. It is used mainly as a nutritional supplement and in organic chemistry. It is produced industrially as the salt formed when acidic iodides react with sodium hydroxide. It is a chaotropic salt.

Barium iodide is an inorganic compound with the formula BaI2. The compound exists as an anhydrous and a hydrate (BaI2(H2O)2), both of which are white solids. When heated, hydrated barium iodide converts to the anhydrous salt. The hydrated form is freely soluble in water, ethanol, and acetone.
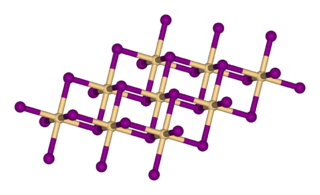
Cadmium iodide is the inorganic compound with the formula CdI2. It is a white hygroscopic solid. It also can be obtained as a mono- and tetrahydrate. It has few applications. It is notable for its crystal structure, which is typical for compounds of the form MX2 with strong polarization effects.

Tellurium tetraiodide (TeI4) is an inorganic chemical compound. It has a tetrameric structure which is different from the tetrameric solid forms of TeCl4 and TeBr4. In TeI4 the Te atoms are octahedrally coordinated and edges of the octahedra are shared.

Calcium iodide (chemical formula CaI2) is the ionic compound of calcium and iodine. This colourless deliquescent solid is a salt that is highly soluble in water. Its properties are similar to those for related salts, such as calcium chloride. It is used in photography. It is also used in cat food as a source of iodine.

Magnesium iodide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula MgI2. It forms various hydrates MgI2·xH2O. Magnesium iodide is a salt of magnesium and hydrogen iodide. These salts are typical ionic halides, being highly soluble in water.

Beryllium iodide is the inorganic compound with the formula BeI2. It is a hygroscopic white solid.
Cobalt(II) iodide or cobaltous iodide are the inorganic compounds with the formula CoI2 and the hexahydrate CoI2(H2O)6. These salts are the principal iodides of cobalt.
Vanadium(III) iodide is the inorganic compound with the formula VI3. This paramagnetic solid is generated by the reaction of vanadium powder with iodine at around 500 °C. The black hygroscopic crystals dissolve in water to give green solutions, characteristic of V(III) ions.

Astatine iodide is an interhalogen compound with the chemical formula AtI. It is the second heaviest known interhalogen compound, after iodine tribromide.

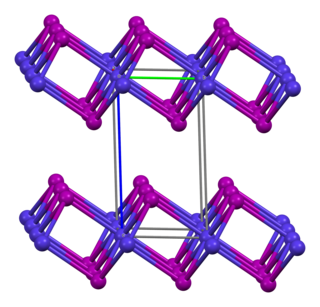
Chromium(II) iodide is the inorganic compound with the formula CrI2. It is a red-brown or black solid. The compound is made by thermal decomposition of chromium(III) iodide. Like many metal diiodides, CrI2 adopts the "cadmium iodide structure" motif, i.e., it features sheets of octahedral Cr(II) centers interconnected by bridging iodide ligands. Reflecting the effects of its d4 configuration, chromium's coordination sphere is highly distorted.
Iron(III) iodide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula FeI3. It is a thermodynamically unstable compound that is difficult to prepare. Nevertheless, iron(III) iodide has been synthesised in small quantities in the absence of air and water.

Neodymium(II) iodide or neodymium diiodide is an inorganic salt of iodine and neodymium the formula NdI2. Neodymium uses the +2 oxidation state in the compound.

Lanthanum(III) iodide is an inorganic compound containing lanthanum and iodine with the chemical formula LaI
3.
Europium(III) iodide is an inorganic compound containing europium and iodine with the chemical formula EuI3.

Lutetium(III) iodide or lutetium iodide is an inorganic compound consisting of iodine and lutetium, with the chemical formula of LuI3.

Astatine compounds are compounds that contain the element astatine (At). As this element is very radioactive, few compounds have been studied. Less reactive than iodine, astatine is the least reactive of the halogens. Its compounds have been synthesized in nano-scale amounts and studied as intensively as possible before their radioactive disintegration. The reactions involved have been typically tested with dilute solutions of astatine mixed with larger amounts of iodine. Acting as a carrier, the iodine ensures there is sufficient material for laboratory techniques to work. Like iodine, astatine has been shown to adopt odd-numbered oxidation states ranging from −1 to +7.
Radium hydroxide is an inorganic compound of radium, hydrogen, and oxygen with the chemical formula Ra(OH)2. Stability constant of aqueous RaOH+ ion pair at zero ionic strength is equal to 5.
Radium iodate is an inorganic compound, a salt of radium and iodic acid with the chemical formula Ra(IO3)2.













