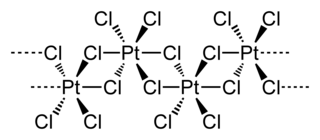
Platinum(IV) chloride is the inorganic compound of platinum and chlorine with the empirical formula PtCl4. This brown solid features platinum in the 4+ oxidation state.
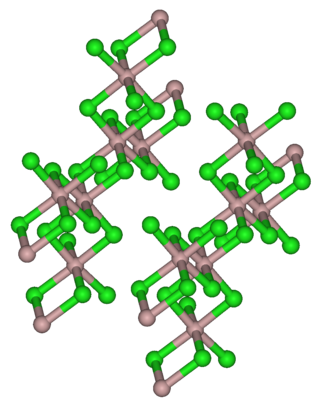
Thulium(III) chloride or thulium trichloride is as an inorganic salt composed of thulium and chlorine with the formula TmCl3. It forms yellow crystals. Thulium(III) chloride has the YCl3 (AlCl3) layer structure with octahedral thulium ions. It has been used as a starting material for some exotic nanostructures prepared for NIR photocatalysis.

Uranium pentachloride is an inorganic chemical compound composed of uranium in the +5 oxidation state and five chlorine atoms.

Uranium(IV) iodide, also known as uranium tetraiodide, is an inorganic chemical compound. It is a salt of uranium in oxidation state +4 and iodine.

Molybdenum(III) iodide is the inorganic compound with the formula MoI3.

Rhodium trifluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula RhF3. It is a red-brown, diamagnetic solid.
Tungsten(III) iodide or tungsten triiodide is a chemical compound of tungsten and iodine with the formula WI3.

Neodymium(II) iodide or neodymium diiodide is an inorganic salt of iodine and neodymium the formula NdI2. Neodymium uses the +2 oxidation state in the compound.
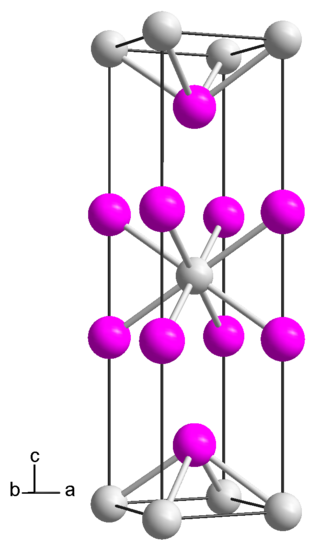
Praseodymium diiodide is a chemical compound with the empirical formula of PrI2, consisting of praseodymium and iodine. It is an electride, with the ionic formula of Pr3+(I−)2e−, and therefore not a true praseodymium(II) compound.
Protactinium(V) bromide is an inorganic compound. It is a halide of protactinium, consisting of protactinium and bromine. It is radioactive and has a chemical formula of PaBr5, which is a red crystal of the monoclinic crystal system.

Lutetium(III) iodide or lutetium iodide is an inorganic compound consisting of iodine and lutetium, with the chemical formula of LuI3.

Gadolinium(III) iodide is an iodide of gadolinium, with the chemical formula of GdI3. It is a yellow, highly hygroscopic solid with a bismuth(III) iodide-type crystal structure. In air, it quickly absorbs moisture and forms hydrates. The corresponding oxide iodide is also readily formed at elevated temperature.

Thulium(III) iodide is an iodide of thulium, with the chemical formula of TmI3. Thulium(III) iodide is used as a component of metal halide lamps.

Cerium diiodide is an iodide of cerium, with the chemical formula of CeI2.

Holmium(III) iodide is an iodide of holmium, with the chemical formula of HoI3. It is used as a component of metal halide lamps.
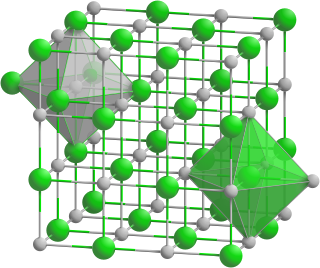
Europium(II) telluride is an inorganic compound of europium and tellurium, with the chemical formula EuTe.

Bismuth oxyiodide is an inorganic compound, an oxyiodide of bismuth, with the chemical formula BiOI.

Neptunium(III) iodide is the iodide of neptunium with the chemical formula NpI3.

Plutonium(III) iodide is the iodide of plutonium with the chemical formula PuI3.
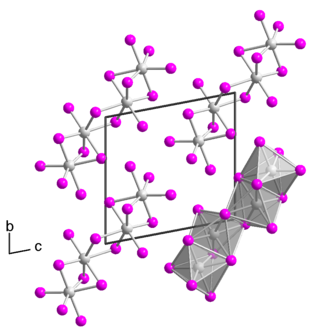
Tantalum(IV) iodide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula TaI4. It dissolves in water to give a green solution, but the color fades when left in the air and produces a white precipitate.













