
Titanium tetraiodide is an inorganic compound with the formula TiI4. It is a black volatile solid, first reported by Rudolph Weber in 1863. It is an intermediate in the van Arkel–de Boer process for the purification of titanium.
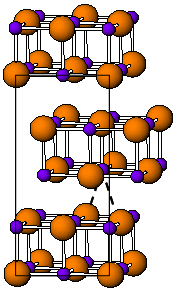
Thallium(I) iodide is a chemical compound with the formula TlI. It is unusual in being one of the few water-insoluble metal iodides, along with AgI, CuI, SnI2, SnI4, PbI2 and HgI2.

Tellurium tetraiodide (TeI4) is an inorganic chemical compound. It has a tetrameric structure which is different from the tetrameric solid forms of TeCl4 and TeBr4. In TeI4 the Te atoms are octahedrally coordinated and edges of the octahedra are shared.
Germanium iodides are inorganic compound with the formula GeIx. Two such compounds exist: germanium(II) iodide, GeI2, and germanium(IV) iodide GeI4.

Germanium(II) iodide is an iodide of germanium, with the chemical formula of GeI2.

Molybdenum(III) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula MoCl3. It forms purple crystals.

Molybdenum(III) bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula MoBr3. It is a black solid that is insoluble in most solvents but dissolves in donor solvents such as pyridine.

Molybdenum(III) iodide is the inorganic compound with the formula MoI3.
Titanium(III) iodide is an inorganic compound with the formula TiI3. It is a dark violet solid that is insoluble in solvents, except upon decomposition.
Iron(III) iodide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula FeI3. It is a thermodynamically unstable compound that is difficult to prepare. Nevertheless, iron(III) iodide has been synthesised in small quantities in the absence of air and water.

Neodymium(II) iodide or neodymium diiodide is an inorganic salt of iodine and neodymium the formula NdI2. Neodymium uses the +2 oxidation state in the compound.
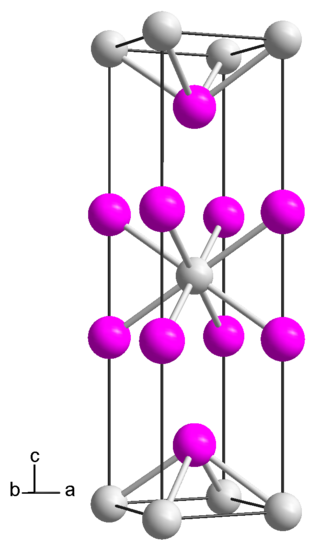
Praseodymium diiodide is a chemical compound with the empirical formula of PrI2, consisting of praseodymium and iodine. It is an electride, with the ionic formula of Pr3+(I−)2e−, and therefore not a true praseodymium(II) compound.

Lanthanum(III) iodide is an inorganic compound containing lanthanum and iodine with the chemical formula LaI
3.
Europium(III) iodide is an inorganic compound containing europium and iodine with the chemical formula EuI3.

Thulium(III) iodide is an iodide of thulium, with the chemical formula of TmI3. Thulium(III) iodide is used as a component of metal halide lamps.

Lanthanum diiodide is an iodide of lanthanum, with the chemical formula of LaI2. It is an electride, actually having a chemical formula of La3+[(I−)2e−].

Cerium diiodide is an iodide of cerium, with the chemical formula of CeI2.

Rhenium(III) iodide is a binary chemical compound of rhenium and iodide with the chemical formula ReI
3.

Tungsten(II) iodide is an iodide of tungsten, with the chemical formula [W6I8]I4, or abbreviated as WI2.













