
Molybdenum is a chemical element; it has symbol Mo and atomic number 42. The name derived from Ancient Greek Μόλυβδος molybdos, meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals have been known throughout history, but the element was discovered in 1778 by Carl Wilhelm Scheele. The metal was first isolated in 1781 by Peter Jacob Hjelm.

An oxide is a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion of oxygen, an O2– ion with oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the Earth's crust consists of oxides. Even materials considered pure elements often develop an oxide coating. For example, aluminium foil develops a thin skin of Al2O3 that protects the foil from further oxidation.

Sulfur monoxide is an inorganic compound with formula SO. It is only found as a dilute gas phase. When concentrated or condensed, it converts to S2O2 (disulfur dioxide). It has been detected in space but is rarely encountered intact otherwise.
Molybdenum trioxide describes a family of inorganic compounds with the formula MoO3(H2O)n where n = 0, 1, 2. The anhydrous compound is produced on the largest scale of any molybdenum compound since it is the main intermediate produced when molybdenum ores are purified. The anhydrous oxide is a precursor to molybdenum metal, an important alloying agent. It is also an important industrial catalyst. It is a yellow solid, although impure samples can appear blue or green.
A non-carbon nanotube is a cylindrical molecule often composed of metal oxides, or group III-Nitrides and morphologically similar to a carbon nanotube. Non-carbon nanotubes have been observed to occur naturally in some mineral deposits.
Potassium hypomanganate is the inorganic compound with the formula K3MnO4. Also known as potassium manganate(V), this bright blue solid is a rare example of a salt with the hypomanganate or manganate(V) anion, where the manganese atom is in the +5 oxidation state. It is an intermediate in the production of potassium permanganate and the industrially most important Mn(V) compound.

Tungsten(IV) oxide is the chemical compound with the formula WO2. The bronze-colored solid crystallizes in a monoclinic cell. The rutile-like structure features distorted octahedral WO6 centers with alternate short W–W bonds (248 pm). Each tungsten center has the d2 configuration, which gives the material a high electrical conductivity.

Tungsten oxytetrafluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula WOF4. It is a colorless diamagnetic solid. The compound is one of many oxides of tungsten. It is usually encountered as product of the partial hydrolysis of tungsten hexafluoride.

In chemistry, a chemical transport reaction describes a process for purification and crystallization of non-volatile solids. The process is also responsible for certain aspects of mineral growth from the effluent of volcanoes. The technique is distinct from chemical vapor deposition, which usually entails decomposition of molecular precursors (e.g. SiH4 → Si + 2 H2) and which gives conformal coatings. The technique, which was popularized by Harald Schäfer, entails the reversible conversion of nonvolatile elements and chemical compounds into volatile derivatives. The volatile derivative migrates throughout a sealed reactor, typically a sealed and evacuated glass tube heated in a tube furnace. Because the tube is under a temperature gradient, the volatile derivative reverts to the parent solid and the transport agent is released at the end opposite to which it originated (see next section). The transport agent is thus catalytic. The technique requires that the two ends of the tube (which contains the sample to be crystallized) be maintained at different temperatures. So-called two-zone tube furnaces are employed for this purpose. The method derives from the Van Arkel de Boer process which was used for the purification of titanium and vanadium and uses iodine as the transport agent.
A transition metal oxo complex is a coordination complex containing an oxo ligand. Formally O2-, an oxo ligand can be bound to one or more metal centers, i.e. it can exist as a terminal or (most commonly) as bridging ligands (Fig. 1). Oxo ligands stabilize high oxidation states of a metal. They are also found in several metalloproteins, for example in molybdenum cofactors and in many iron-containing enzymes. One of the earliest synthetic compounds to incorporate an oxo ligand is potassium ferrate (K2FeO4), which was likely prepared by Georg E. Stahl in 1702.

In chemistry, a molybdate is a compound containing an oxyanion with molybdenum in its highest oxidation state of 6: O−−Mo(=O)2−O−. Molybdenum can form a very large range of such oxyanions, which can be discrete structures or polymeric extended structures, although the latter are only found in the solid state. The larger oxyanions are members of group of compounds termed polyoxometalates, and because they contain only one type of metal atom are often called isopolymetalates. The discrete molybdenum oxyanions range in size from the simplest MoO2−
4, found in potassium molybdate up to extremely large structures found in isopoly-molybdenum blues that contain for example 154 Mo atoms. The behaviour of molybdenum is different from the other elements in group 6. Chromium only forms the chromates, CrO2−
4, Cr
2O2−
7, Cr
3O2−
10 and Cr
4O2−
13 ions which are all based on tetrahedral chromium. Tungsten is similar to molybdenum and forms many tungstates containing 6 coordinate tungsten.
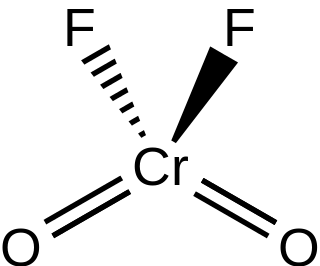
Chromyl fluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula CrO2F2. It is a violet-red colored crystalline solid that melts to an orange-red liquid.
The chalcogens react with each other to form interchalcogen compounds.
In chemistry, molybdenum bronze is a generic name for certain mixed oxides of molybdenum with the generic formula A
xMo
yO
z where A may be hydrogen, an alkali metal cation (such as Li+, Na+, K+), and Tl+. These compounds form deeply coloured plate-like crystals with a metallic sheen, hence their name. These bronzes derive their metallic character from partially occupied 4d bands. The oxidation states in K0.28MoO3 are K+1, O2−, and Mo+5.72. MoO3 is an insulator, with an unfilled 4d band.
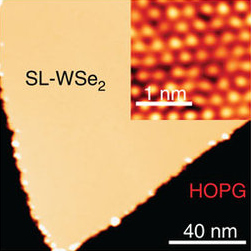
Tungsten diselenide is an inorganic compound with the formula WSe2. The compound adopts a hexagonal crystalline structure similar to molybdenum disulfide. The tungsten atoms are covalently bonded to six selenium ligands in a trigonal prismatic coordination sphere while each selenium is bonded to three tungsten atoms in a pyramidal geometry. The tungsten–selenium bond has a length of 0.2526 nm, and the distance between selenium atoms is 0.334 nm. It is a well studied example of a layered material. The layers stack together via van der Waals interactions. WSe2 is a very stable semiconductor in the group-VI transition metal dichalcogenides.

Molybdenum(IV) telluride, molybdenum ditelluride or just molybdenum telluride is a compound of molybdenum and tellurium with formula MoTe2, corresponding to a mass percentage of 27.32% molybdenum and 72.68% tellurium.

Molybdenum oxytetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the formula MoOCl4. This thermally unstable, dark green solid is used to prepare other complexes of molybdenum. It adopts a square pyramidal structure of C4v symmetry. As for other Mo(VI) compounds, it is diamagnetic. It decomposes thermally to MoOCl3.
Rhenium compounds are compounds formed by the transition metal rhenium (Re). Rhenium can form in many oxidation states, and compounds are known for every oxidation state from -3 to +7 except -2, although the oxidation states +7, +4, and +3 are the most common. Rhenium is most available commercially as salts of perrhenate, including sodium and ammonium perrhenates. These are white, water-soluble compounds. The tetrathioperrhenate anion [ReS4]− is possible.

Molybdenum oxytetrafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula MoOF4. It is a white, diamagnetic solid. According to X-ray crystallography, it is a coordination polymer consisting of a linear chain of alternating Mo and F atoms. Each Mo center is octahedral, the coordination sphere being defined by oxide, three terminal fluorides, and two bridging fluorides. In contrast to this motif, tungsten oxytetrafluoride crystallizes as a tetramer, again with bridging fluoride ligands.

Molybdenum difluoride dioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula MoF2O2. It is a white, diamagnetic, volatile solid.












