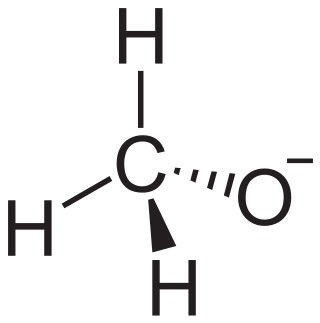
A transition metal alkoxide complex is a kind of coordination complex containing one or more alkoxide ligands, written as RO−, where R is the organic substituent. Metal alkoxides are used for coatings and as catalysts.

A triple bond in chemistry is a chemical bond between two atoms involving six bonding electrons instead of the usual two in a covalent single bond. Triple bonds are stronger than the equivalent single bonds or double bonds, with a bond order of three. The most common triple bond is in a nitrogen N2 molecule; the second most common is that between two carbon atoms, which can be found in alkynes. Other functional groups containing a triple bond are cyanides and isocyanides. Some diatomic molecules, such as diphosphorus and carbon monoxide, are also triple bonded. In skeletal formulae the triple bond is drawn as three parallel lines (≡) between the two connected atoms.
Octahedral clusters are inorganic or organometallic cluster compounds composed of six metals in an octahedral array. Many types of compounds are known, but all are synthetic.
Molybdenum(V) chloride is the inorganic compound with the empirical formula MoCl5. This dark volatile solid is used in research to prepare other molybdenum compounds. It is moisture-sensitive and soluble in chlorinated solvents.

A sextuple bond is a type of covalent bond involving 12 bonding electrons and in which the bond order is 6. The only known molecules with true sextuple bonds are the diatomic dimolybdenum (Mo2) and ditungsten (W2), which exist in the gaseous phase and have boiling points of 4,639 °C (8,382 °F) and 5,930 °C (10,710 °F) respectively.

Molybdenum tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the empirical formula MoCl4. The material exists as two polymorphs, both being dark-colored paramagnetic solids. These compounds are mainly of interest as precursors to other molybdenum complexes.

Organomolybdenum chemistry is the chemistry of chemical compounds with Mo-C bonds. The heavier group 6 elements molybdenum and tungsten form organometallic compounds similar to those in organochromium chemistry but higher oxidation states tend to be more common.

Molybdenum(II) acetate is a coordination compound with the formula Mo2(O2CCH3)4. It is a yellow, diamagnetic, air-stable solid that is slightly soluble in organic solvents. Molybdenum(II) acetate is an iconic example of a compound with a metal-metal quadruple bond.
Transition metal carbyne complexes are organometallic compounds with a triple bond between carbon and the transition metal. This triple bond consists of a σ-bond and two π-bonds. The HOMO of the carbyne ligand interacts with the LUMO of the metal to create the σ-bond. The two π-bonds are formed when the two HOMO orbitals of the metal back-donate to the LUMO of the carbyne. They are also called metal alkylidynes—the carbon is a carbyne ligand. Such compounds are useful in organic synthesis of alkynes and nitriles. They have been the focus on much fundamental research.
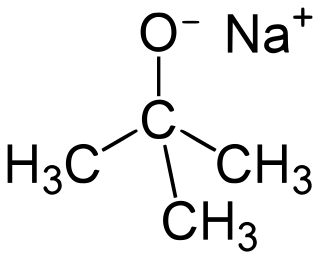
Sodium tert-butoxide (or sodium t-butoxide) is a chemical compound with the formula (CH3)3CONa (abbr. NaOtBu). It is a strong, non-nucleophilic base. It is flammable and moisture sensitive. It is sometimes written in the chemical literature as sodium t-butoxide. It is similar in reactivity to the more common potassium tert-butoxide.

Molybdenum(III) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula MoCl3. It forms purple crystals.

trans-Bis(dinitrogen)bis[1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane]molybdenum(0) is a coordination complex with the formula Mo(N2)2(dppe)2. It is a relatively air stable yellow-orange solid. It is notable as being the first discovered dinitrogen containing complex of molybdenum.
Tungsten(IV) chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula WCl4. It is a diamagnetic black solid. The compound is of interest in research as one of a handful of binary tungsten chlorides.

Transition metal nitrile complexes are coordination compounds containing nitrile ligands. Because nitriles are weakly basic, the nitrile ligands in these complexes are often labile.

Malcolm Harold Chisholm was a British inorganic chemist who worked mainly in North America, a Professor of Chemistry and Biochemistry, and Distinguished University Professor of Mathematical and Physical Sciences at Ohio State University who contributed to the synthesis and structural chemistry of transition metal complexes.
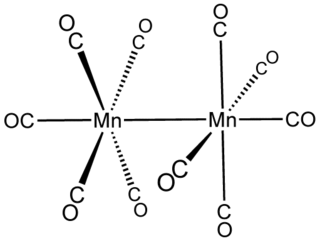
In inorganic chemistry, metal–metal bonds describe attractive interactions between metal centers. The simplest examples are found in bimetallic complexes. Metal–metal bonds can be "supported", i.e. be accompanied by one or more bridging ligands, or "unsupported". They can also vary according to bond order. The topic of metal–metal bonding is usually discussed within the framework of coordination chemistry, but the topic is related to extended metallic bonding, which describes interactions between metals in extended solids such as bulk metals and metal subhalides.

Hexa(tert-butoxy)ditungsten(III) is a coordination complex of tungsten(III). It is one of the homoleptic alkoxides of tungsten. A red, air-sensitive solid, the complex has attracted academic attention as the precursor to many organotungsten derivatives. It an example of a charge-neutral complex featuring a W≡W bond, arising from the coupling of a pair of d3 metal centers.

Lithium tert-butoxide is the metalorganic compound with the formula LiOC(CH3)3. A white solid, it is used as a strong base in organic synthesis. The compound is often depicted as a salt, and it often behaves as such, but it is not ionized in solution. Both octameric and hexameric forms have been characterized by X-ray crystallography

In chemistry, a transition metal ether complex is a coordination complex consisting of a transition metal bonded to one or more ether ligand. The inventory of complexes is extensive. Common ether ligands are diethyl ether and tetrahydrofuran. Common chelating ether ligands include the glymes, dimethoxyethane (dme) and diglyme, and the crown ethers. Being lipophilic, metal-ether complexes often exhibit solubility in organic solvents, a property of interest in synthetic chemistry. In contrast, the di-ether 1,4-dioxane is generally a bridging ligand.
Transition metal phosphate complexes are coordination complexes with one or more phosphate ligands. Phosphate binds to metals through one, two, three, or all four oxygen atoms. The bidentate coordination mode is common. The second and third pKa's of phosphoric acid, pKa2 and pKa3, are 7.2 and 12.37, respectively. It follows that HPO2−4 and PO3−4 are sufficiently basic to serve as ligands. The examples below confirm this expectation. Molecular metal phosphate complexes have no or few applications.
















