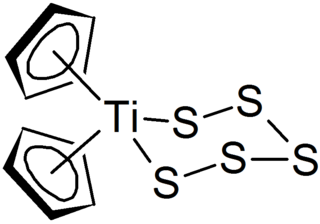In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds—that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as inorganic chemistry.

Zinc chloride is the name of inorganic chemical compounds with the formula ZnCl2·nH2O, with x ranging from 0 to 4.5, forming hydrates. Zinc chloride, anhydrous and its hydrates are colorless or white crystalline solids, and are highly soluble in water. Five hydrates of zinc chloride are known, as well as four forms of anhydrous zinc chloride. This salt is hygroscopic and even deliquescent. Zinc chloride finds wide application in textile processing, metallurgical fluxes, and chemical synthesis. No mineral with this chemical composition is known aside from the very rare mineral simonkolleite, Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O.

Praseodymium(III) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula PrCl3. Like other lanthanide trichlorides, it exists both in the anhydrous and hydrated forms. It is a blue-green solid that rapidly absorbs water on exposure to moist air to form a light green heptahydrate.
Neodymium(III) chloride or neodymium trichloride is a chemical compound of neodymium and chlorine with the formula NdCl3. This anhydrous compound is a mauve-colored solid that rapidly absorbs water on exposure to air to form a purple-colored hexahydrate, NdCl3·6H2O. Neodymium(III) chloride is produced from minerals monazite and bastnäsite using a complex multistage extraction process. The chloride has several important applications as an intermediate chemical for production of neodymium metal and neodymium-based lasers and optical fibers. Other applications include a catalyst in organic synthesis and in decomposition of waste water contamination, corrosion protection of aluminium and its alloys, and fluorescent labeling of organic molecules (DNA).
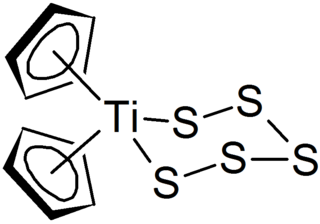
Polysulfides are a class of chemical compounds derived from anionic chains of sulfur atoms. There are two main classes of polysulfides: inorganic and organic. The inorganic polysulfides have the general formula S2−
n. These anions are the conjugate bases of polysulfanes H2Sn. Organic polysulfides generally have the formulae R1SnR2, where R = alkyl or aryl.
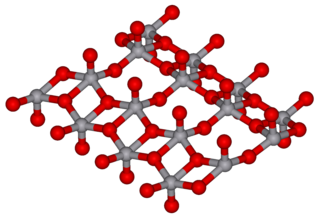
Vanadium(V) oxide (vanadia) is the inorganic compound with the formula V2O5. Commonly known as vanadium pentoxide, it is a brown/yellow solid, although when freshly precipitated from aqueous solution, its colour is deep orange. Because of its high oxidation state, it is both an amphoteric oxide and an oxidizing agent. From the industrial perspective, it is the most important compound of vanadium, being the principal precursor to alloys of vanadium and is a widely used industrial catalyst.

Ammonium persulfate (APS) is the inorganic compound with the formula (NH4)2S2O8. It is a colourless (white) salt that is highly soluble in water, much more so than the related potassium salt. It is a strong oxidizing agent that is used as a catalyst in polymer chemistry, as an etchant, and as a cleaning and bleaching agent.

Erbium(III) chloride is a violet solid with the formula ErCl3. It is used in the preparation of erbium metal.

Copper(I) iodide is the inorganic compound with the formula CuI. It is also known as cuprous iodide. It is useful in a variety of applications ranging from organic synthesis to cloud seeding.

Scandium(III) fluoride, ScF3, is an ionic compound. This salt is slightly soluble in water but dissolves in the presence of excess fluoride to form the ScF63− anion.

Ammonium metavanadate is the inorganic compound with the formula NH4VO3. It is a white salt, although samples are often yellow owing to impurities of V2O5. It is an important intermediate in the purification of vanadium.

Aluminium fluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula AlF3. It forms hydrates AlF3·xH2O. Anhydrous AlF3 and its hydrates are all colorless solids. Anhydrous AlF3 is used in the production of aluminium metal. Several occur as minerals.

Yttrium(III) chloride is an inorganic compound of yttrium and chloride. It exists in two forms, the hydrate (YCl3(H2O)6) and an anhydrous form (YCl3). Both are colourless salts that are highly soluble in water and deliquescent.

Ammonium polyphosphate is an inorganic salt of polyphosphoric acid and ammonia containing both chains and possibly branching. Its chemical formula is H(NH4PO3)nOH showing that each monomer consists of an orthophosphate radical of a phosphorus atom with three oxygens and one negative charge neutralized by an ammonium cation leaving two bonds free to polymerize. In the branched cases some monomers are missing the ammonium anion and instead link to three other monomers.

Potassium hexachloroplatinate is the inorganic compound with the formula K2PtCl6. It is a yellow solid that is an example of a comparatively insoluble potassium salt. The salt features the hexachloroplatinate(IV) dianion, which has octahedral coordination geometry.
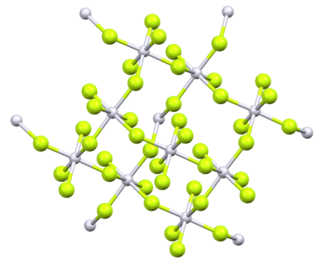
Platinum tetrafluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula PtF
4. In the solid state, the compound features platinum(IV) in octahedral coordination geometry.

Copper oxalate is an inorganic compound, a salt of copper metal and oxalic acid with the chemical formula CuC
2O
4. The compound is practically insoluble in water, alcohol, ether, and acetic acid but soluble in ammonium hydroxide. Copper oxalate forms a hydrate, which forms acid-blue crystals.
Erbium compounds are compounds containing the element erbium (Er). These compounds are usually dominated by erbium in the +3 oxidation state, although the +2, +1 and 0 oxidation states have also been reported.
Potassium hexafluorotitanate is an inorganic compound of potassium, fluorine, and titanium with the chemical formula K2TiF6.

Potassium hexafluorozirconate is an inorganic compound of potassium, fluorine, and zirconium with the chemical formula K2ZrF6.