
Thulium is a chemical element with the symbol Tm and atomic number 69. It is the thirteenth and third-last element in the lanthanide series. Like the other lanthanides, the most common oxidation state is +3, seen in its oxide, halides and other compounds; however, the +2 oxidation state can also be stable. In aqueous solution, like compounds of other late lanthanides, soluble thulium compounds form coordination complexes with nine water molecules.

Ytterbium is a chemical element with the symbol Yb and atomic number 70. It is a metal, the fourteenth and penultimate element in the lanthanide series, which is the basis of the relative stability of its +2 oxidation state. However, like the other lanthanides, its most common oxidation state is +3, as in its oxide, halides, and other compounds. In aqueous solution, like compounds of other late lanthanides, soluble ytterbium compounds form complexes with nine water molecules. Because of its closed-shell electron configuration, its density and melting and boiling points differ significantly from those of most other lanthanides.
In chemistry, azide is a linear, polyatomic anion with the formula N−3 and structure −N=N+=N−. It is the conjugate base of hydrazoic acid HN3. Organic azides are organic compounds with the formula RN3, containing the azide functional group. The dominant application of azides is as a propellant in air bags.

Ozonide is the polyatomic anion O−3. Cyclic organic compounds formed by the addition of ozone to an alkene are also called ozonides.
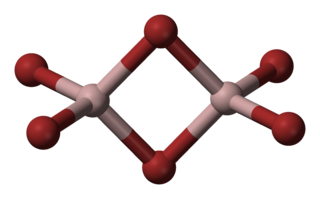
Aluminium bromide is any chemical compound with the empirical formula AlBrx. Aluminium tribromide is the most common form of aluminium bromide. It is a colorless, sublimable hygroscopic solid; hence old samples tend to be hydrated, mostly as aluminium tribromide hexahydrate (AlBr3·6H2O).

Thallium(I) hydroxide, also called thallous hydroxide, TlOH, is a hydroxide of thallium, with thallium in oxidation state +1.
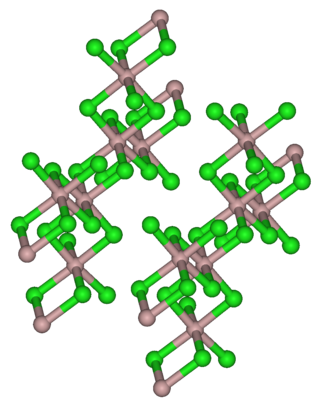
Indium(III) bromide, (indium tribromide), InBr3, is a chemical compound of indium and bromine. It is a Lewis acid and has been used in organic synthesis.
There are three sets of Indium halides, the trihalides, the monohalides, and several intermediate halides. In the monohalides the oxidation state of indium is +1 and their proper names are indium(I) fluoride, indium(I) chloride, indium(I) bromide and indium(I) iodide.
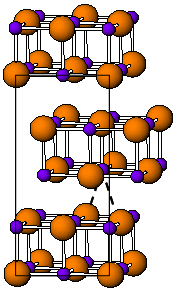
Indium(I) bromide is a chemical compound of indium and bromine. It is a red crystalline compound that is isostructural with β-TlI and has a distorted rock salt structure. Indium(I) bromide is generally made from the elements, heating indium metal with InBr3. It has been used in the sulfur lamp. In organic chemistry, it has been found to promote the coupling of α, α-dichloroketones to 1-aryl-butane-1,4-diones. Oxidative addition reactions with for example alkyl halides to give alkyl indium halides and with NiBr complexes to give Ni-In bonds are known. It is unstable in water decomposing into indium metal and indium tribromide. When indium dibromide is dissolved in water, InBr is produced as a, presumably, insoluble red precipitate, that then rapidly decomposes.

Thulium(III) chloride or thulium trichloride is as an inorganic salt composed of thulium and chlorine with the formula TmCl3. It forms yellow crystals. Thulium(III) chloride has the YCl3 (AlCl3) layer structure with octahedral thulium ions.
Difluorides are chemical compounds with two fluorine atoms per molecule.

Compounds of lead exist with lead in two main oxidation states: +2 and +4. The former is more common. Inorganic lead(IV) compounds are typically strong oxidants or exist only in highly acidic solutions.

Uranium triiodide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula UI3. It is a black solid that is soluble in water.
Thulium(III) bromide is a crystalline compound of one thulium atom and three bromine atoms. The salt is a white powder at room temperature. It is hygroscopic.
Thullium(III) fluoride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula TmF3.

Thiothionyl fluoride is a chemical compound of fluorine and sulfur and an isomer of disulfur difluoride.
Thulium phosphide is an inorganic compound of thulium and phosphorus with the chemical formula TmP.

Neodymium(II) iodide or neodymium diiodide is an inorganic salt of iodine and neodymium the formula NdI2. Neodymium uses the +2 oxidation state in the compound.

Dysprosium(III) bromide is an inorganic compound of bromine and dysprosium, with the chemical formula of DyBr3.

Thulium(III) iodide is an iodide of thulium, with the chemical formula of TmI3. Thulium(III) iodide is used as a component of metal halide lamps.













