
Zinc acetate is a salt with the formula Zn(CH3CO2)2, which commonly occurs as the dihydrate Zn(CH3CO2)2·2H2O. Both the hydrate and the anhydrous forms are colorless solids that are used as dietary supplements. When used as a food additive, it has the E number E650.

Iron(II) acetate describes compounds with formula Fe(CH3CO2)2·(H2O)x where x can be 0 (anhydrous) or 4 (tetrahydrate). The anhydrous compound is a white solid, although impure samples can be slightly colored. The tetrahydrate is light green solid that is highly soluble in water.
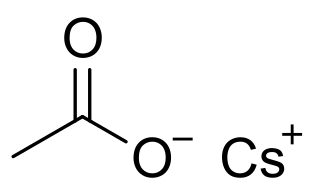
Caesium acetate or cesium acetate is an ionic caesium compound with the molecular formula CH3COOCs. It is a white solid that may be formed by the reaction of caesium hydroxide or caesium carbonate with acetic acid.
Trirhenium nonachloride is a compound with the formula ReCl3, sometimes also written Re3Cl9. It is a dark red hygroscopic solid that is insoluble in ordinary solvents. The compound is important in the history of inorganic chemistry as an early example of a cluster compound with metal-metal bonds. It is used as a starting material for synthesis of other rhenium complexes.

Cobalt(II) acetate is the cobalt salt of acetic acid. It is commonly found as the tetrahydrate Co(CH3CO2)2·4 H2O, abbreviated Co(OAc)2·4 H2O. It is used as a catalyst.

Nickel(II) acetate is the name for the coordination compounds with the formula Ni(CH3CO2)2·x H2O where x can be 0, 2, and 4. The mint-green tetrahydrate Ni(CH3CO2)2·4 H2O is most common. It is used for electroplating.

Neodymium(III) acetate is an inorganic salt composed of a neodymium atom trication and three acetate groups as anions where neodymium exhibits the +3 oxidation state. It has a chemical formula of Nd(CH3COO)3 although it can be informally referred to as NdAc because Ac is an informal symbol for acetate. It commonly occurs as a light purple powder.

Praseodymium(III) acetate is an inorganic salt composed of a Praseodymium atom trication and three acetate groups as anions. This compound commonly forms the dihydrate, Pr(O2C2H3)3·2H2O.

Neodymium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal neodymium (Nd). In these compounds, neodymium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as NdCl3, Nd2(SO4)3 and Nd(CH3COO)3. Compounds with neodymium in the +2 oxidation state are also known, such as NdCl2 and NdI2. Some neodymium compounds have colors that vary based upon the type of lighting.
Carbide iodides are mixed anion compounds containing iodide and carbide anions. Many carbide iodides are cluster compounds, containing one, two or more carbon atoms in a core, surrounded by a layer of metal atoms, and encased in a shell of iodide ions. These ions may be shared between clusters to form chains, double chains or layers.
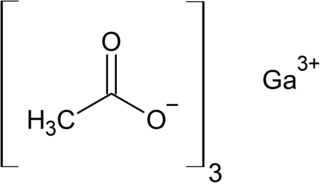
Gallium acetate is a salt composed of a gallium atom trication and three acetate groups as anions where gallium exhibits the +3 oxidation state. It has a chemical formula of Ga(CH3COO)3 although it can be informally referred to as GaAc because Ac is an informal symbol for acetate. Gallium is moderately water-soluble and decomposes to gallium oxide when heated to around 70 °C. Gallium acetate, like other acetate compounds, is a good precursor to ultra-pure compounds, catalysts and nanoscale materials. Gallium acetate is being considered as a substitute in de-icing compounds like calcium chloride and magnesium chloride.

Europium(III) acetate is an inorganic salt of europium and acetic acid with the chemical formula of Eu(CH3COO)3. In this compound, europium exhibits the +3 oxidation state. It can exist in the anhydrous form, sesquihydrate and tetrahydrate. Its hydrate molecule is a dimer.

Dysprosium acetate is a hypothetical salt of dysprosium and acetate. Its proposed chemical formula is Dy(CH3COO)3.

Erbium(III) acetate is the acetate salt of erbium, with the proposed chemical formula of Er(CH3COO)3. It can be used to synthesize some optical materials.

Holmium(III) iodide is an iodide of holmium, with the chemical formula of HoI3. It is used as a component of metal halide lamps.

Scandium acetate is an compound, with the chemical formula of Sc(CH3COO)3. It exists in the anhydrous and the hydrate forms. It can be obtained by reacting scandium hydroxide or scandium oxide with acetic acid. It is a colorless, water-soluble solid. It decomposes into scandium oxide at high temperature. It can be used to prepare other scandium-containing materials.

Terbium(III) acetate is the acetate salt of terbium, with a chemical formula of Tb(CH3COO)3.

Gadolinium acetate is the acetate salt of the lanthanide element gadolinium, with the chemical formula Gd(CH3COO)3. It is a colorless crystal that is soluble in water and can form a hydrate. Its tetrahydrate has ground state ferromagnetism.

Samarium(III) acetate is an acetate salt of samarium, with the chemical formula of Sm(CH3COO)3. It exists in the hydrate and tetrahydrate form. Its tetrahydrate can be obtained by dissolving samarium(III) oxide in 50% acetic acid solution, crystallizing and vacuum drying. The mixed anion acetate [Sm(CH3COO)(H2O)6]Cl2·H2O and [Sm(CH3COO)2(H2O)3]Cl can be crystallized from SmCl3·6H2O and SmOCl in acetic acid solution respectively.

Lanthanum acetate is an inorganic compound, a salt of lanthanum with acetic acid with the chemical formula La(CH3CO2)3. According to X-ray crystallography, anhydrous lanthanum acetate is a coordination polymer. Each La(III) center is nine-coordinate, with two bidentate acetate ligands and the remaining sites occupied by oxygens provided by bridging acetate ligands. The praseodymium and holmium compounds are isostructural.



















