 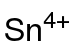 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names Tin(IV) acetate Tin tetraacetate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.157.007 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Sn(CH3COO)4 | |
| Molar mass | 354.886 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white needles [1] |
| Melting point | 242 °C (468 °F; 515 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: [2] | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H302, H312, H332 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P317, P302+P352, P304+P340, P317, P321, P330, P362+P364, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions | Tin(IV) fluoroacetate |
Other cations | Lead(IV) acetate |
Related compounds | Tin(II) acetate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Tin(IV) acetate, also known as stannic acetate, is the tin(IV) salt of acetic acid, with the chemical formula of Sn(CH3COO)4.