 | |
 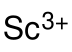 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names Scandium(III) acetate Scandium ethanoate Scandium(III) ethanoate | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.021.159 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H9O6Sc | |
| Molar mass | 222.088 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Scandium acetate is a compound, with the chemical formula of Sc(CH3COO)3. It exists in the anhydrous and the hydrate forms. It can be obtained by reacting scandium hydroxide or scandium oxide with acetic acid. [1] [2] It is a colorless, water-soluble solid. It decomposes into scandium oxide at high temperature. It can be used to prepare other scandium-containing materials. [3]
The structure of the anhydrous form was determined by X-ray crystallography. It consists of a chain of octahedral Sc(III) centers linked by bridging acetate ligands. [1]