 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Scandium nitride | |
| Other names Azanylidynescandium Nitridoscandium | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.042.938 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| ScN | |
| Molar mass | 58.963 |
| Density | 4.4 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 2,600 °C (4,710 °F; 2,870 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Danger | |
| H228 | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions | Scandium phosphide Scandium arsenide Scandium antimonide Scandium bismuthide |
Other cations | Yttrium nitride Lutetium nitride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
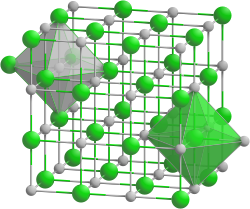
Scandium nitride (ScN) is a binary III-V indirect bandgap semiconductor. It is composed of the scandium cation and the nitride anion. It forms crystals that can be grown on tungsten foil through sublimation and recondensation. [1] It has a rock-salt crystal structure with octahedral bonding coordination. It exhibits lattice constant of 0.451 nm and an indirect bandgap of 0.9 eV and direct bandgap of 2 to 2.4 eV. [1] [2] These crystals can be synthesized by dissolving nitrogen gas with indium-scandium melts, magnetron sputtering, Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE), HVPE and other deposition methods. [2] [3] Scandium nitride is also an effective gate for semiconductors on a silicon dioxide (SiO2) or hafnium dioxide (HfO2) substrate. [4] Scandium nitride is the first nitride semiconductor reported to be synthesized without an active Nitrogen plasma source using the Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE) technique. It exhibits a scavenging effect, in which scandium at the growth front dissociates molecular nitrogen and incorporates it into the lattice. [5] Scandium nitride can be potentially used in thermoelectric materials as a semiconducting layer in epitaxial single-crystalline metal/semiconductor superlattices for thermoelectric, plasmonic and thermophotonic applications, and as a substrate material for high-quality GaN-based devices and other solid-state applications. [6]