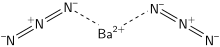| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names Barium dinitride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.038.706 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID | |
| UN number | 1687 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Ba(N3)2 | |
| Molar mass | 221.37 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Odor | Odourless |
| Density | 2.936 g/cm3 [1] |
| Melting point | 126 °C (259 °F; 399 K) |
| Boiling point | 160 °C (320 °F; 433 K) (initial decomposition) [2] >217 °C (deflagrates) 180 °C (initial decomposition), [3] 225 °C explosion |
| 11.5 g/100 mL (0 °C) 14.98 g/100 mL (15.7 °C) 15.36 g/100 mL (20 °C) 22.73 g/100 mL (52.1 °C) 24.75 g/100 mL (70 °C) [4] | |
| Solubility in ethanol | 0.017 g/100 mL (16 °C) [5] |
| Solubility in acetone | Insoluble |
| Solubility in ether | Insoluble |
| Structure | |
| Monoclinic | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Danger | |
| H200, H301, H315, H319, H331, H335 | |
| P210, P240, P264, P280, P305+P351+P338, P310 | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Barium azide is an inorganic azide with the formula Ba(N3)2. It is a barium salt of hydrazoic acid. Like all azides, it is explosive. It is less sensitive to mechanical shock than lead azide.