
Bromine is a chemical element with the symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is the third-lightest halogen, and is a fuming red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a similarly coloured vapour. Its properties are intermediate between those of chlorine and iodine. Isolated independently by two chemists, Carl Jacob Löwig and Antoine Jérôme Balard, its name was derived from the Ancient Greek βρῶμος ("stench"), referring to its sharp and disagreeable smell.

Barium is a chemical element with the symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in group 2 and is a soft, silvery alkaline earth metal. Because of its high chemical reactivity, barium is never found in nature as a free element.

Barium hydroxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula Ba(OH)2. The monohydrate (x = 1), known as baryta or baryta-water, is one of the principal compounds of barium. This white granular monohydrate is the usual commercial form.

Barium oxide, BaO, baria, is a white hygroscopic non-flammable compound. It has a cubic structure and is used in cathode ray tubes, crown glass, and catalysts. It is harmful to human skin and if swallowed in large quantity causes irritation. Excessive quantities of barium oxide may lead to death.

Barium chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula BaCl2. It is one of the most common water-soluble salts of barium. Like most other barium salts, it is white, toxic, and imparts a yellow-green coloration to a flame. It is also hygroscopic, converting first to the dihydrate BaCl2(H2O)2. It has limited use in the laboratory and industry.

Barium nitrate is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ba(NO3)2. It, like most barium salts, is colorless, toxic, and water-soluble. It burns with a green flame and is an oxidizer; the compound is commonly used in pyrotechnics.

Lead(II) chloride (PbCl2) is an inorganic compound which is a white solid under ambient conditions. It is poorly soluble in water. Lead(II) chloride is one of the most important lead-based reagents. It also occurs naturally in the form of the mineral cotunnite.

The bromate anion, BrO−
3, is a bromine-based oxoanion. A bromate is a chemical compound that contains this ion. Examples of bromates include sodium bromate,, and potassium bromate,.
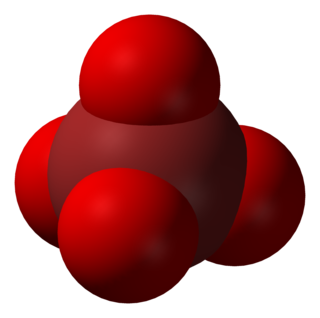
In chemistry, the perbromate ion is the anion having the chemical formula BrO−
4. It is an oxyanion of bromine, the conjugate base of perbromic acid, in which bromine has the oxidation state +7. Unlike its chlorine and iodine analogs, it is difficult to synthesize. It has tetrahedral molecular geometry.

Sodium bromate, the inorganic compound with the chemical formula of NaBrO3, is the sodium salt of bromic acid. It is a strong oxidant.

Bromic acid, also known as hydrogen bromate, is an oxoacid with the molecular formula HBrO3. It only exists in aqueous solution. It is a colorless solution that turns yellow at room temperature as it decomposes to bromine. Bromic acid and bromates are powerful oxidizing agents and are common ingredients in Belousov–Zhabotinsky reactions. Belousov-Zhabotinsky reactions are a classic example of non-equilibrium thermodynamics.

A uranate is a ternary oxide involving the element uranium in one of the oxidation states 4, 5 or 6. A typical chemical formula is MxUyOz, where M represents a cation. The uranium atom in uranates(VI) has two short collinear U–O bonds and either four or six more next nearest oxygen atoms. The structures are infinite lattice structures with the uranium atoms linked by bridging oxygen atoms.
Strontium bromate is a rarely considered chemical in the laboratory or in industries. It is, however, mentioned in the book Uncle Tungsten: Memories of a Chemical Boyhood by Oliver Sacks. There it is said that this salt glows when crystallized from a saturated aqueous solution. Chemically this salt is soluble in water, and is a moderately strong oxidizing agent.

Barium chlorate, Ba(ClO3)2, is the barium salt of chloric acid. It is a white crystalline solid, and like all soluble barium compounds, irritant and toxic. It is sometimes used in pyrotechnics to produce a green color. It also finds use in the production of chloric acid.

Barium bromide is the chemical compound with the formula BaBr2. Like barium chloride, it dissolves well in water and is toxic.

Bromous acid is the inorganic compound with the formula of HBrO2. It is an unstable compound, although salts of its conjugate base – bromites – have been isolated. In acidic solution, bromites decompose to bromine.
Calcium bromate, Ca(BrO3)2, is a calcium salt of bromic acid. It is most commonly encountered as the monohydrate, Ca(BrO3)2•H2O.
Barium perchlorate is a powerful oxidizing agent, with the formula Ba(ClO4)2. It is used in the pyrotechnic industry.

Barium manganate is an inorganic compound with the formula BaMnO4. It is used as an oxidant in organic chemistry. It belongs to a class of compounds known as manganates in which the manganese resides in a +6 oxidation state. Manganate should not to be confused with permanganate in which contains manganese(VII). Barium manganate is a powerful oxidant, popular in organic synthesis and can be used in a wide variety of oxidation reactions.
Sodium perbromate is the chemical compound composed of the sodium ion and the perbromate ion, with the chemical formula NaBrO4.

















