
Basic copper carbonate is a chemical compound, more properly called copper(II) carbonate hydroxide. It is an ionic compound consisting of the ions copper(II) Cu2+
, carbonate CO2−
3, and hydroxide OH−
.
In chemistry, azide is a linear, polyatomic anion with the formula N−3 and structure −N=N+=N−. It is the conjugate base of hydrazoic acid HN3. Organic azides are organic compounds with the formula RN3, containing the azide functional group. The dominant application of azides is as a propellant in air bags.

Copper(II) nitrate describes any member of the family of inorganic compounds with the formula Cu(NO3)2(H2O)x. The hydrates are blue solids. Anhydrous copper nitrate forms blue-green crystals and sublimes in a vacuum at 150-200 °C. Common hydrates are the hemipentahydrate and trihydrate.

Sodium azide is an inorganic compound with the formula NaN3. This colorless salt is the gas-forming component in some car airbag systems. It is used for the preparation of other azide compounds. It is an ionic substance, is highly soluble in water, and is very acutely poisonous.
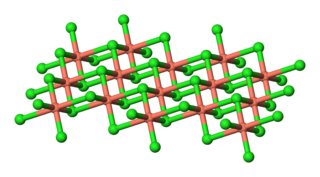
Copper(II) chloride, also known as cupric chloride, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CuCl2. The monoclinic yellowish-brown anhydrous form slowly absorbs moisture to form the orthorhombic blue-green dihydrate CuCl2·2H2O, with two water molecules of hydration. It is industrially produced for use as a co-catalyst in the Wacker process.

Hydrazoic acid, also known as hydrogen azide or azoimide, is a compound with the chemical formula HN3. It is a colorless, volatile, and explosive liquid at room temperature and pressure. It is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen, and is therefore a pnictogen hydride. The oxidation state of the nitrogen atoms in hydrazoic acid is fractional and is -1/3. It was first isolated in 1890 by Theodor Curtius. The acid has few applications, but its conjugate base, the azide ion, is useful in specialized processes.
The azide-alkyne Huisgen cycloaddition is a 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between an azide and a terminal or internal alkyne to give a 1,2,3-triazole. Rolf Huisgen was the first to understand the scope of this organic reaction. American chemist Karl Barry Sharpless has referred to this cycloaddition as "the cream of the crop" of click chemistry and "the premier example of a click reaction".

Silver azide is the chemical compound with the formula AgN3. It is a silver(I) salt of hydrazoic acid. It forms a colorless crystals. Like most azides, it is a primary explosive.
The chemical element nitrogen is one of the most abundant elements in the universe and can form many compounds. It can take several oxidation states; but the most common oxidation states are -3 and +3. Nitrogen can form nitride and nitrate ions. It also forms a part of nitric acid and nitrate salts. Nitrogen compounds also have an important role in organic chemistry, as nitrogen is part of proteins, amino acids and adenosine triphosphate.

Silver is a relatively unreactive metal, although it can form several compounds. The common oxidation states of silver are (in order of commonness): +1 (the most stable state; for example, silver nitrate, AgNO3); +2 (highly oxidising; for example, silver(II) fluoride, AgF2); and even very rarely +3 (extreme oxidising; for example, potassium tetrafluoroargentate(III), KAgF4). The +3 state requires very strong oxidising agents to attain, such as fluorine or peroxodisulfate, and some silver(III) compounds react with atmospheric moisture and attack glass. Indeed, silver(III) fluoride is usually obtained by reacting silver or silver monofluoride with the strongest known oxidizing agent, krypton difluoride.
Copper(I) acetylide, or cuprous acetylide, is a chemical compound with the formula Cu2C2. Although never characterized by X-ray crystallography, the material has been claimed at least since 1856. One form is claimed to be a monohydrate with formula Cu
2C
2.H
2O is a reddish-brown explosive powder.
Copper(I) hydroxide is the hydroxide of the metal copper with the chemical formula of CuOH. It is a mild, highly unstable alkali. The color of pure CuOH is yellow or orange-yellow, but it usually appears rather dark red because of impurities. It is extremely easily oxidized even at room temperature. It is useful for some industrial processes and in preventing condensation of formaldehyde. It is also an important reactant and intermediate for several important products including Cu2O3 and Cu(OH)2. Additionally, it can act as a catalyst in the synthesis pyrimidopyrrolidone derivatives.
Explosophores are functional groups in organic chemistry that give organic compounds explosive properties.
Beryllium azide, Be(N3)2, is an inorganic compound. It is a beryllium salt of hydrazoic acid HN3.

Silicon tetraazide is a thermally unstable binary compound of silicon and nitrogen with a nitrogen content of 85.7%. This high-energy compound combusts spontaneously and can only be studied in a solution. A further coordination to a six-fold coordinated structure such as a hexaazidosilicate ion [Si(N3)6]2− or as an adduct with bicationic ligands Si(N3)4·L2 will result in relatively stable, crystalline solids that can be handled at room temperature.

4-Chlorophenyl azide is an organic aryl azide compound with the chemical formula C6H4ClN3. The geometry between the nitrogen atoms in the azide functional group is approximately linear while the geometry between the nitrogen and the carbon of the benzene is trigonal planar.

Rubidium azide is an inorganic compound with the formula RbN3. It is the rubidium salt of the hydrazoic acid HN3. Like most azides, it is explosive.

Transition metal azide complexes are coordination complexes containing one or more azide (N3−) ligands.
Iron(III) azide, also called ferric azide, is a chemical compound with the formula Fe(N3)3. It is an extremely explosive, impact-sensitive, hygroscopic dark brown solid. This compound is used to prepare various azidoalkanes, such as n-butyl azide.
Homoleptic azido compounds are chemical compounds in which the only anion or ligand is the azide group, -N3. The breadth of homoleptic azide compounds spans nearly the entire periodic table. With rare exceptions azido compounds are highly shock sensitive and need to be handled with the upmost caution. Binary azide compounds can take on several different structures including discrete compounds, or one- two, and three-dimensional nets, leading some to dub them as "polyazides". Reactivity studies of azide compounds are relatively limited due to how sensitive they can be. The sensitivity of these compounds tends to be correlated with the amount of ionic or covalent character the azide-element bond has, with ionic character being far more stable than covalent character. Therefore, compounds such as silver or sodium azide – which have strong ionic character – tend to possess more synthetic utility than their covalent counterparts. A few other notable exceptions include polymeric networks which possess unique magnetic properties, group 13 azides which unlike most other azides decompose to nitride compounds (important materials for semiconductors), other limited uses as synthetic reagents for the transfer for azide groups, or interest in high energy density materials.













