
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic table: carbon is above it; and germanium, tin, lead, and flerovium are below it. It is relatively unreactive.

Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula SiO2, commonly found in nature as quartz. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is abundant as it comprises several minerals and as a synthetic products. All forms are white or colorless, although impure samples can be colored.

Phosphoric acid is a colorless, odorless phosphorus-containing solid, and inorganic compound with the chemical formula H3PO4. It is commonly encountered as an 85% aqueous solution, which is a colourless, odourless, and non-volatile syrupy liquid. It is a major industrial chemical, being a component of many fertilizers.
Silane (Silicane) is an inorganic compound with chemical formula SiH4. It is a colourless, pyrophoric, toxic gas with a sharp, repulsive, pungent smell, somewhat similar to that of acetic acid. Silane is of practical interest as a precursor to elemental silicon. Silane with alkyl groups are effective water repellents for mineral surfaces such as concrete and masonry. Silanes with both organic and inorganic attachments are used as coupling agents. Silanes are commonly used to apply coatings to surfaces or as an adhesion promoter.

Tetrahydrofuran (THF), or oxolane, is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4O. The compound is classified as heterocyclic compound, specifically a cyclic ether. It is a colorless, water-miscible organic liquid with low viscosity. It is mainly used as a precursor to polymers. Being polar and having a wide liquid range, THF is a versatile solvent.
Cyanogen is the chemical compound with the formula (CN)2. The simplest stable carbon nitride, it is a colorless and highly toxic gas with a pungent odor. The molecule is a pseudohalogen. Cyanogen molecules consist of two CN groups – analogous to diatomic halogen molecules, such as Cl2, but far less oxidizing. The two cyano groups are bonded together at their carbon atoms: N≡C‒C≡N, although other isomers have been detected. The name is also used for the CN radical, and hence is used for compounds such as cyanogen bromide (NCBr) (but see also Cyano radical.)

Copper(I) oxide or cuprous oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Cu2O. It is one of the principal oxides of copper, the other being or copper(II) oxide or cupric oxide (CuO). Cuprous oxide is a red-coloured solid and is a component of some antifouling paints. The compound can appear either yellow or red, depending on the size of the particles. Copper(I) oxide is found as the reddish mineral cuprite.

Tungsten(VI) fluoride, also known as tungsten hexafluoride, is an inorganic compound with the formula WF6. It is a toxic, corrosive, colorless gas, with a density of about 13 kg/m3 (22 lb/cu yd). It is one of the densest known gases under standard conditions. WF6 ls commonly used by the semiconductor industry to form tungsten films, through the process of chemical vapor deposition. This layer is used in a low-resistivity metallic "interconnect". It is one of seventeen known binary hexafluorides.

Copper(II) oxide or cupric oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula CuO. A black solid, it is one of the two stable oxides of copper, the other being Cu2O or copper(I) oxide (cuprous oxide). As a mineral, it is known as tenorite. It is a product of copper mining and the precursor to many other copper-containing products and chemical compounds.

An intermetallic is a type of metallic alloy that forms an ordered solid-state compound between two or more metallic elements. Intermetallics are generally hard and brittle, with good high-temperature mechanical properties. They can be classified as stoichiometric or nonstoichiometic intermetallic compounds.

Copper(I) chloride, commonly called cuprous chloride, is the lower chloride of copper, with the formula CuCl. The substance is a white solid sparingly soluble in water, but very soluble in concentrated hydrochloric acid. Impure samples appear green due to the presence of copper(II) chloride (CuCl2).
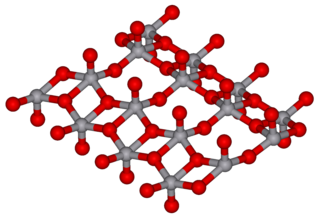
Vanadium(V) oxide (vanadia) is the inorganic compound with the formula V2O5. Commonly known as vanadium pentoxide, it is a brown/yellow solid, although when freshly precipitated from aqueous solution, its colour is deep orange. Because of its high oxidation state, it is both an amphoteric oxide and an oxidizing agent. From the industrial perspective, it is the most important compound of vanadium, being the principal precursor to alloys of vanadium and is a widely used industrial catalyst.
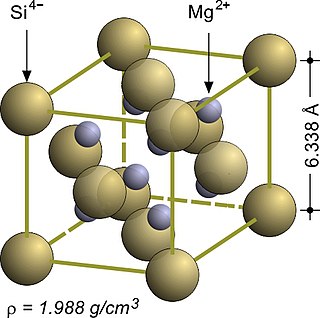
Magnesium silicide, Mg2Si, is an inorganic compound consisting of magnesium and silicon. As-grown Mg2Si usually forms black crystals; they are semiconductors with n-type conductivity and have potential applications in thermoelectric generators.

A silicide is a type of chemical compound that combines silicon and a usually more electropositive element.

Platinum silicide, also known as platinum monosilicide, is the inorganic compound with the formula PtSi. It is a semiconductor that turns into a superconductor when cooled to 0.8 K.
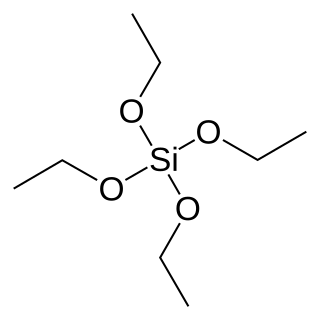
Tetraethyl orthosilicate, formally named tetraethoxysilane (TEOS), ethyl silicate is the organic chemical compound with the formula Si(OC2H5)4. TEOS is a colorless liquid. It degrades in water. TEOS is the ethyl ester of orthosilicic acid, Si(OH)4. It is the most prevalent alkoxide of silicon.

Binary compounds of silicon are binary chemical compounds containing silicon and one other chemical element. Technically the term silicide is reserved for any compounds containing silicon bonded to a more electropositive element. Binary silicon compounds can be grouped into several classes. Saltlike silicides are formed with the electropositive s-block metals. Covalent silicides and silicon compounds occur with hydrogen and the elements in groups 10 to 17.
Chromium(II) silicide or chromium disilicide is an inorganic compound of chromium and silicon. Its chemical formula is CrSi2. It is a p-type thermoelectric semiconductor with an indirect bandgap of 0.35 eV.

Hexachlorodisilane is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Si2Cl6. It is a colourless liquid that fumes in moist air. It has specialty applications in as a reagent and as a volatile precursor to silicon metal.

Nickel silicides include several intermetallic compounds of nickel and silicon. Nickel silicides are important in microelectronics as they form at junctions of nickel and silicon. Additionally thin layers of nickel silicides may have application in imparting surface resistance to nickel alloys.














