
Tellurium is a chemical element; it has symbol Te and atomic number 52. It is a brittle, mildly toxic, rare, silver-white metalloid. Tellurium is chemically related to selenium and sulfur, all three of which are chalcogens. It is occasionally found in its native form as elemental crystals. Tellurium is far more common in the Universe as a whole than on Earth. Its extreme rarity in the Earth's crust, comparable to that of platinum, is due partly to its formation of a volatile hydride that caused tellurium to be lost to space as a gas during the hot nebular formation of Earth.
A period 5 element is one of the chemical elements in the fifth row of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when chemical behaviour begins to repeat, meaning that elements with similar behaviour fall into the same vertical columns. The fifth period contains 18 elements, beginning with rubidium and ending with xenon. As a rule, period 5 elements fill their 5s shells first, then their 4d, and 5p shells, in that order; however, there are exceptions, such as rhodium.

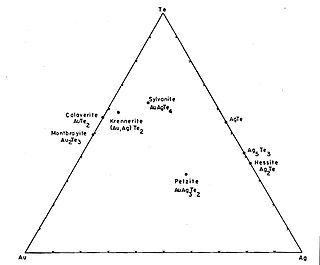
The mineral petzite, Ag3AuTe2, is a soft, steel-gray telluride mineral generally deposited by hydrothermal activity. It forms isometric crystals, and is usually associated with rare tellurium and gold minerals, often with silver, mercury, and copper.

Copper(II) sulfate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CuSO4. It forms hydrates CuSO4·nH2O, where n can range from 1 to 7. The pentahydrate (n = 5), a bright blue crystal, is the most commonly encountered hydrate of copper(II) sulfate, while its anhydrous form is white. Older names for the pentahydrate include blue vitriol, bluestone, vitriol of copper, and Roman vitriol. It exothermically dissolves in water to give the aquo complex [Cu(H2O)6]2+, which has octahedral molecular geometry. The structure of the solid pentahydrate reveals a polymeric structure wherein copper is again octahedral but bound to four water ligands. The Cu(II)(H2O)4 centers are interconnected by sulfate anions to form chains.

Rickardite is a telluride mineral, a copper telluride (Cu7Te5) or Cu3-x (x = 0 to 0.36)Te2. It was first described for an occurrence in the Good Hope Mine, Vulcan district, Gunnison County, Colorado, US, and named for mining engineer Thomas Arthur Rickard (1864–1953). It is a low temperature hydrothermal mineral that occurs associated with vulcanite, native tellurium, cameronite, petzite, sylvanite, berthierite, pyrite, arsenopyrite and bornite.
A telluride mineral is a mineral that has the telluride anion as a main component.

Copper(I) iodide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CuI. It is also known as cuprous iodide. It is useful in a variety of applications ranging from organic synthesis to cloud seeding.

Copper arsenate (Cu3(AsO4)2·4H2O, or Cu5H2(AsO4)4·2H2O), also called copper orthoarsenate, tricopper arsenate, cupric arsenate, or tricopper orthoarsenate, is a blue or bluish-green powder insoluble in water and alcohol and soluble in aqueous ammonium and dilute acids. Its CAS number is 7778-41-8 or 10103-61-4.

Bismuth telluride is a gray powder that is a compound of bismuth and tellurium also known as bismuth(III) telluride. It is a semiconductor, which, when alloyed with antimony or selenium, is an efficient thermoelectric material for refrigeration or portable power generation. Bi2Te3 is a topological insulator, and thus exhibits thickness-dependent physical properties.
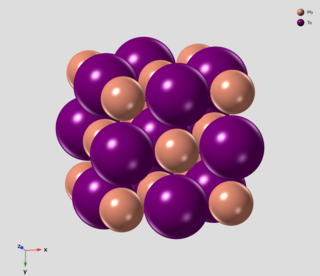
Lead telluride is a compound of lead and tellurium (PbTe). It crystallizes in the NaCl crystal structure with Pb atoms occupying the cation and Te forming the anionic lattice. It is a narrow gap semiconductor with a band gap of 0.32 eV. It occurs naturally as the mineral altaite.
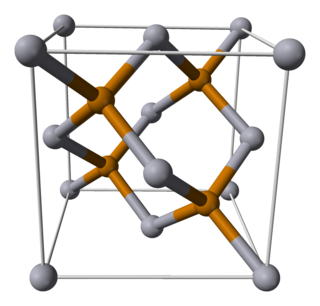
Mercury telluride (HgTe) is a binary chemical compound of mercury and tellurium. It is a semi-metal related to the II-VI group of semiconductor materials. Alternative names are mercuric telluride and mercury(II) telluride.

Hydrogen telluride is the inorganic compound with the formula H2Te. A hydrogen chalcogenide and the simplest hydride of tellurium, it is a colorless gas. Although unstable in ambient air, the gas can exist long enough to be readily detected by the odour of rotting garlic at extremely low concentrations; or by the revolting odour of rotting leeks at somewhat higher concentrations. Most compounds with Te–H bonds (tellurols) are unstable with respect to loss of H2. H2Te is chemically and structurally similar to hydrogen selenide, both are acidic. The H–Te–H angle is about 90°. Volatile tellurium compounds often have unpleasant odours, reminiscent of decayed leeks or garlic.

Temagamite is a bright white palladium mercury telluride mineral with a hardness of 2+1⁄2 on the Mohs scale. Its chemical formula is Pd3HgTe3. It was discovered at the Temagami Mine on Temagami Island, Lake Temagami in 1973, and it represents a rare mineral in the Temagami Greenstone Belt.

Vulcanite is a rare copper telluride mineral. The mineral has a metallic luster, and has a green or bronze-yellow tint. It has a hardness between 1 and 2 on the Mohs scale. Its crystal structure is orthorhombic.

Copper(II) phosphate are inorganic compounds with the formula Cu3(PO4)2. They can be regarded as the cupric salts of phosphoric acid. Anhydrous copper(II) phosphate and a trihydrate are blue solids.
Copper telluride may refer to:

Copper(II) oxalate are inorganic compounds with the chemical formula CuC2O4(H2O)x. The value of x can be 0, 0.44, and 1. Two of these species are found as secondary minerals, whewellite (monohydrate) and moolooite. The anhydrous compound has been characterized by X-ray crystallography. Many transition metal oxalate complexes are known.
Copper(I) telluride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Cu2Te. It can be synthesized by reacting elemental copper and tellurium with a molar ratio of 2:1 at 1200 °C in a vacuum. Cu2Te has potential applications in thermoelectric elements and in solar cells, where it is alloyed with cadmium telluride to create a heterojunction.
Vladimir Vasilyevich Bezsmertny was a Russian geologist, mineralogist, petrographer and petrologist, candidate of geological and mineralogical sciences, specialist in the field of ore deposits, associate professor at the Moscow Pedagogical Institute.















