
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement.

A noble metal is ordinarily regarded as a metallic chemical element that is generally resistant to corrosion and is usually found in nature in its raw form. Gold, platinum, and the other platinum group metals are most often so classified. Silver, copper, and mercury are sometimes included as noble metals, but each of these usually occurs in nature combined with sulfur.

Copper(II) sulfate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CuSO4. It forms hydrates CuSO4·nH2O, where n can range from 1 to 7. The pentahydrate (n = 5), a bright blue crystal, is the most commonly encountered hydrate of copper(II) sulfate, while its anhydrous form is white. Older names for the pentahydrate include blue vitriol, bluestone, vitriol of copper, and Roman vitriol. It exothermically dissolves in water to give the aquo complex [Cu(H2O)6]2+, which has octahedral molecular geometry. The structure of the solid pentahydrate reveals a polymeric structure wherein copper is again octahedral but bound to four water ligands. The Cu(II)(H2O)4 centers are interconnected by sulfate anions to form chains.

Group 12, by modern IUPAC numbering, is a group of chemical elements in the periodic table. It includes zinc (Zn), cadmium (Cd), mercury (Hg), and copernicium (Cn). Formerly this group was named IIB by CAS and old IUPAC system.

Copper(I) chloride, commonly called cuprous chloride, is the lower chloride of copper, with the formula CuCl. The substance is a white solid sparingly soluble in water, but very soluble in concentrated hydrochloric acid. Impure samples appear green due to the presence of copper(II) chloride (CuCl2).
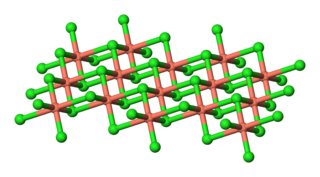
Copper(II) chloride, also known as cupric chloride, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CuCl2. The monoclinic yellowish-brown anhydrous form slowly absorbs moisture to form the orthorhombic blue-green dihydrate CuCl2·2H2O, with two water molecules of hydration. It is industrially produced for use as a co-catalyst in the Wacker process.

Copper(II) acetate, also referred to as cupric acetate, is the chemical compound with the formula Cu(OAc)2 where AcO− is acetate (CH
3CO−
2). The hydrated derivative, Cu2(OAc)4(H2O)2, which contains one molecule of water for each copper atom, is available commercially. Anhydrous copper(II) acetate is a dark green crystalline solid, whereas Cu2(OAc)4(H2O)2 is more bluish-green. Since ancient times, copper acetates of some form have been used as fungicides and green pigments. Today, copper acetates are used as reagents for the synthesis of various inorganic and organic compounds. Copper acetate, like all copper compounds, emits a blue-green glow in a flame.
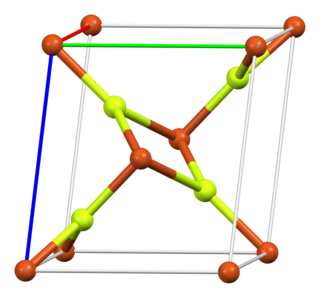
Copper(II) fluoride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CuF2. The anhydrous form is a white, ionic, crystalline, hygroscopic salt with a distorted rutile-type crystal structure, similar to other fluorides of chemical formulae MF2 (where M is a metal). The dihydrate, CuF2·2H2O, is blue in colour.

The metallic elements in the periodic table located between the transition metals to their left and the chemically weak nonmetallic metalloids to their right have received many names in the literature, such as post-transition metals, poor metals, other metals, p-block metals and chemically weak metals. The most common name, post-transition metals, is generally used in this article.

Transition metal carboxylate complexes are coordination complexes with carboxylate (RCO2−) ligands. Reflecting the diversity of carboxylic acids, the inventory of metal carboxylates is large. Many are useful commercially, and many have attracted intense scholarly scrutiny. Carboxylates exhibit a variety of coordination modes, most common are κ1- (O-monodentate), κ2 (O,O-bidentate), and bridging.

Copper forms a rich variety of compounds, usually with oxidation states +1 and +2, which are often called cuprous and cupric, respectively. Copper compounds, whether organic complexes or organometallics, promote or catalyse numerous chemical and biological processes.
Lithium laurate is an metallorganic compound with the chemical formula LiO2C(CH2)10CH3. It is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid. In contrast to the lubricants lithium stearate and lithium 12-hydroxystearate, lithium laurate is of minor commercial value..
Lead(II) laurate is an metal-organic compound with the chemical formula Pb(O2C 10CH3)2. It is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid. Like most soaps, it does not dissolve in water. Lead soaps have been used as stabilizers and plasticizers in PVC.
Cobalt laurate is an metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C
24H
48CoO
4. It is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Nickel(II) laurate is an metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C
24H
46NiO
4. It is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Zinc laurate is an metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C
24H
46ZnO
4. It is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Manganese laurate is an metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C
24H
48MnO
4. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Lanthanum laurate is an metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C
36H
72LaO
6. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Magnesium laurate is a metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C
24H
46MgO
4. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Potassium laurate is a metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C
12H
23KO
2. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.











