
Europium is a chemical element; it has symbol Eu and atomic number 63. Europium is a silvery-white metal of the lanthanide series that reacts readily with air to form a dark oxide coating. It is the most chemically reactive, least dense, and softest of the lanthanide elements. It is soft enough to be cut with a knife. Europium was isolated in 1901 and named after the continent of Europe. Europium usually assumes the oxidation state +3, like other members of the lanthanide series, but compounds having oxidation state +2 are also common. All europium compounds with oxidation state +2 are slightly reducing. Europium has no significant biological role and is relatively non-toxic compared to other heavy metals. Most applications of europium exploit the phosphorescence of europium compounds. Europium is one of the rarest of the rare-earth elements on Earth.

Samarium is a chemical element; it has symbol Sm and atomic number 62. It is a moderately hard silvery metal that slowly oxidizes in air. Being a typical member of the lanthanide series, samarium usually has the oxidation state +3. Compounds of samarium(II) are also known, most notably the monoxide SmO, monochalcogenides SmS, SmSe and SmTe, as well as samarium(II) iodide.

Tellurium is a chemical element; it has symbol Te and atomic number 52. It is a brittle, mildly toxic, rare, silver-white metalloid. Tellurium is chemically related to selenium and sulfur, all three of which are chalcogens. It is occasionally found in its native form as elemental crystals. Tellurium is far more common in the Universe as a whole than on Earth. Its extreme rarity in the Earth's crust, comparable to that of platinum, is due partly to its formation of a volatile hydride that caused tellurium to be lost to space as a gas during the hot nebular formation of Earth.

Terbium is a chemical element; it has symbol Tb and atomic number 65. It is a silvery-white, rare earth metal that is malleable, and ductile. The ninth member of the lanthanide series, terbium is a fairly electropositive metal that reacts with water, evolving hydrogen gas. Terbium is never found in nature as a free element, but it is contained in many minerals, including cerite, gadolinite, monazite, xenotime and euxenite.

In crystallography, the cubiccrystal system is a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals.

Europium(III) chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula EuCl3. The anhydrous compound is a yellow solid. Being hygroscopic it rapidly absorbs water to form a white crystalline hexahydrate, EuCl3·6H2O, which is colourless. The compound is used in research.

Telluric acid, or more accurately orthotelluric acid, is a chemical compound with the formula Te(OH)6, often written as H6TeO6. It is a white crystalline solid made up of octahedral Te(OH)6 molecules which persist in aqueous solution. In the solid state, there are two forms, rhombohedral and monoclinic, and both contain octahedral Te(OH)6 molecules, containing one hexavalent tellurium (Te) atom in the +6 oxidation state, attached to six hydroxyl (–OH) groups, thus, it can be called tellurium(VI) hydroxide. Telluric acid is a weak acid which is dibasic, forming tellurate salts with strong bases and hydrogen tellurate salts with weaker bases or upon hydrolysis of tellurates in water. It is used as tellurium-source in the synthesis of oxidation catalysts.

Zinc telluride is a binary chemical compound with the formula ZnTe. This solid is a semiconductor material with a direct band gap of 2.26 eV. It is usually a p-type semiconductor. Its crystal structure is cubic, like that for sphalerite and diamond.

Bismuth telluride is a gray powder that is a compound of bismuth and tellurium also known as bismuth(III) telluride. It is a semiconductor, which, when alloyed with antimony or selenium, is an efficient thermoelectric material for refrigeration or portable power generation. Bi2Te3 is a topological insulator, and thus exhibits thickness-dependent physical properties.

Tin telluride is a compound of tin and tellurium (SnTe); is a IV-VI narrow band gap semiconductor and has direct band gap of 0.18 eV. It is often alloyed with lead to make lead tin telluride, which is used as an infrared detector material.
Tellurium hexafluoride is the inorganic compound of tellurium and fluorine with the chemical formula TeF6. It is a colorless, highly toxic gas with an unpleasant odor.

Hydrogen telluride is the inorganic compound with the formula H2Te. A hydrogen chalcogenide and the simplest hydride of tellurium, it is a colorless gas. Although unstable in ambient air, the gas can exist at very low concentrations long enough to be readily detected by the odour of rotting garlic at extremely low concentrations; or by the revolting odour of rotting leeks at somewhat higher concentrations. Most compounds with Te–H bonds (tellurols) are unstable with respect to loss of H2. H2Te is chemically and structurally similar to hydrogen selenide, both are acidic. The H–Te–H angle is about 90°. Volatile tellurium compounds often have unpleasant odours, reminiscent of decayed leeks or garlic.
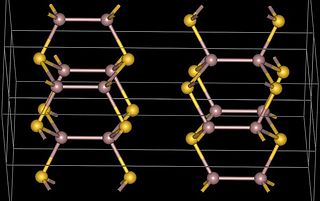
Gallium(II) telluride, GaTe, is a chemical compound of gallium and tellurium. There is research interest in the structure and electronic properties of GaTe because of the possibility that it, or related compounds, may have applications in the electronics industry. Gallium telluride can be made by reacting the elements or by metal organic vapour deposition (MOCVD).

Antimony telluride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Sb2Te3. As is true of other pnictogen chalcogenide layered materials, it is a grey crystalline solid with layered structure. Layers consist of two atomic sheets of antimony and three atomic sheets of tellurium and are held together by weak van der Waals forces. Sb2Te3 is a narrow-gap semiconductor with a band gap 0.21 eV; it is also a topological insulator, and thus exhibits thickness-dependent physical properties.
Tellurium compounds are compounds containing the element tellurium (Te). Tellurium belongs to the chalcogen family of elements on the periodic table, which also includes oxygen, sulfur, selenium and polonium: Tellurium and selenium compounds are similar. Tellurium exhibits the oxidation states −2, +2, +4 and +6, with +4 being most common.
The telluride bromides are chemical compounds that contain both telluride ions (Te2−) and bromide ions (Br−). They are in the class of mixed anion compounds or chalcogenide halides.

Europium(II) iodide is the iodide salt of divalent europium cation.
Tellurogallates are chemical compounds which contain anionic units of tellurium connected to gallium. They can be considered as gallates where tellurium substitutes for oxygen. Similar compounds include the thiogallates, selenogallates, telluroaluminates, telluroindates and thiostannates. They are in the category of chalcogenotrielates or more broadly tellurometallates or chalcogenometallates.

Europium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal europium (Eu). In these compounds, europium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as EuCl3, Eu(NO3)3 and Eu(CH3COO)3. Compounds with europium in the +2 oxidation state are also known. The +2 ion of europium is the most stable divalent ion of lanthanide metals in aqueous solution. Many europium compounds fluoresce under ultraviolet light due to the excitation of electrons to higher energy levels. Lipophilic europium complexes often feature acetylacetonate-like ligands, e.g., Eufod.
Europium(III) iodide is an inorganic compound containing europium and iodine with the chemical formula EuI3.
















